|
Tolkappiyam Chapter 1–3
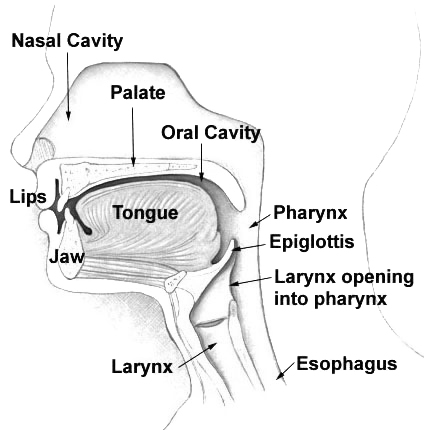
Articulations of Tamil-phonemes are discussed here based on Tolkappiyam. Propelling air in mouth makes sound if articulated. The least part of human language is phoneme. It varies in languages. Generally some points in the mouth and nose help to propel phoneme. Tamil phonemes are thirty. They are 12 vowels and 18 consonants. Tolkappiyam, the earliest Tamil classical work defines scientifically the positions and functions of the speech organs, which produce phonemes. Speech organs and their functions Raising wind starts from diaphragm. On the way it touches 8 vocal organs. Head the oral cavity, pharynx The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ..., larynx are the three places where they touch. Teeth, lip, tongue, nose and palate are the five places where they pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Phonology
Tamil phonology is characterised by the presence of “true-subapical” retroflex consonants and multiple rhotic consonants. Its script does not distinguish between voiced and unvoiced consonants; phonetically, voice is assigned depending on a consonant's position in a word, voiced intervocalically and after nasals except when geminated. Tamil phonology permits few consonant clusters, which can never be word initial. Vowels The vowels are called ' ('life letter'). The vowels are classified into short and long (five of each type) and two diphthongs. The long (''nedil'') vowels are about twice as long as the short (''kuṟil'') vowels. The diphthongs are usually pronounced about 1.5 times as long as the short vowels, though most grammatical texts place them with the long vowels. Tamil has two diphthongs: and , the latter of which is restricted to a few lexical items. Some like Krishnamurti consider the diphthongs as clusters of /a/ + /j, ʋ/ as they pattern with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil To Roman Script
Tamil may refer to: * Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia **Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils **Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia * Tamil language, natively spoken by the Tamils * Tamil script, primarily used to write the Tamil language **Tamil (Unicode block), a block of Tamil characters in Unicode * Tamil dialects, referencing geographical variations in speech See also * Tamil cinema, also known as Kollywood, the word being a portmanteau of Kodambakkam and Hollywood. * Tamil cuisine * Tamil culture, is considered to be one of the world's oldest civilizations. * Tamil diaspora * Tamil Eelam, a proposed independent state in the north and east of Sri Lanka * Tamil Nadu, one of the 28 states of India * Tamil nationalism * ''Tamil News'', a daily Tamil-language television news program in Tamil Nadu * Tamilakam, the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covered today's Tam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India. Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages of India.. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). A. K. Ramanujan described it as "the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
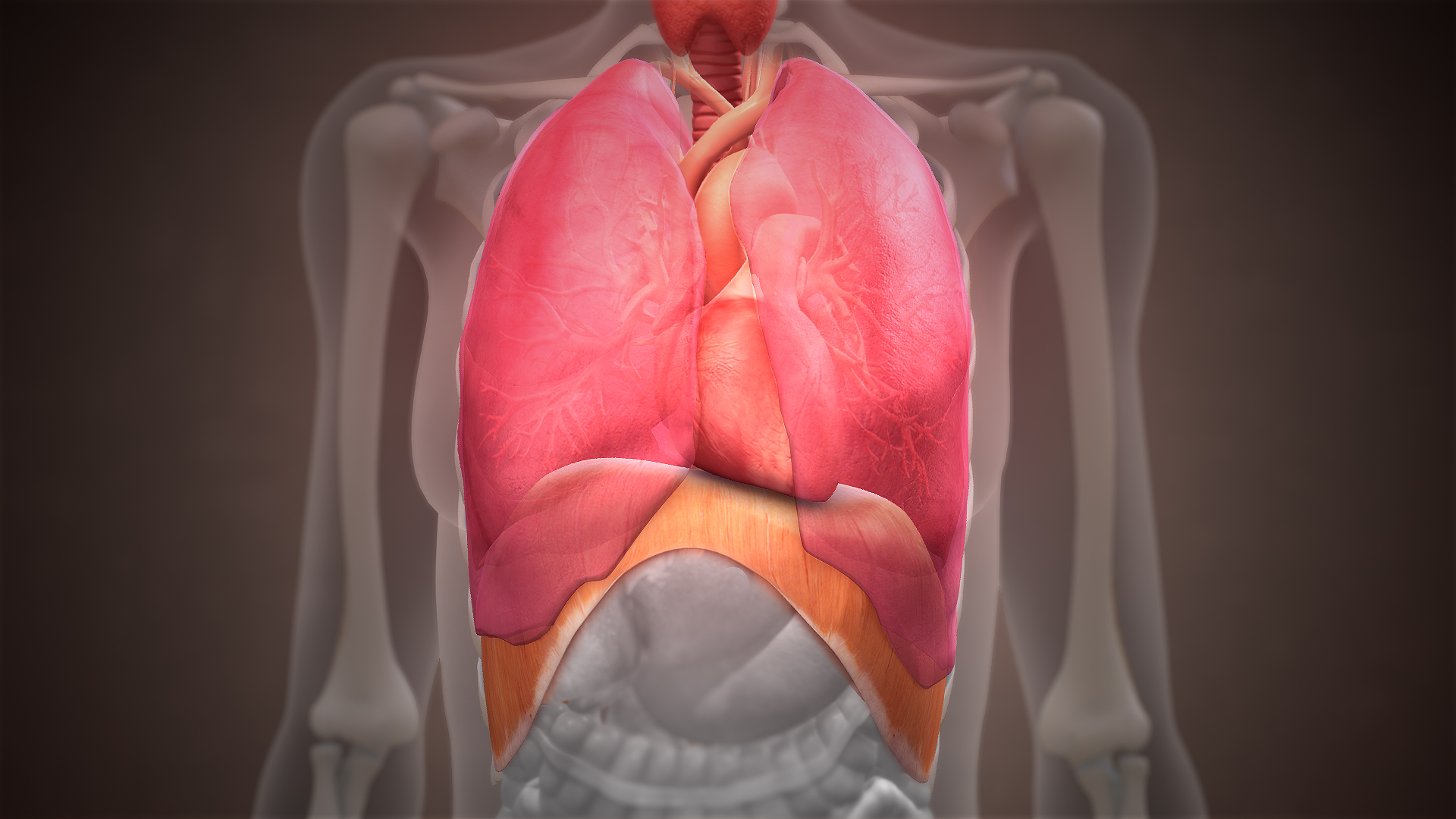
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |