|
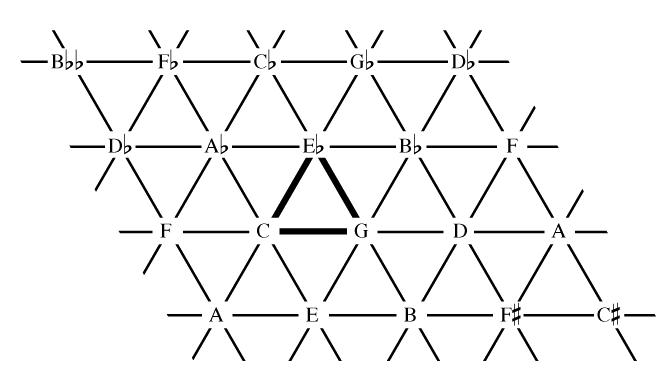
Tonnetz
In musical tuning and harmony, the (German for 'tone network') is a conceptual lattice diagram representing tonal space first described by Leonhard Euler in 1739. Various visual representations of the ''Tonnetz'' can be used to show traditional harmonic relationships in European classical music. History through 1900 The ''Tonnetz'' originally appeared in Leonhard Euler's 1739 . Euler's ''Tonnetz'', pictured at left, shows the triadic relationships of the perfect fifth and the major third: at the top of the image is the note F, and to the left underneath is C (a perfect fifth above F), and to the right is A (a major third above F). The ''Tonnetz'' was rediscovered in 1858 by Ernst Naumann, and was disseminated in an 1866 treatise of Arthur von Oettingen. Oettingen and the influential musicologist Hugo Riemann (not to be confused with the mathematician Bernhard Riemann) explored the capacity of the space to chart harmonic motion between chords and modulation between keys. Simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Riemannian Tonnetz
Neo-Riemannian theory is a loose collection of ideas present in the writings of music theorists such as David Lewin, Brian Hyer, Richard Cohn, and Henry Klumpenhouwer. What binds these ideas is a central commitment to relating harmonies directly to each other, without necessary reference to a tonic. Initially, those harmonies were major and minor triads; subsequently, neo-Riemannian theory was extended to standard dissonant sonorities as well. Harmonic proximity is characteristically gauged by efficiency of voice leading. Thus, C major and E minor triads are close by virtue of requiring only a single semitonal shift to move from one to the other. Motion between proximate harmonies is described by simple transformations. For example, motion between a C major and E minor triad, in either direction, is executed by an "L" transformation. Extended progressions of harmonies are characteristically displayed on a geometric plane, or map, which portrays the entire system of harmonic relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Riemannian Theory
Neo-Riemannian theory is a loose collection of ideas present in the writings of music theorists such as David Lewin, Brian Hyer, Richard Cohn, and Henry Klumpenhouwer. What binds these ideas is a central commitment to relating harmonies directly to each other, without necessary reference to a tonic. Initially, those harmonies were major and minor triads; subsequently, neo-Riemannian theory was extended to standard dissonant sonorities as well. Harmonic proximity is characteristically gauged by efficiency of voice leading. Thus, C major and E minor triads are close by virtue of requiring only a single semitonal shift to move from one to the other. Motion between proximate harmonies is described by simple transformations. For example, motion between a C major and E minor triad, in either direction, is executed by an "L" transformation. Extended progressions of harmonies are characteristically displayed on a geometric plane, or map, which portrays the entire system of harmonic rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice (music)
In musical tuning, a lattice "is a way of modeling the tuning relationships of a just intonation system. It is an array of points in a periodic multidimensional pattern. Each point on the lattice corresponds to a ratio (i.e., a pitch, or an interval with respect to some other point on the lattice). The lattice can be two-, three-, or ''n''-dimensional, with each dimension corresponding to a different prime-number partial ."Gilmore, Bob (2006). "Introduction", p.xviii, ''"Maximum Clarity" and Other Writings on Music'', edited by Bob Gilmore. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. . When listed in a spreadsheet a lattice may be referred to as a tuning table. The points in a lattice represent pitch classes (or pitches if octaves are represented), and the connectors in a lattice represent the intervals between them. The connecting lines in a lattice display intervals as vectors, so that a line of the same length and angle always has the same intervalic relationship between the point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a spindle torus. If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a ''toroid'', as in a square toroid. Real-world objects that approximate a torus of revolution include swim rings, inner tubes and ringette rings. Eyeglass lenses that combine spherical and cylindrical correction are toric lenses. A torus should not be confused with a '' solid torus'', which is formed by r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Riemann
Karl Wilhelm Julius Hugo Riemann (18 July 1849 – 10 July 1919) was a German musicologist and composer who was among the founders of modern musicology. The leading European music scholar of his time, he was active and influential as both a music theorist and music historian. Many of his contributions are now termed as Riemannian theory, a variety of related ideas on many aspects of music theory. Biography Riemann was born at Grossmehlra, Schwarzburg-Sondershausen. His first musical training came from his father Robert Riemann, a land owner, bailiff and, to judge from locally surviving listings of his songs and choral works, an active music enthusiast. Hugo Riemann was educated by Heinrich Frankenberger, the Sondershausen Choir Master, in Music theory. He was taught the piano by August Barthel and Theodor Ratzenberger (who had once studied under Liszt). He studied law, and finally philosophy and history at Berlin and Tübingen. After participating in the Franco-Prussian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is also known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy and music theory. Euler is held to be one of the greatest mathematicians in history and the greatest of the 18th century. A statement attributed to Pierre-Simon Laplace expresses Euler's influence on mathematics: "Read Euler, read Euler, he is the master of us all." Carl Friedrich Gauss remarked: "The study of Euler's works will remain the best school for the different fields of mathematics, and nothing else can replace it." Euler is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Table Note Layout
The Harmonic Table note-layout, or tonal array, is a key layout for musical instruments that offers interesting advantages over the traditional keyboard layout. Its symmetrical, hexagonal pattern of interval sequences places the notes of the major and minor triads together. It is sometimes called the ''Melodic Table'' note-layout, and more rarely the ''Triad'' note-layout. It is related to the Wicki-Hayden based keyboards and other isomorphic keyboards, both of which can be utilized on the jammer keyboard musical interface. History The structure and properties of the Harmonic Table have been well known since at least the 18th century. Indeed, as a pitch space, the Harmonic Table is topologically equivalent to Euler's Tonnetz, discovered by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler in 1739. The two pitch arrays are trivially obtained from each other by direct shear mapping. This note layout created by Euler is utilised in Neo-Riemannian theory to geometrically model its musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Third
In classical music, a third is a musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four semitones. Forte, Allen (1979). ''Tonal Harmony in Concept and Practice'', p.8. Holt, Rinehart, and Winston. Third edition . "A large 3rd, or ''major 3rd'' (M3) encompassing four half steps." Along with the minor third, the major third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is qualified as ''major'' because it is the larger of the two: the major third spans four semitones, the minor third three. For example, the interval from C to E is a major third, as the note E lies four semitones above C, and there are three staff positions from C to E. Diminished and augmented thirds span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (two and five). The major third may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the fourth and fifth harmonics. The maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntonic Temperament
A regular diatonic tuning is any musical scale consisting of " tones" (T) and "semitones" (S) arranged in any rotation of the sequence TTSTTTS which adds up to the octave with all the T's being the same size and all the S's the being the same size, with the 'S's being smaller than the 'T's. In such a tuning, then the notes are connected together in a chain of seven fifths, all the same size (TTTS or a permutation of that) which makes it a Linear temperament with the tempered fifth as a generator. Overview In the ordinary diatonic scales the T's here are tones and the S's are semitones which are half, or approximately half the size of the tone. But in the more general regular diatonic tunings, the two steps can be of any relation within the range between T=171.43 (S=T) and T=240 (S=0) cents (fifth between 685.71 and 720). Note that regular diatonic tunings are not limited to the notes of the diatonic scale which defines them. One may determine the corresponding cents of S, T, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomorphic Keyboard
An isomorphic keyboard is a musical input device consisting of a two-dimensional grid of note-controlling elements (such as buttons or keys) on which any given sequence and/or combination of musical intervals has the "same shape" on the keyboard wherever it occurs – within a key, across keys, across octaves, and across tunings. Examples Helmholtz's 1863 book ''On the Sensations of Tone'' gave several possible layouts. Practical isomorphic keyboards were developed by Bosanquet (1875), Janko (1882), Wicki (1896), Fokker (1951), Erv Wilson (1975–present), William Wesley (2001), and Antonio Fernández (2009). Accordions have been built since the 19th century using various isomorphic keyboards, typically with dimensions of semitones and tones. The keyboards of Bosanquet and Erv Wilson are also known as generalized keyboards. The keyboard of Antonio Fernández is also known as Transclado. The Ragzpole is a recently developed cylindrical MIDI controller having dimensions in fift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Third
In music theory, a minor third is a musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval number). The minor third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is called ''minor'' because it is the smaller of the two: the major third spans an additional semitone. For example, the interval from A to C is a minor third, as the note C lies three semitones above A. Coincidentally, there are three staff positions from A to C. Diminished and augmented thirds span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (two and five). The minor third is a skip melodically. Notable examples of ascending minor thirds include the opening two notes of " Greensleeves" and of " Light My Fire". The minor third may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the fifth and sixth harmonics, or from the 19th harmonic. The minor third is co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so. In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval from the first to the last of five consecutive Musical note, notes in a diatonic scale. The perfect fifth (often abbreviated P5) spans seven semitones, while the Tritone, diminished fifth spans six and the augmented fifth spans eight semitones. For example, the interval from C to G is a perfect fifth, as the note G lies seven semitones above C. The perfect fifth may be derived from the Harmonic series (music), harmonic series as the interval between the second and third harmonics. In a diatonic scale, the dominant (music), dominant note is a perfect fifth above the tonic (music), tonic note. The perfect fifth is more consonance and dissonance, consonant, or stable, than any other interval except the unison and the octave. It occurs above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |