|
Tonna Perdix
''Tonna perdix'', common name the partridge tun, is a species of very large sea snail, a marine (ocean), marine gastropod mollusc in the family (biology), family Tonnidae, the tun Gastropod shell, shells.Vos, C. (2010)Tonna perdix (Linnaeus, 1758) Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species on 2011-04-26. Description The pattern and brownish colour of the shell is reminiscent of a partridge's plumage hence the common name. The size of an adult shell varies between 70 mm and 220 mm. The ovate-oblong shell is ventricose and pretty thin. It is of a reddish-brown color, pleasingly varied with white spots in transverse series, for the most part semi-lunar, and more or less distant. The conical Spire (mollusc), spire is slightly projecting and, pointed. It is composed of from five to six Whorl (mollusc), whorls which are furnished with numerous ribs, often widened, feebly convex, and separated by furrows hardly apparent. The suture is very distinct and is slightly cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod Shell
The gastropod shell is part of the body of a Gastropoda, gastropod or snail, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or in some cases the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within it (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the Aperture (mollusc), aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group. Shell layers The gastropod shell has three major layers secreted by the Mantle (mollusc), mantle. The calcareous central layer, tracum, is typically made of calcium carbonate precipitated into an organic matrix known as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whorl (mollusc)
A whorl is a single, complete 360° revolution or turn in the spiral growth of a mollusc shell. A spiral configuration of the shell is found in numerous gastropods, but it is also found in shelled cephalopods including ''Nautilus'', ''Spirula'' and the large extinct subclass of cephalopods known as the ammonites. A spiral shell can be visualized as consisting of a long conical tube, the growth of which is coiled into an overall helical or planispiral shape, for reasons of both strength and compactness. The number of whorls which exist in an adult shell of a particular species depends on mathematical factors in the geometric growth, as described in D'Arcy Wentworth Thompson's classic 1917 book ''On Growth and Form'', and by David Raup. The main factor is how rapidly the conical tube expands (or flares-out) over time. When the rate of expansion is low, such that each subsequent whorl is not that much wider than the previous one, then the adult shell has numerous whorls. When the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus ''Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of '' Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga and St. Brandon. The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where most of the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans and has an exclusive economic zone covering . Arab sailors were the first to discover the uninhabited island, around 975, and they called it ''Dina Arobi''. The earliest discovery was in 1507 by Portuguese sailors, who otherwise took little interest in the islands. The Dutch took possession in 1598, establishing a succession of short-lived settlements over a period of about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mascarene
The Mascarene Islands (, ) or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of the islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of Réunion. Their name derives from the Portuguese navigator Pedro Mascarenhas, who first visited them in April 1512. The islands share a common geologic origin in the volcanism of the Réunion hotspot beneath the Mascarene Plateau and form a distinct ecoregion with a unique flora and fauna. Geography The archipelago comprises three large islands, Mauritius, Réunion, and Rodrigues, plus a number of volcanic remnants in the tropics of the southwestern Indian Ocean, generally between 700 and 1500 kilometres east of Madagascar. The terrain includes a variety of reefs, atolls, and small islands. They present various topographical and edaphic regions. On the largest islands these gave rise to unusual biodiversity. The climate is oceanic and tropical. Mauriti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa across the Mozambique Channel. At Madagascar is the world's List of island countries, second-largest island country, after Indonesia. The nation is home to around 30 million inhabitants and consists of the island of Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar (the List of islands by area, fourth-largest island in the world), along with numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from the Indian subcontinent around 90 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot; over 90% of wildlife of Madagascar, its wildlife is endemic. Human settlement of Madagascar occurred during or befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
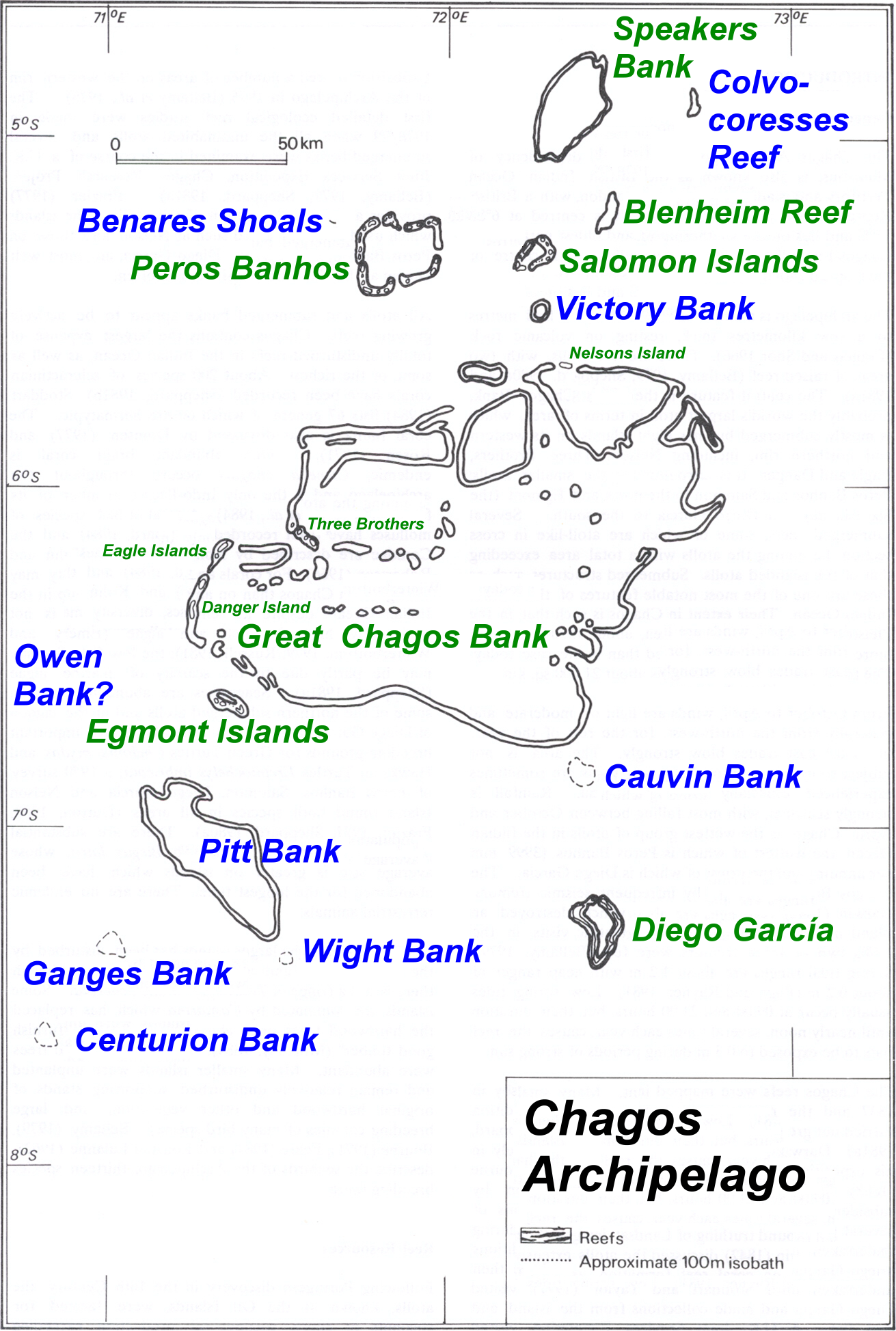
Chagos
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelson's Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont and Danger Island(s); southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. The Chagos Islands had been home to the native Chagossians, a Bourbonnais Creole-speaking people, until the United Kingdom expelled them from the archipelago at the request of the United States between 1967 and 1973 to allow the United States to build a military base on Diego Garcia. Since 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldabra
Aldabra is the world's second-largest coral atoll, lying south-east of the continent of Africa. It is part of the Aldabra Group of islands in the Indian Ocean that are part of the Outer Islands of the Seychelles, with a distance of 1,120 km (700 mi) southwest of the capital, Victoria on Mahé Island. History The name Aldabra, originally Al-Hadra or Al-Khadra (with several variants), was given by Arab seafarers for "the atoll’s harsh, sun-baked environment"; this name was included in the Portuguese maps of the 16th century. The islands were already known to the Persians and Arabs, from whom they got their name. They had named the Indian Ocean as Bahr-el zanj. It was visited by Portuguese navigators in 1511. In the middle of the 18th century, the atoll became a dependency of the French colony of Réunion, from where expeditions were made for the capture of the Aldabra giant tortoises. As there are no surface freshwater sources on Aldabra, the interests of the explor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after Indian subcontinent, India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' (Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic) before the Pacific Ocean, Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Ming treasure voyages, Chinese explorers in the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; Tigrinya: ቀይሕ ባሕሪ ''Qeyih Bahri''; ) is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (leading to the Suez Canal). It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly 438,000 km2 (169,100 mi2), is about 2250 km (1398 mi) long, and — at its widest point — 355 km (220.6 mi) wide. It has an average depth of 490 m (1,608 ft), and in the central ''Suakin Trough'' it reaches its maximum depth of . The Red Sea also has exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columella (gastropod)
The columella (meaning "little column") or (in older texts) pillar is a central anatomical feature of a coiled snail shell, a gastropod shell. The columella is often only clearly visible as a structure when the shell is broken, sliced in half vertically, or viewed as an X-ray image. The columella runs from the apex of the shell to the midpoint of the undersurface of the shell, or the tip of the siphonal canal in those shells which have a siphonal canal. If a snail shell is visualized as a cone of shelly material which is wrapped around a central axis, then the columella more or less coincides spatially with the central axis of the shell. In the case of shells that have an umbilicus, the columella is a hollow structure. The columella of some groups of gastropod shells can have a number of plications or folds (the columellar fold, plaits or plicae), which are usually visible when looking to the inner lip into the aperture of the shell. These folds can be wide or narrow, prominent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilicus (mollusc)
The umbilicus of a shell is the axially aligned, hollow cone-shaped space within the whorls of a coiled mollusc shell. The term umbilicus is often used in descriptions of gastropod shells, i.e. it is a feature present on the ventral (or under) side of many (but not all) snail shells, including some species of sea snails, land snails, and freshwater snails. The word is also applied to the depressed central area on the planispiral coiled shells of ''Nautilus'' species and fossil ammonites. (These are not gastropods, but shelled cephalopods.) In gastropods The spirally coiled whorls of gastropod shells frequently connect to each other by their inner sides, during the natural course of its formation. This results in a more or less solid central axial pillar, known as the columella. The more intimate the contact between the concave side of the whorls is, the more solid the columella becomes. On the other hand, if this connection is less intense, a hollow space inside the whorls may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |