|
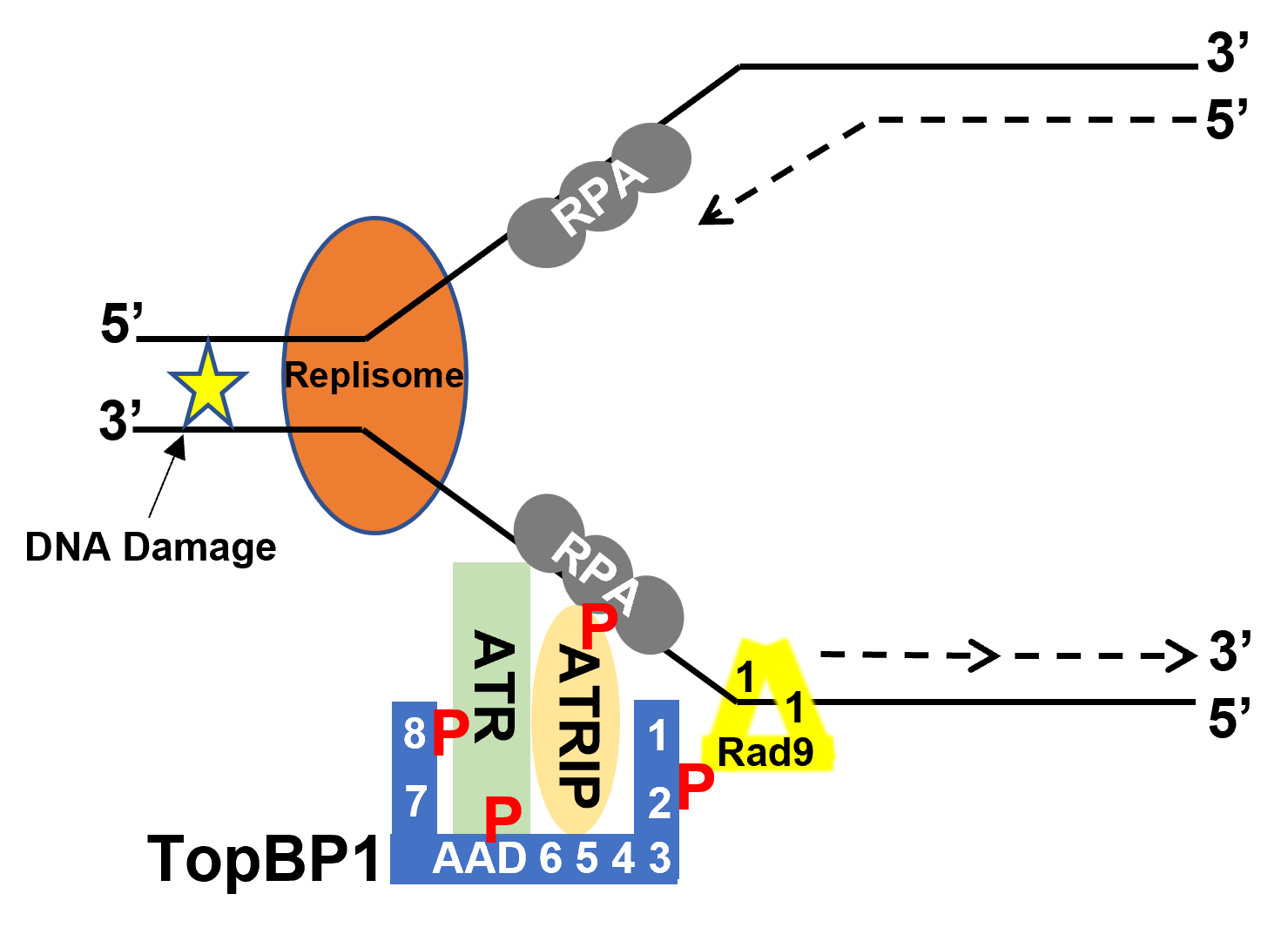
TopBP1 BRCT Domains
DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 (TOPBP1) is a scaffold protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TOPBP1'' gene. TOPBP1 was first identified as a protein binding partner of DNA TOP2B, topoisomerase-IIβ by a Two-hybrid screening, yeast 2-hybrid screen, giving it its name. TOPBP1 is involved in a variety of nuclear specific events. These include DNA repair, DNA damage repair, Eukaryotic DNA replication, DNA replication, transcriptional regulation, and Cell cycle checkpoint, cell cycle checkpoint activation. TOPBP1 primarily regulates the DNA damage repair response through its ability to activate the damage response kinase, Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated and RAD3-related (ATR). It also plays a critical role in DNA replication initiation and regulation of the cell cycle. Changes in TOPBP1 gene expression are associated with pulmonary hypertension, breast cancer, glioblastoma, Non-small-cell lung carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TopBP1 BRCT Domains
DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 (TOPBP1) is a scaffold protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TOPBP1'' gene. TOPBP1 was first identified as a protein binding partner of DNA TOP2B, topoisomerase-IIβ by a Two-hybrid screening, yeast 2-hybrid screen, giving it its name. TOPBP1 is involved in a variety of nuclear specific events. These include DNA repair, DNA damage repair, Eukaryotic DNA replication, DNA replication, transcriptional regulation, and Cell cycle checkpoint, cell cycle checkpoint activation. TOPBP1 primarily regulates the DNA damage repair response through its ability to activate the damage response kinase, Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated and RAD3-related (ATR). It also plays a critical role in DNA replication initiation and regulation of the cell cycle. Changes in TOPBP1 gene expression are associated with pulmonary hypertension, breast cancer, glioblastoma, Non-small-cell lung carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaffold Protein
In biology, scaffold proteins are crucial regulators of many key signalling pathways. Although scaffolds are not strictly defined in function, they are known to interact and/or bind with multiple members of a signalling pathway, tethering them into complexes. In such pathways, they regulate signal transduction and help localize pathway components (organized in complexes) to specific areas of the cell such as the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm, the nucleus, the Golgi, endosomes, and the mitochondria. History The first signaling scaffold protein discovered was the Ste5 protein from the yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. Three distinct domains of Ste5 were shown to associate with the protein kinases Ste11, Ste7, and Fus3 to form a multikinase complex. Function Scaffold proteins act in at least four ways: tethering signaling components, localizing these components to specific areas of the cell, regulating signal transduction by coordinating positive and negative feedback s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, notably Alzheimer's disease. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. A refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLK1
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK1, also known as polo-like kinase 1 (PLK-1) or serine/threonine-protein kinase 13 (STPK13), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLK1'' (polo-like kinase 1) gene. Structure PLK1 consists of 603 amino acids and is 66kDa. In addition to the N-terminus kinase domain, there are two conserved polo-box regions of 30 amino acids at the C-terminus. Kinase activity is regulated at least in part, by the polo-boxes that are functionally important for both auto-inhibition and subcellular localization. Localization During interphase, PLK1 localizes to centrosomes. In early mitosis, it associates with mitotic spindle poles. A recombinant GFP-PLK1 protein localizes to centromere/kinetochore region, suggesting a possible role for chromosome separation. Cell cycle regulation Plk1 is an early trigger for G2/M transition. Plk1 supports the functional maturation of the centrosome in late G2/early prophase and establishment of the bipolar spindl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PARP1
Poly DP-ribosepolymerase 1 (PARP-1) also known as NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase 1 or poly DP-ribosesynthase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PARP1'' gene. It is the most abundant of the PARP family of enzymes, accounting for 90% of the NAD+ used by the family. PARP1 is mostly present in cell nucleus, but cytosolic fraction of this protein was also reported. Function PARP1 works: * By using NAD+ to synthesize poly ADP ribose (PAR) and transferring PAR moieties to proteins (ADP-ribosylation). * In conjunction with BRCA, which acts on double strands; members of the PARP family act on single strands; or, when BRCA fails, PARP takes over those jobs as well (in a DNA repair context). PARP1 is involved in: * Differentiation, proliferation, and tumor transformation * Normal or abnormal recovery from DNA damage * May be the site of mutation in Fanconi anemia * Induction of inflammation. * The pathophysiology of type I diabetes. PARP1 is activated by: * Helicobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E2F1
Transcription factor E2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''E2F1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the E2F family of transcription factors. The E2F family plays a crucial role in the control of cell cycle and action of tumor suppressor proteins and is also a target of the transforming proteins of small DNA tumor viruses. The E2F proteins contain several evolutionarily conserved domains found in most members of the family. These domains include a DNA binding domain, a dimerization domain which determines interaction with the differentiation regulated transcription factor proteins (DP), a transactivation domain enriched in acidic amino acids, and a tumor suppressor protein association domain which is embedded within the transactivation domain. This protein and another 2 members, E2F2 and E2F3, have an additional cyclin binding domain. This protein binds preferentially to retinoblastoma protein pRB in a cell-cycle dependent manner. It ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BLM Protein
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating two hybridized nucleic acid strands (hence '' helic- + -ase''), using energy from ATP hydrolysis. There are many helicases, representing the great variety of processes in which strand separation must be catalyzed. Approximately 1% of eukaryotic genes code for helicases. The human genome codes for 95 non-redundant helicases: 64 RNA helicases and 31 DNA helicases. Many cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, recombination, DNA repair, and ribosome biogenesis involve the separation of nucleic acid strands that necessitates the use of helicases. Some specialized helicases are also involved in sensing of viral nucleic acids during infection and fulfill a immunological function. Function Helicases are oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TP53BP1
Tumor suppressor p53-binding protein 1 also known as p53-binding protein 1 or 53BP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TP53BP1'' gene. Clinical significance 53BP1 is underexpressed in most cases of triple-negative breast cancer. DNA repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are cytotoxic damages that can be repaired either by the homologous recombinational repair (HR) pathway or by the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway. NHEJ, although faster than HR, is less accurate. The early divergent step between the two pathways is end resection, and this step is regulated by numerous factors. In particular, BRCA1 and 53BP1 play a role in determining the balance between the two pathways. 53BP1 restricts resection and promotes NHEJ. Age-associated deficient repair Ordinarily during the G1 phase of the cell cycle, when a sister chromatid is unavailable for HR, NHEJ is the predominant pathway for repairing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). However, as individuals age, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDC45-related Protein
CDC45 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDC45L'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene was identified by its strong similarity with Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc45, an essential protein required to the initiation of DNA replication. Cdc45 is a member of the highly conserved multiprotein complex including Cdc6/Cdc18, the minichromosome maintenance proteins (MCMs) and DNA polymerase, which is important for early steps of DNA replication in eukaryotes. This protein has been shown to interact with MCM7 and DNA polymerase alpha. Studies of the similar gene in Xenopus suggested that this protein plays a pivotal role in the loading of DNA polymerase alpha onto chromatin. Multiple polyadenlyation sites of this gene are reported. Interactions CDC45-related protein has been shown to interact with: * MCM3, * MCM6, * MCM7, * ORC1L, and * ORC6L Origin recognition complex subunit 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ORC6 (ORC6L) gene. Background Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAD9A
Cell cycle checkpoint control protein RAD9A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAD9A'' gene.''Rad9'' has been shown to induce G2 arrest in the cell cycle in response to DNA damage in yeast cells. ''Rad9'' was originally found in budding yeast cells but a human homolog has also been found and studies have suggested that the molecular mechanisms of the S and G2 checkpoints are conserved in eukaryotes. Thus, what is found in yeast cells are likely to be similar in human cells. Function This gene product is highly similar to S. pombe rad9, a cell cycle checkpoint protein required for cell cycle arrest and DNA damage repair in response to DNA damage. This protein is found to possess 3' to 5' exonuclease activity, which may contribute to its role in sensing and repairing DNA damage. It forms a checkpoint protein complex with Rad1 and Hus1. This is also known as the Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 or 9-1-1 complex. This complex is recruited by checkpoint protein Rad17 to the sites of DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MDC1
Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1 is a 2080 amino acid long protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MDC1'' gene located on the short arm (p) of chromosome 6. MDC1 protein is a regulator of the Intra-S phase and the G2/M cell cycle checkpoints and recruits repair proteins to the site of DNA damage. It is involved in determining cell survival fate in association with tumor suppressor protein p53. This protein also goes by the name Nuclear Factor with BRCT Domain 1 (NFBD1). Function Role in DNA damage response The ''MDC1'' gene encodes the MDC1 nuclear protein which is part of the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway, the mechanism through which eukaryotic cells respond to damaged DNA, specifically DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) that are caused by ionizing radiation or chemical clastogens. The DDR of mammalian cells is made up of kinases, and mediator/adaptors factors. In mammalian cells the DDR is a network of pathways made up of proteins that function as either kinas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |