|
Tomb Of The Augurs
The Tomb of the Augurs (Italian ''Tomba degli Àuguri'') is an Etruscan burial chamber so called because of a misinterpretation of one of the fresco figures on the right wall thought to be a Roman priest known as an augur. The tomb is located within the Necropolis of Monterozzi near Tarquinia, Lazio, Italy, and dates to around 530-520 BC. This tomb is one of the first tombs in Tarquinia to have figural decoration on all four walls of its main or only chamber.''A History of Roman Art'', Enhanced Edition, Wadsworth CENGAGE Learning, Boston, 2010 The wall decoration was frescoed between 530-520 BC by an Ionian Greek painter, perhaps from Phocaea, whose style was associated with that of the Northern Ionic workers active in Elmali. This tomb is also the first time a theme not of mythology, but instead depictions of funerary rites and funerary games are seen.''The Great Centuries of Painting: Etruscan Painting'', Second Edition, The World Publishing Company, Cleveland, 1952 Descript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of The Bulls
The Tomb of the Bulls ( it, Tomba dei Tori) is an Etruscan tomb in the Necropolis of Monterozzi near Tarquinia, Lazio, Italy. It was discovered in 1892 and has been dated back to either 540–530 BC or 530–520 BC. According to an inscription Arath Spuriana apparently commissioned the construction of the tomb. It is named after the two bulls which appear on one of its frescoes. It is the earliest example of a tomb with complex frescoes in the necropolis, and the stylistic elements are derived from Ionian Greek culture. Along with the frescoes of the Tomb of the Whipping these paintings are relatively rare examples of explicit sexual scenes in Etruscan art, which were far more common in Ancient Greek art. Like other Etruscan tombs, it would originally have contained many grave goods, especially Etruscan pottery, now removed. Description The entrance to the tomb leads to the main chamber. The back wall of the main chamber is opposite to the entrance and contains two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Art
Etruscan art was produced by the Etruscan civilization in central Italy between the 10th and 1st centuries BC. From around 750 BC it was heavily influenced by Greek art, which was imported by the Etruscans, but always retained distinct characteristics. Particularly strong in this tradition were figurative sculpture in terracotta (especially life-size on sarcophagi or temples), wall-painting and metalworking especially in bronze. Jewellery and engraved gems of high quality were produced. Etruscan sculpture in cast bronze was famous and widely exported, but relatively few large examples have survived (the material was too valuable, and recycled later). In contrast to terracotta and bronze, there was relatively little Etruscan sculpture in stone, despite the Etruscans controlling fine sources of marble, including Carrara marble, which seems not to have been exploited until the Romans. The great majority of survivals came from tombs, which were typically crammed with sarcophagi an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Architecture
Etruscan architecture was created between about 900 BC and 27 BC, when the expanding civilization of ancient Rome finally absorbed Etruscan civilization. The Etruscans were considerable builders in stone, wood and other materials of temples, houses, tombs and city walls, as well as bridges and roads. The only structures remaining in quantity in anything like their original condition are tombs and walls, but through archaeology and other sources we have a good deal of information on what once existed. From about 630 BC, Etruscan architecture was heavily influenced by Greek architecture, which was itself developing through the same period. In turn it influenced Roman architecture, which in its early centuries can be considered as just a regional variation of Etruscan architecture. But increasingly, from about 200 BC, the Romans looked directly to Greece for their styling, while sometimes retaining Etruscan shapes and purposes in their buildings. The main monumental forms of Etru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulos
An ''aulos'' ( grc, αὐλός, plural , ''auloi'') or ''tibia'' (Latin) was an ancient Greek wind instrument, depicted often in art and also attested by archaeology. Though ''aulos'' is often translated as "flute" or "double flute", it was usually a double-reeded instrument, and its sound—described as "penetrating, insisting and exciting"—was more akin to that of the bagpipes, with a chanter and (modulated) drone. An aulete (, ) was the musician who performed on an ''aulos''. The ancient Roman equivalent was the ''tibicen'' (plural ''tibicines''), from the Latin ''tibia,'' "pipe, ''aulos''." The neologism aulode is sometimes used by analogy with ''rhapsode'' and ''citharode'' ( citharede) to refer to an ''aulos'' player, who may also be called an aulist; however, aulode more commonly refers to a singer who sang the accompaniment to a piece played on the aulos. Background There were several kinds of ''aulos'', single or double. The most common variety was a reed instrumen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also made him the last son to be regurgitated by his father. He and his brothers, Zeus and Poseidon, defeated their father's generation of gods, the Titans, and claimed rulership over the cosmos. Hades received the underworld, Zeus the sky, and Poseidon the sea, with the solid earth, long the province of Gaia, available to all three concurrently. In artistic depictions, Hades is typically portrayed holding a bident and wearing his helm with Cerberus, the three-headed guard dog of the underworld, standing to his side. The Etruscan god Aita and the Roman gods Dis Pater and Orcus were eventually taken as equivalent to Hades and merged into Pluto, a Latinisation of Plouton ( grc-gre, , Ploútōn), itself a euphemistic title often given to Had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charun
In Etruscan mythology, Charun (also spelled Charu, or Karun) acted as one of the psychopompoi of the underworld (not to be confused with the god of the underworld, known to the Etruscans as Aita). He is often portrayed with Vanth, a winged figure also associated with the underworld. Origins His name was imported from Greek Charon, although it is uncertain whether Etruscans had a native name for a god of the underworld before this. As suggested by alternations in the Etruscan language such as ''θu'' "one" changing to ''θunśna'' "first", ''lev'' "lion" (from Greek leōn) and ''Apulu'' (from Greek ''Apóllōn''), words ending in ''-n'' after ''u'' were disappearing from the language which is why we see his name spelled ''Xarun'' and later ''Xaru''. Appearance The Etruscan Charun was fundamentally different from his Greek counterpart. Guarding the entry to the underworld he is depicted with a hammer (his religious symbol) and is shown with pointed ears, snakes around his arms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lituus
The word ''lituus'' originally meant a curved augural staff, or a curved war-trumpet in the ancient Latin language. This Latin word continued in use through the 18th century as an alternative to the vernacular names of various musical instruments. Roman ritual wand The ''lituus'' was a crooked wand (similar in shape to the top part of some Western European crosiers) used as a cult instrument in ancient Roman religion by augurs to mark out a ritual space in the sky (a ''templum''). The passage of birds through this ''templum'' indicated divine favor or disfavor for a given undertaking. The ''lituus'' was also used as a symbol of office for the college of the augurs to mark them out as a priestly group. Music instrument Antiquity The ancient ''lituus'' was an Etruscan high-pitched brass instrument, which was straight but bent at the end, in the shape of a letter J, similar to the Gallic carnyx. It was later used by the Romans, especially for processional music and as a signalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonothetes
In ancient Greece, an ''agonothetes'' (plural '; grc, ἀγωνοθέτης) was the president or superintendent of one of the sacred Panhellenic Games. At first the person who instituted the games and defrayed the expenses was the ''agonothetes''; but in the great public games, such as the Olympic Games and Pythian Games, these presidents were the representatives of different states, or were chosen from the people in whose country the games were celebrated; thus at the Pythian Games at Athens Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ... ten ' were elected for four years to superintend the various contests. In English, by confusion with the native ''-s'' plural form, the singular ''agonothete'' and plural ''agonothetes'' are sometimes encountered. Bibliography Clément Sarraz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
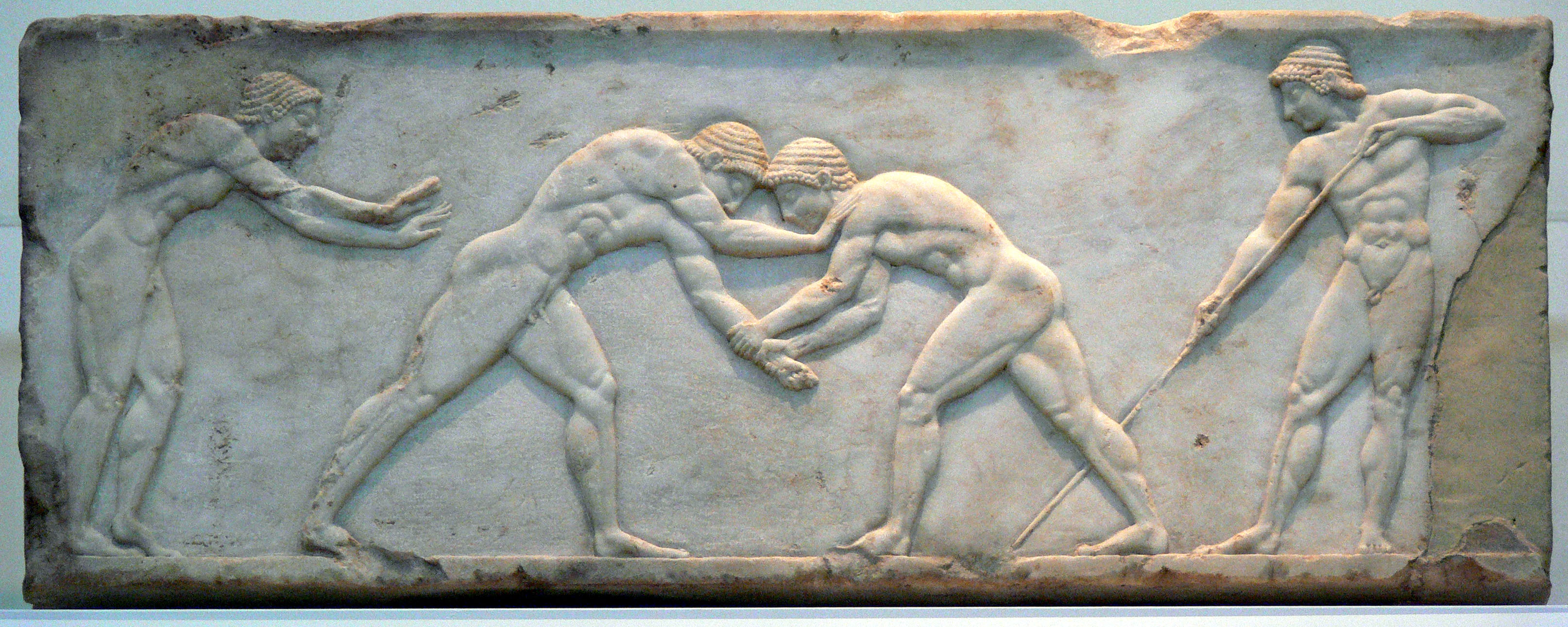
Greek Wrestling
Greek wrestling ( grc-gre, πάλη, pálē), also known as Ancient Greek wrestling and Palé, was the most popular organized sport in Ancient Greece. A point was scored when one player touched the ground with his back, hip or shoulder, or conceding defeat due to a submission-hold or was forced out of the wrestling-area. Three points had to be scored to win the match. One particularly important position in this form of wrestling was one where one of the contestants was lying on his abdomen with the other on his back trying to strangle him (back mount). The athlete on the bottom would try to grasp an arm of the one on top and turn him over onto his back while the athlete on top would try to complete the choke without being rolled. Wrestling was the first competition to be added to the Olympic Games that was not a footrace. It was added in 708 B.C. (Miller, 46). The competitions were held in elimination-tournament style until one wrestler was crowned the victor. The wrestling area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their lives and their legal and social standing by appearing in the arena. Most were despised as slaves, schooled under harsh conditions, socially marginalized, and segregated even in death. Irrespective of their origin, gladiators offered spectators an example of Rome's martial ethics and, in fighting or dying well, they could inspire admiration and popular acclaim. They were celebrated in high and low art, and their value as entertainers was commemorated in precious and commonplace objects throughout the Roman world. The origin of gladiatorial combat is open to debate. There is evidence of it in funeral rites during the Punic Wars of the 3rd century BC, and thereafter it rapidly became an essential fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)