|
Chagos
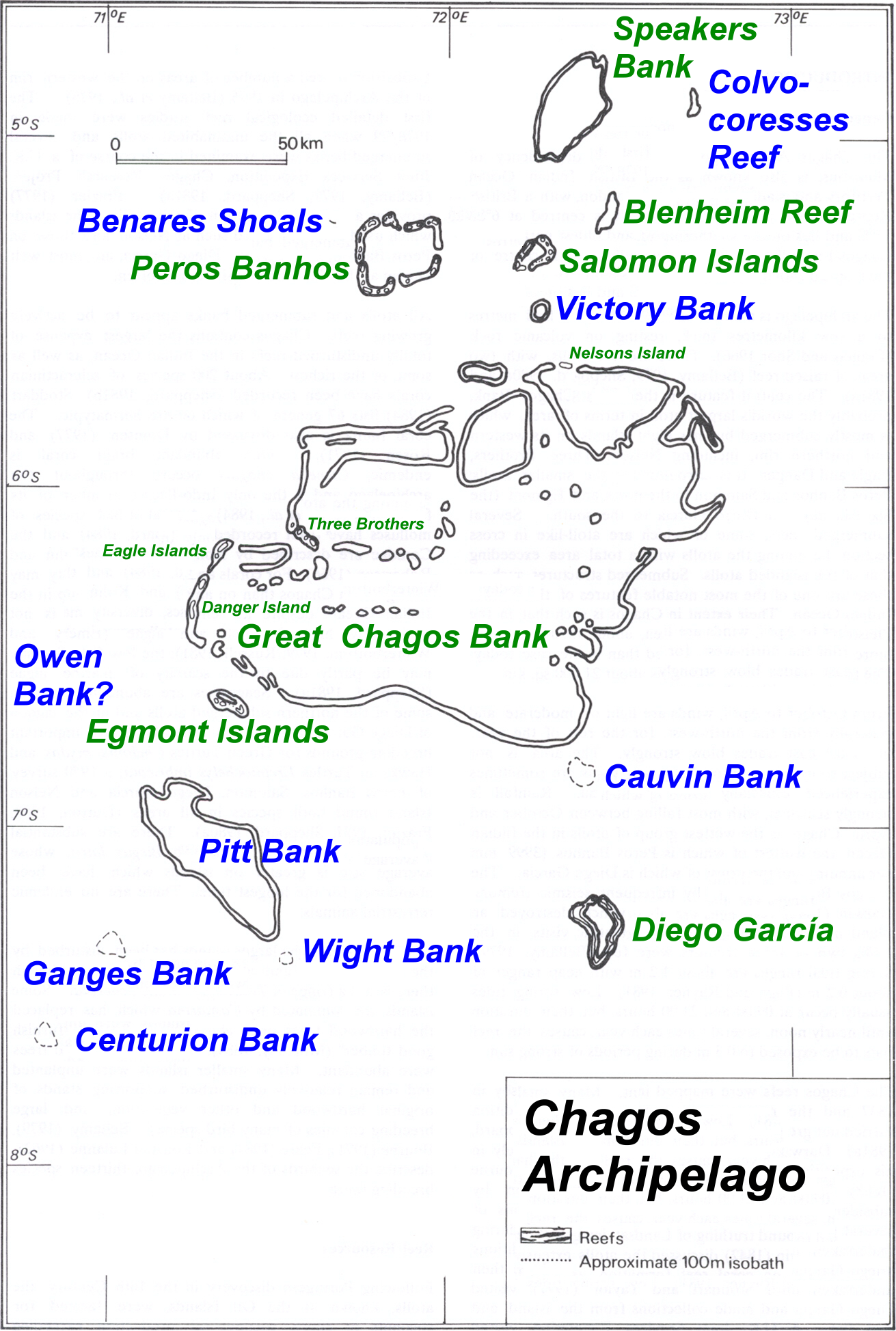
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelson's Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont and Danger Island(s); southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. The Chagos Islands had been home to the native Chagossians, a Bourbonnais Creole-speaking people, until the United Kingdom expelled them from the archipelago at the request of the United States between 1967 and 1973 to allow the United States to build a military base on Diego Garcia. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagos Large
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelson's Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont and Danger Island(s); southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. The Chagos Islands had been home to the native Chagossians, a Bourbonnais Creole-speaking people, until the United Kingdom expelled them from the archipelago at the request of the United States between 1967 and 1973 to allow the United States to build a military base on Diego Gar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expulsion Of The Chagossians
The United Kingdom, at the request of the United States, began expelling the native inhabitants of the Chagos Archipelago in 1968, concluding its forced deportations on 27 April 1973 with the evacuation of Peros Banhos atoll.The High Court of Justice Queens Bench Division, Case No: HQ02X01287, Approved Judgment, 2003 Paragraph 396. The inhabitants, known at the time as the ''Ilois'', are today known as Chagossians, Chagos Islanders or Chagossians. Chagossians and human rights advocates have said that the Chagossian right of occupation was violated by the British Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office, Foreign Office as a result of the 1966 agreement between the Government of the United Kingdom, British and Federal government of the United States, Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego Garcia
Diego Garcia is an island of the British Indian Ocean Territory, a disputed overseas territory of the United Kingdom. It is a militarised atoll just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, and the largest of the 60 small islands of the Chagos Archipelago. The Portuguese were the first Europeans to find it and it was then settled by the French in the 1790s and transferred to British rule after the Napoleonic Wars. It was one of the "Dependencies" of the British Colony of Mauritius until the Chagos Islands were detached for inclusion in the newly created British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) in 1965. In 1966, the population of the island was 924. These people were employed as contract farm workers primarily on copra plantations owned by the Chagos-Agalega company. Although it was common for local plantation managers to allow pensioners and the disabled to remain in the islands and continue to receive housing and rations in exchange for light work, children after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
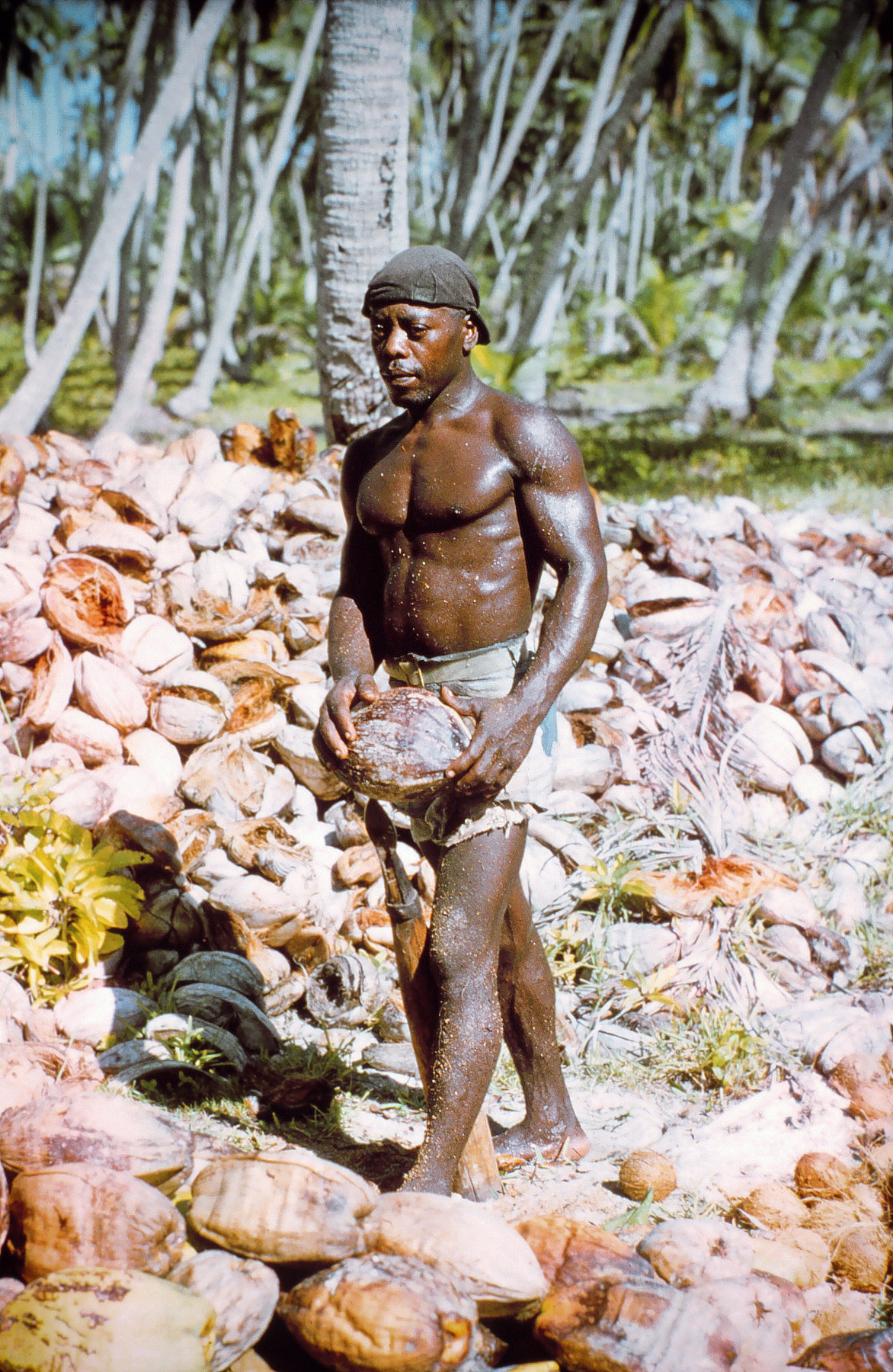
Chagossians
The Chagossians (also Îlois or Chagos Islanders) are a currently exiled Creole ethnic group native to the Chagos Islands, specifically Diego Garcia, Peros Banhos, and the Salomon island chain, as well as other parts of the Chagos Archipelago, from the late 18th century until the middle of 20th century. Most Chagossians now live in Mauritius and the United Kingdom after being forcibly removed by the British government in the late 1960s and early 1970s so that Diego Garcia, the island where most Chagossians lived, could serve as the location for a United States military base. Today, no Chagossians are allowed to live on the island of Diego Garcia, as it is now the site of the military base dubbed Camp Thunder Cove. The Chagossian people's ancestry is mostly African, particularly from Madagascar, Mozambique and other African nations including Mauritius. There is also a significant proportion of Indian and Malay ancestry. The French brought some to the Chagos Islands a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Indian Ocean Territory
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 individual islandsmany very smallamounting to a total land area of . The largest and most southerly island is Diego Garcia, , the site of a Joint Military Facility of the United Kingdom and the United States. The only inhabitants are British and United States military personnel, and associated contractors, who collectively number around 3,000 (2018 figures). The forced removal of Chagossians from the Chagos Archipelago occurred between 1968 and 1973. The Chagossians, then numbering about 2,000 people, were expelled by the UK government to Mauritius and Seychelles in order to construct the military base. Today, the exiled Chagossians are still trying to return, saying that the forced expulsion and dispossession was unlawful, but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Agaléga and St. Brandon. The islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, along with nearby Réunion (a French overseas department), are part of the Mascarene Islands. The main island of Mauritius, where most of the population is concentrated, hosts the capital and largest city, Port Louis. The country spans and has an exclusive economic zone covering . Arab sailors were the first to discover the uninhabited island, around 975, and they called it ''Dina Arobi''. The earliest discovery was in 1507 by Portuguese sailors, who otherwise took little interest in the islands. The Dutch took possession in 1598, establishing a succession of short-lived settlements over a period of about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egmont Islands
Egmont Islands (also known as Egmont Atoll, or Six Iles) is an uninhabited atoll administered by the United Kingdom. They are one of the few emerged coral atolls that make up the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory. This small atoll lies less than 10km south of the southwestern rim of the Great Chagos Bank submerged coral reef. Its total size is 29km², including the lagoon and the fringing coral reef. The land area totals about 4km². The nearest island is Danger Island on the Great Chagos Bank, less than 30km due north. There are two passages into the lagoon along the Northern Rim, Fausse Passe in the northeast and a wider passage in the northwest. The Egmont Islands are one of the favorite anchoring spots for itinerant yachtsmen passing through the Chagos. Islands The largest island is "Île Sud-Est" (Eastern Egmont), where the settlement was located, with an area of 1.5km². While "Île Lubine" is similar in size, the other islets are smaller. All islands ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
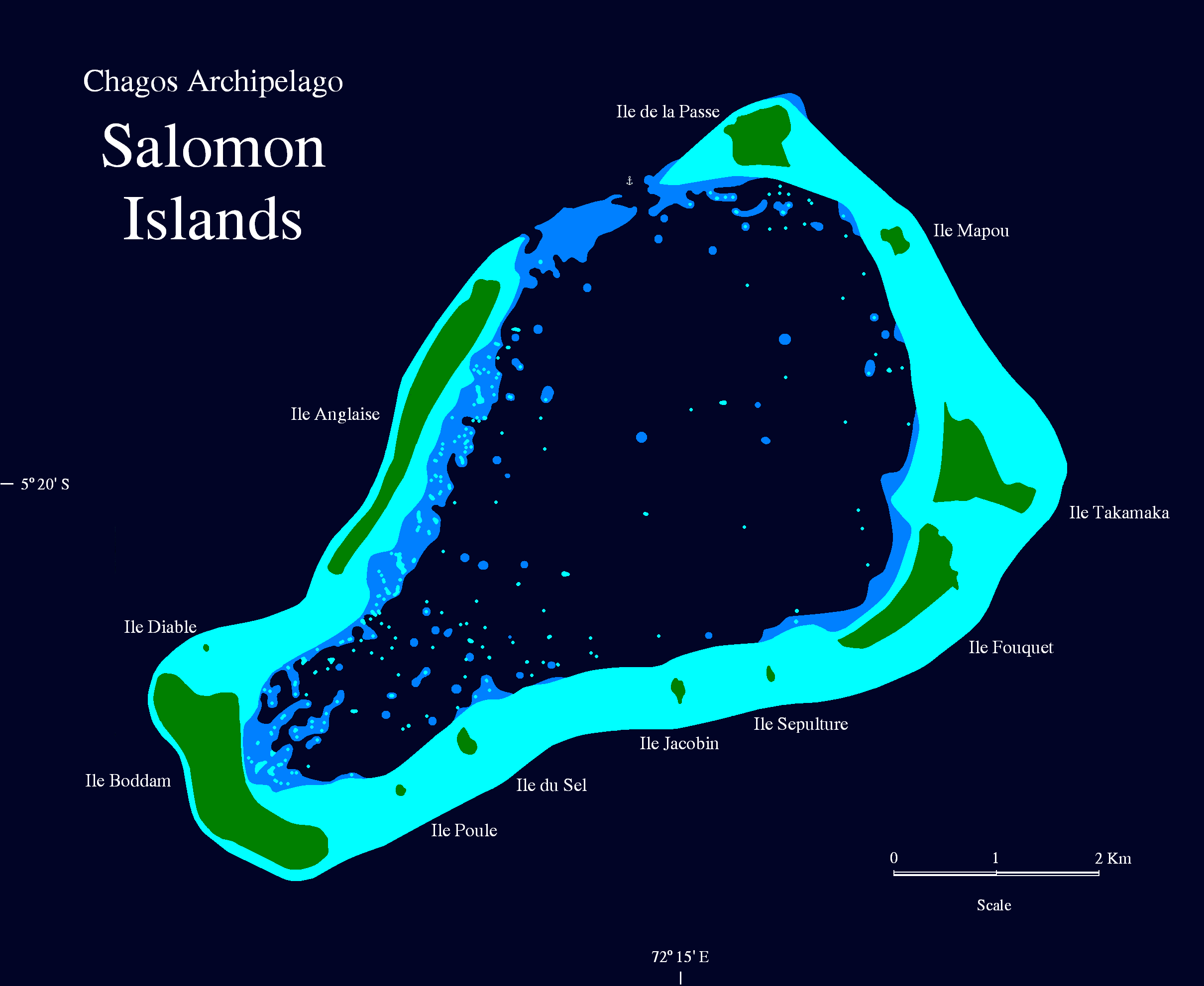
Salomon Islands
The Salomon Islands or Salomon Atoll is a small atoll of the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory. Description The atoll is located in the northeast of the Chagos Archipelago, between Blenheim Reef and Peros Banhos. The main islands in the group are Île Boddam, with the former main settlement, and a land area of , and Île Anglaise (), both on the western rim of the reef. There were smaller settlements of Chagossians in Fouquet () and Takamaka () Islands. Île de la Passe is in area, and Île Mapou . The remaining islets are much smaller. The total land area is . There is a passage into the lagoon, named Baie de Salomon, on the Northern side, between Île Anglaise and Île de la Passe. The Salomon Islands are one of the favorite anchoring spots for itinerant yachtsmen passing through the Chagos, even though there are no proper moorings for yachts and a permit of the BIOT authorities is needed. Now uninhabited, the islands are overrun by low jungle between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chagos–Laccadive Ridge
The Chagos–Laccadive Ridge (CLR), also known as the Chagos–Laccadive Plateau, is a prominent volcanic ridge and oceanic plateau extending between the Northern and the Central Indian Ocean. Extending from 10°S to 15°N, the CLR includes the Laccadive, Maldives, and Chagos archipelagos and can be divided into three corresponding blocks, of which the first is continental and the two latter are oceanic. The CLR is asymmetrical with a steeper eastern slope and has an average depth of less than . It formed south of or near the Equator together with the remaining western continental margin of India, when India separated first from Madagascar in the Mid-Cretaceous and then from the Seychelles Islands in the Late Cretaceous. Extent The CLR extends northward for from 10°S at the southern end of the Chagos Archipelago to 14°N around the Adas Bank. The second element of the name is for the Laccadive Islands, among the islands of Lakshadweep. ("Laccadive" is a form of the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peros Banhos
Peros Banhos, Pedro dos Banhos or Baixos de Pêro dos Banhos in old maps, is a formerly inhabited atoll in the Chagos Archipelago of the British Indian Ocean Territory, also claimed by Mauritius. Île Yeye, located at the northeastern corner of the atoll, is the island of the Chagos Archipelago that is closest to the Maldives. Geography The atoll has a total area of , but a land area of only , made up by some 32 islets. , most of the remaining surface, is occupied by the lagoon, which is connected to the open sea, and the reef flat. Peros Banhos is a medium-sized coralline atoll circled by a regular coral reef, similar to those in the neighboring Maldives. The diameter of the lagoon, known as ''Baie de Peros Banhos'' in French, is just above 20 km. The circling reef is sunken on its southeastern rim. All islands are flat and sandy and the largest ones are covered with coconut trees. The largest and most important island in the group is Île du Coin. It was home to the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has some large marginal or regional seas such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Andaman Sea. Etymology The Indian Ocean has been known by its present name since at least 1515 when the Latin form ''Oceanus Orientalis Indicus'' ("Indian Eastern Ocean") is attested, named after India, which projects into it. It was earlier known as the ''Eastern Ocean'', a term that was still in use during the mid-18th century (see map), as opposed to the ''Western Ocean'' ( Atlantic) before the Pacific was surmised. Conversely, Chinese explorers in the Indian Ocean during the 15th century called it the Western Oceans. In Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sega Tambour Chagos
Sega tambour Chagos is one of the types of Sega music of Mauritius, with origins in the Chagos Archipelago. It is sung in the Chagossian creole language of the islands. History Chagos is part of the British Indian Ocean Territory and is claimed by Mauritius. Diego Garcia, the largest and most southerly of the islands, is inhabited. It contains a joint UK-US naval support facility. Between 1967 and 1973, former agricultural workers, earlier residents in the islands, were relocated primarily to Mauritius, but also to the Seychelles. Instruments Instruments used in Chagos Sega include: * Tambour, a large, circular, percussive instrument that provides the basic rhythm * Whistle * Triangle * rattle See also * Music of Mauritius * Sega * Jessy Marcelin Jessy Marcelin (born 1934) is a Chagossian musician and activist who was born in the Chagos Islands and forced to leave as part of Britain's displacement of the Chagossian people. Marcelin was born in 1934 on the atoll of Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |