|
Hambergbreen
Hambergbreen is a glacier on Spitsbergen, Svalbard, dividing Torell Land and Sørkapp Land, and debouching into the sea at the eastern coast of Spitsbergen. The glacier is named after Swedish geographer and explorer Axel Hamberg Axel Hamberg (17 January 1863 – 28 June 1933) was a Swedish mineralogist, geographer and explorer. Biography Hamberg was born in Stockholm, Sweden. He was the son of Nils Peter Hamberg (1815-1902) and Emma Augusta Christina Härnström (18 .... References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axel Hamberg
Axel Hamberg (17 January 1863 – 28 June 1933) was a Swedish mineralogist, geographer and explorer. Biography Hamberg was born in Stockholm, Sweden. He was the son of Nils Peter Hamberg (1815-1902) and Emma Augusta Christina Härnström (1833-1914). Hamberg became a student at Uppsala University in 1881, philosophy candidate in 1888 and was awarded a Licentiate degree in 1893. He became an associate professor of mineralogy and crystallography in the same year at Stockholm University. In 1907, he received his philosophy doctor and was appointed as an extra ordinary professor at the University of Uppsala. He served as a professor in geography at Uppsala until 1928. In 1883, he attended the expedition of Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld to Greenland and in 1898 accompanied on the expedition of Alfred Nathorst on the ship "Antarctic" to Svalbard and Kong Karls Land. At the General Art and Industrial Exposition of Stockholm of 1897, he received a gold medal for an exhibition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
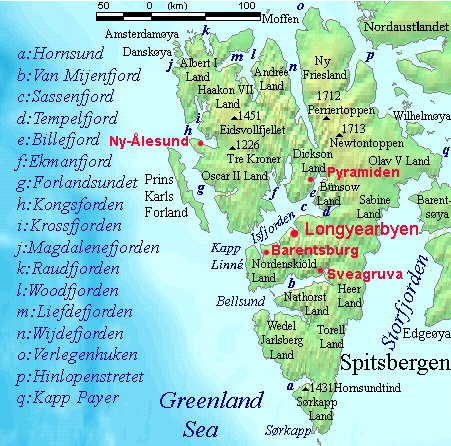
Torell Land
Torell Land is a land area at the southeast part of Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is named after Otto Martin Torell. Two glaciers, Hornbreen and Hambergbreen, divide Torell Land from Sørkapp Land. Torell Land is included in the Sør-Spitsbergen National Park Sør-Spitsbergen National Park ( no, Sør-Spitsbergen nasjonalpark, eng, South Spitzbergen National Park) encompasses the southern end of Spitsbergen island in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. The park was opened in 1973 and includes Wedel Jarl .... References Geography of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sørkapp Land
Sørkapp Land is the land area south of Hornsund, at the southern part of Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Two glaciers, Hornbreen and Hambergbreen, divide Sørkapp Land from Torell Land. Sørkapp Land is included in the Sør-Spitsbergen National Park Sør-Spitsbergen National Park ( no, Sør-Spitsbergen nasjonalpark, eng, South Spitzbergen National Park) encompasses the southern end of Spitsbergen island in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. The park was opened in 1973 and includes Wedel Jarl .... References Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debouch
In hydrology, a debouch (or debouche) is a place where runoff from a small, confined space discharges into a larger, broader body of water. The word is derived from the French verb ''déboucher'' (), which means "to unblock, to clear". The term also has a military usage. Geology In fluvial geomorphology, a debouch is a place where runoff from a small, confined space emerges into a larger, broader space. Common examples are when a stream runs into a river or when a river runs into an ocean. Debouching can generate massive amounts of sediment transport. When a narrow stream travels down a mountain pass into a basin, an alluvial fan will form from the mass deposit of the sediment. The four largest rivers (the Amazon, the Ganges-Brahmaputra, the Yangtze and the Yellow) are responsible for 20% of the global discharge of sediment in to the oceans by debouches. Geography In fluvial geography, a debouch is a place where a body of water pours forth from a narrow opening. Some examples ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |