|
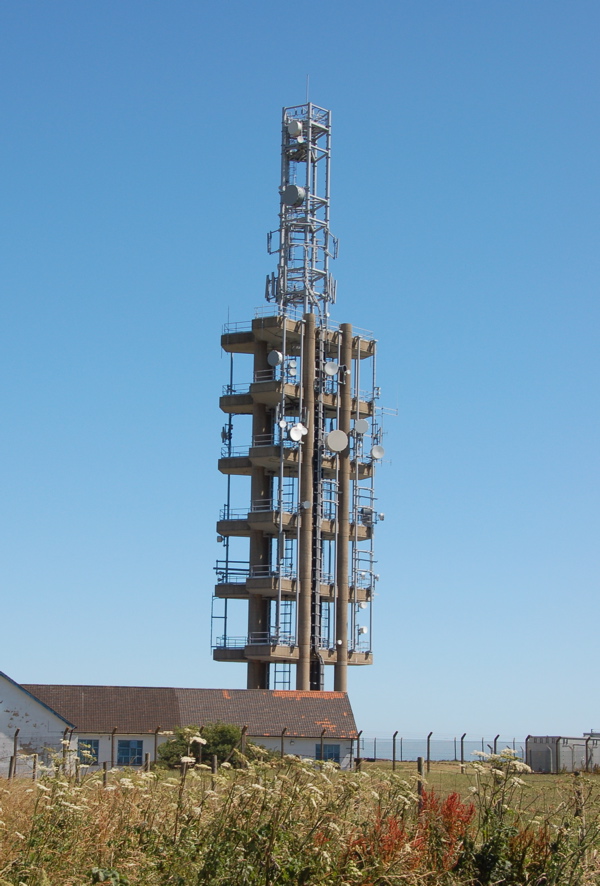
Tolsford Hill BT Tower
Tolsford Hill BT Tower is a telecommunication tower built of reinforced concrete at Tolsford Hill on the North Downs near Folkestone, Kent. Tolsford Hill BT Tower is one of the few British towers built of reinforced concrete and is 67.36 metres ( 221 ft) high. See also * British Telecom microwave network * Telecommunications towers in the United Kingdom Telecommunications towers in the United Kingdom are operated mainly by Arqiva. Arqiva operates the transmitters for UK terrestrial TV and most radio broadcasting, both analogue and digital. BT also operates a number of telecommunications towe ... References RSG: Features: The Towers of Backbone. Communication towers in the United Kingdom Towers in Kent British Telecom buildings and structures Transmitter sites in England {{Europe-mast-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolsford 1
The Folkestone Downs are an area of chalk downland above Folkestone, where the eastern end of the North Downs escarpment meets the English Channel. Part of the Downs is the Folkestone to Etchinghill Escarpment Site of Special Scientific Interest, designated for its geological and biological interest. Topography Folkestone Downs stretch for 5 kilometres from East Cliff and Warren Country Park in the east to Peene Quarry in the west. The downs rise steeply above the town of Folkestone to heights in excess of 150 metres. The highest point is Dover Hill at 170 metres. The Channel Tunnel Terminal lies at the foot of the downs and the British portal is directly below the slopes of Castle Hill. The downland is classified as CG4 ''Brachypodium pinnatum'' and CG5 ''Bromus erectus - Brachypodium pinnatum'' calcareous grassland with smaller areas of CG2 ''Festuca ovina - Avenula pratensis'' grassland. There are also areas of scrubland and woodland. Ecology Flora Folkestone Downs is on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folkestone
Folkestone ( ) is a port town on the English Channel, in Kent, south-east England. The town lies on the southern edge of the North Downs at a valley between two cliffs. It was an important harbour and shipping port for most of the 19th and 20th centuries. There has been a settlement in this location since the Mesolithic era. A nunnery was founded by Eanswith, granddaughter of Æthelberht of Kent in the 7th century, who is still commemorated as part of the town's culture. During the 13th century it subsequently developed into a seaport and the harbour developed during the early 19th century to provide defence against a French invasion. Folkestone expanded further west after the arrival of the railway in 1843 as an elegant coastal resort, thanks to the investment of the Earl of Radnor under the urban plan of Decimus Burton. In its heyday - during the Edwardian era - Folkestone was considered the most fashionable resort of the time, visited by royalties - amongst them Queen Victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces the French department of Pas-de-Calais across the Strait of Dover. The county town is Maidstone. It is the fifth most populous county in England, the most populous non-Metropolitan county and the most populous of the home counties. Kent was one of the first British territories to be settled by Germanic tribes, most notably the Jutes, following the withdrawal of the Romans. Canterbury Cathedral in Kent, the oldest cathedral in England, has been the seat of the Archbishops of Canterbury since the conversion of England to Christianity that began in the 6th century with Saint Augustine. Rochester Cathedral in Medway is England's second-oldest cathedral. Located between London and the Strait of Dover, which separates England from mainla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolsford Hill
The Folkestone Downs are an area of chalk downland above Folkestone, where the eastern end of the North Downs escarpment meets the English Channel. Part of the Downs is the Folkestone to Etchinghill Escarpment Site of Special Scientific Interest, designated for its geological and biological interest. Topography Folkestone Downs stretch for 5 kilometres from East Cliff and Warren Country Park in the east to Peene Quarry in the west. The downs rise steeply above the town of Folkestone to heights in excess of 150 metres. The highest point is Dover Hill at 170 metres. The Channel Tunnel Terminal lies at the foot of the downs and the British portal is directly below the slopes of Castle Hill. The downland is classified as CG4 ''Brachypodium pinnatum'' and CG5 ''Bromus erectus - Brachypodium pinnatum'' calcareous grassland with smaller areas of CG2 ''Festuca ovina - Avenula pratensis'' grassland. There are also areas of scrubland and woodland. Ecology Flora Folkestone Downs is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
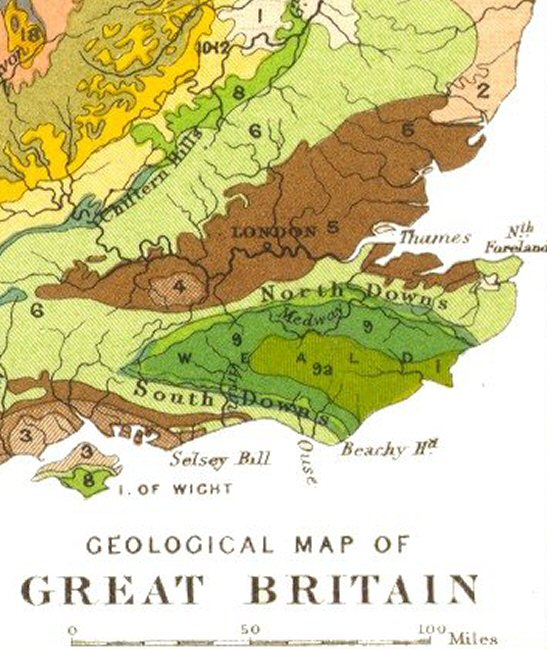
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but some to the south. Geography The narrow spine of the Hog's Back between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Telecom Microwave Network
The British Telecom microwave network was a network of point-to-point microwave radio links in the United Kingdom, operated at first by the General Post Office, and subsequently by its successor BT plc. From the late 1950s to the 1980s it provided a large part of BT's trunk communications capacity, and carried telephone, television and radar signals and digital data, both civil and military. Its use of line-of-sight microwave transmission was particularly important during the Cold War for its resilience against nuclear attack. It was rendered obsolete, at least for normal civilian purposes, by the installation of a national optical fibre communication network with considerably higher reliability and vastly greater capacity. BT remains one of the largest owners of transmission and microwave towers in the UK. The most famous of these is the BT Tower in London, which was the tallest building in the UK from its construction in the 1960s until the early 1980s, and a major node in the BT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications Towers In The United Kingdom
Telecommunications towers in the United Kingdom are operated mainly by Arqiva. Arqiva operates the transmitters for UK terrestrial TV and most radio broadcasting, both analogue and digital. BT also operates a number of telecommunications towers in the UK. BT BT's towers were, at one time, the backbone for a national line-of-sight microwave telecommunications network. One of the most famous of these is the BT Tower in London. However, the introduction of fibre optic network technology rendered these microwave towers largely obsolete for their original purpose. Nowadays they tend to be used mainly for relatively low capacity fixed links to customer sites and mobile telephony. List of BT towers BT Group owns at least 200 radio masts and towers in Britain. Of these, fourteen are reinforced concrete towers. The rest are of steel lattice construction. Seven of the fourteen are of similar design, known as the 'Chilterns' type, after the first one which was built at Stokenchurc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Towers In The United Kingdom
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquiry studying them. There are many disagreements about its precise definition. John Peters argues that the difficulty of defining communication emerges from the fact that communication is both a universal phenomenon and a specific discipline of institutional academic study. One definitional strategy involves limiting what can be included in the category of communication (for example, requiring a "conscious intent" to persuade). By this logic, one possible definition of communication is the act of developing meaning among entities or groups through the use of sufficiently mutually understood signs, symbols, and semiotic conventions. An important distinction is between verbal communication, which happens through the use of a language, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towers In Kent
A tower is a tall structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures. Towers are specifically distinguished from buildings in that they are built not to be habitable but to serve other functions using the height of the tower. For example, the height of a clock tower improves the visibility of the clock, and the height of a tower in a fortified building such as a castle increases the visibility of the surroundings for defensive purposes. Towers may also be built for observation, leisure, or telecommunication purposes. A tower can stand alone or be supported by adjacent buildings, or it may be a feature on top of a larger structure or building. Etymology Old English ''torr'' is from Latin ''turris'' via Old French ''tor''. The Latin term together with Greek τύρσις was loaned from a pre-Indo-European Mediterranean language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Telecom Buildings And Structures
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |