|
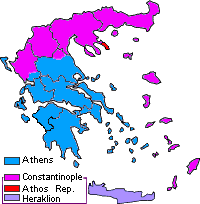
Tomos Dated June 29, 1850
The ''tomos'' dated 29 June 1850 is the official decree of the Ecumenical Patriarchate which gave ''de jure'' autocephaly to the then-''de facto'' autocephalous Church of Greece. History Declaration of autocephaly by Greece The decision to create an independent Kingdom of Greece from the Three Great Powers (the British Empire, the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of France), finalized by the Treaty of Constantinople (1832), posed a dilemma for Greek patriarchal and religious society: whether there is an independent Church of Greece or in the independent state extends the ecclesiastical jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. The government declared the Church of Greece to be autocephalous in 1833 in a political decision of the Bavarian regents acting for King Otto, who was a minor. The decision roiled Greek politics for decades as royal authorities took increasing control. Signing of the ''tomos'' In the end, the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Of Greece
Otto (, ; 1 June 181526 July 1867) was a Bavarian prince who ruled as King of Greece from the establishment of the monarchy on 27 May 1832, under the Convention of London, until he was deposed on 23 October 1862. The second son of King Ludwig I of Bavaria, Otto ascended the newly created throne of Greece at age 17. His government was initially run by a three-man regency council made up of Bavarian court officials. Upon reaching his majority, Otto removed the regents when they proved unpopular with the people, and he ruled as an absolute monarch. Eventually his subjects' demands for a constitution proved overwhelming, and in the face of an armed (but bloodless) insurrection, Otto granted a constitution in 1843. Throughout his reign Otto was unable to resolve Greece's poverty and prevent economic meddling from outside. Greek politics in this era were based on affiliations with the three Great Powers that had guaranteed Greece's independence, Britain, France and Russia, and Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is the internal ecclesiastical law, or operational policy, governing the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and the Eastern Catholic Churches), the Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches, and the individual national churches within the Anglican Communion. The way that such church law is legislated, interpreted and at times adjudicated varies widely among these four bodies of churches. In all three traditions, a canon was originally a rule adopted by a church council; these canons formed the foundation of canon law. Etymology Greek / grc, κανών, Arabic / , Hebrew / , 'straight'; a rule, code, standard, or measure; the root meaning in all these languages is 'reed'; see also the Romance-language ancestors of the English wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Greece
Religion in Greece is dominated by Christianity, in particular the Greek Orthodox Church, which is within the larger communion of the Eastern Orthodox Church. It represented 90% of the total population in 2015 and is constitutionally recognized as the "prevailing religion" of Greece. Religions with smaller numbers of followers include Islam (comprising 2% of the population), Catholicism (comprising less than 1% of the population), Evangelicalism, Hellenic Paganism, Sikhism and Hinduism. Also a small number of Greek Atheists exists, not self-identifying as religious. Religion is key part of identity for most Greeks, with 76% of Greeks in a 2015-17 survey saying that their nationality is defined by Christianity. Statistics on metaphysics and worldview, do not concern narrowly only the hyponym religion. According to other sources, 81.4% of Greeks identify as Orthodox Christians and 14.7% are atheists. Christianity As of 2015, 93% of the population of Greece was Christian. Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Church
A national church is a Christian church associated with a specific ethnic group or nation state. The idea was notably discussed during the 19th century, during the emergence of modern nationalism. Samuel Taylor Coleridge, in a draft discussing the question of church and state around 1828 wrote that :"a National Church might exist, and has existed, without Christianity, because before the institution of the ''Christian'' Church - as ..the Levitical Church in the Hebrew Constitution, ndthe Druidical in the Celtic, would suffice to prove". John Wordsworth, Bishop of Salisbury, wrote about the National Church of Sweden in 1911, interpreting the Church of Sweden and the Church of England as national churches of the Swedish and the English peoples, respectively. The concept of a national church remains alive in the Protestantism of United Kingdom and Scandinavia in particular. While, in a context of England, the national church remains a common denominator for the Church of Engla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey ( East Thrace). The region's boundaries are based on that of the Roman Province of Thrace; the lands inhabited by the ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into the region of Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'' was first used by the Greeks when referring to the Thracian tribes, from ancient Greek Thrake (Θρᾴκη), descending from ''Thrāix'' (Θρᾷξ). It referred originally to the Thracians, an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' first referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Macedonia
Macedonia (; el, Μακεδονία, Makedonía ) is a geographic and former administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and Greek geographic region, with a population of 2.36 million in 2020. It is highly mountainous, with most major urban centres such as Thessaloniki and Kavala being concentrated on its southern coastline. Together with Thrace, and sometimes also Thessaly and Epirus, it is part of Northern Greece. Greek Macedonia encompasses entirely the southern part of the wider region of Macedonia, making up 51% of the total area of that region. Additionally, it forms part of Greece's borders with three countries: Bulgaria to the northeast, North Macedonia to the north, and Albania to the northwest. Greek Macedonia incorporates most of the territories of ancient Macedon, a kingdom ruled by the Argeads, whose most celebrated members were Alexander the Great and his father Philip II. Before the expansion of Macedonia under Phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Athos
Mount Athos (; el, Ἄθως, ) is a mountain in the distal part of the eponymous Athos peninsula and site of an important centre of Eastern Orthodox monasticism in northeastern Greece. The mountain along with the respective part of the peninsula have been governed as the monastic community of Mount Athos, an autonomous region within the Hellenic Republic, ecclesiastically under the direct jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople, while the remainder of the peninsula forms part of the Aristotelis municipality. Mount Athos has been inhabited since ancient times and is known for its long Christian presence and historical monastic traditions, which date back to at least AD 800 and the Byzantine era. Because of its long history of religious importance, the well-preserved agrarian architecture within the monasteries, and the preservation of the flora and fauna around the mountain, Mount Athos was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1988. In modern Greek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnophyletism
Phyletism or ethnophyletism (from Greek ἔθνος ''ethnos'' "nation" and φυλετισμός ''phyletismos'' "tribalism") is the principle of nationalities applied in the ecclesiastical domain: in other words, the conflation between church and nation. The term ''ethnophyletismos'' designates the idea that a local autocephalous church should be based not on a local ( ecclesial) criterion, but on an ethnophyletist, national or linguistic one. It was used at the local council held in Constantinople on 10 September 1872 to qualify "phyletist (religious) nationalism", which was condemned as a modern ecclesial heresy: the church should not be confused with the destiny of a single nation or a single race. Appearance of the term in 19th century The term ''phyletism'' was used for the first time by a Synod convened by the Ecumenical patriarchate in Constantinople, then the capital of the Ottoman Empire, in 1872 to define and condemn an alleged heretical teaching espoused by the Bulgari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Exarchate
The Bulgarian Exarchate ( bg, Българска екзархия, Balgarska ekzarhiya; tr, Bulgar Eksarhlığı) was the official name of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church before its autocephaly was recognized by the Ecumenical See in 1945 and the Bulgarian Patriarchate was restored in 1953. The Exarchate (a de facto autocephaly) was unilaterally (without the blessing of the Ecumenical Patriarch) promulgated on , in the Bulgarian church in Constantinople in pursuance of the firman of Sultan Abdülaziz of the Ottoman Empire. The foundation of the Exarchate was the direct result of the struggle of the Bulgarian Orthodox against the domination of the Greek Patriarchate of Constantinople in the 1850s and 1860s. In 1872, the Patriarchate accused the Exarchate that it introduced ''ethno-national'' characteristics in the religious organization of the Orthodox Church, and the secession from the Patriarchate was officially condemned by the Council in Constantinople in September 1872 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |