Larynx on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an
 The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a
The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a

organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
in the top of the neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In ...
involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid fo ...
. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ
Structure
ciliated columnar epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar Epithelium#Cell types, epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped Cell nucleus, nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple c ...
except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet
An inlet is a (usually long and narrow) indentation of a shoreline, such as a small arm, bay, sound, fjord, lagoon or marsh, that leads to an enclosed larger body of water such as a lake, estuary, gulf or marginal sea.
Overview
In marine geogra ...
, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the lower border of the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
, where it is continuous with the lumen of the trachea. The mucous membrane lining the larynx forms two pairs of lateral folds that project inward into its cavity. The upper folds are called the vestibular folds. They are also sometimes called the false vocal cords for the rather obvious reason that they play no part in vocalization. The Kargyraa
Tuvan throat singing, the main technique of which is known as ''khoomei'' ( tyv, хөөмей, xöömej, mn, хөөмий; ᠬᠦᠭᠡᠮᠡᠢ, khöömii, russian: хоомей, Chinese: 呼麦, pinyin: ''hūmài''), includes a type of overt ...
style of Tuvan throat singing makes use of these folds to sing an octave lower, and they are used in Umngqokolo, a type of Xhosa throat singing. The lower pair of folds are known as the vocal cords, which produce sounds needed for speech and other vocalizations. The slit-like space between the left and right vocal cords, called the rima glottidis, is the narrowest part of the larynx. The vocal cords and the rima glottidis are together designated as the glottis. The laryngeal cavity above the vestibular folds is called the vestibule. The very middle portion of the cavity between the vestibular folds and the vocal cords is the ventricle of the larynx, or laryngeal ventricle. The infraglottic cavity is the open space below the glottis.
Location
In adult humans, the larynx is found in theanterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
neck at the level of the cervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In ...
C3–C6. It connects the inferior part of the pharynx (hypopharynx) with the trachea. The laryngeal skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
consists of nine cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck ...
s: three single ( epiglottic, thyroid and cricoid) and three paired ( arytenoid, corniculate, and cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedg ...
). The hyoid bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebr ...
is not part of the larynx, though the larynx is suspended from the hyoid. The larynx extends vertically from the tip of the epiglottis to the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
. Its interior can be divided in supraglottis, glottis
The glottis is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing vowels and voiced consonants.
Etymology
From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), va ...
and subglottis.

Cartilages
There are nine cartilages, three unpaired and three paired (3 pairs=6), that support the mammalian larynx and form its skeleton. Unpaired cartilages: * Thyroid cartilage: This forms theAdam's apple
The Adam's apple or laryngeal prominence is the protrusion in the human neck formed by the angle of the thyroid cartilage surrounding the larynx, typically visible in men, less frequently in women.
Structure
The topographic structure which is ...
(also called the laryngeal prominence). It is usually larger in males than in females. The thyrohyoid membrane is a ligament associated with the thyroid cartilage that connects it with the hyoid bone. It supports the front portion of the larynx.
* Cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
: A ring of hyaline cartilage that forms the inferior wall of the larynx. It is attached to the top of the trachea. The median cricothyroid ligament connects the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage.
* Epiglottis: A large, spoon-shaped piece of elastic cartilage. During swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing i ...
, the pharynx and larynx rise. Elevation of the pharynx widens it to receive food and drink; elevation of the larynx causes the epiglottis to move down and form a lid over the glottis, closing it off.
Paired cartilages:
* Arytenoid cartilage
The arytenoid cartilages () are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx. They are the site of attachment of the vocal cords. Each is pyramidal or ladle-shaped and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex. The arytenoi ...
s: Of the paired cartilages, the arytenoid cartilages are the most important because they influence the position and tension of the vocal cords. These are triangular pieces of mostly hyaline cartilage located at the posterosuperior border of the cricoid cartilage.
* Corniculate cartilages: Horn-shaped pieces of elastic cartilage located at the apex of each arytenoid cartilage.
* Cuneiform cartilages: Club-shaped pieces of elastic cartilage located anterior to the corniculate cartilages.
Muscles
The muscles of the larynx are divided into ''intrinsic'' and ''extrinsic'' muscles. The extrinsic muscles act on the region and pass between the larynx and parts around it but have their origin elsewhere; the intrinsic muscles are confined entirely within the larynx and have their origin and insertion there. The intrinsic muscles are divided into respiratory and the phonatory muscles (the muscles ofphonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
). The respiratory muscles move the vocal cords apart and serve breathing. The phonatory muscles move the vocal cords together and serve the production of voice. The main respiratory muscles are the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles. The phonatory muscles are divided into adductors ( lateral cricoarytenoid muscles, arytenoid muscles) and tensors ( cricothyroid muscles, thyroarytenoid muscles).
Intrinsic
The intrinsic laryngeal muscles are responsible for controlling sound production. * Cricothyroid muscle lengthen and tense the vocal cords. * Posterior cricoarytenoid muscles abduct and externally rotate the arytenoid cartilages, resulting in abducted vocal cords. * Lateral cricoarytenoid muscles adduct and internally rotate the arytenoid cartilages, increase medial compression. * Transverse arytenoid muscle adduct the arytenoid cartilages, resulting in adducted vocal cords. * Oblique arytenoid muscles narrow the laryngeal inlet by constricting the distance between the arytenoid cartilages. * Thyroarytenoid muscles narrow the laryngeal inlet, shortening the vocal cords, and lowering voice pitch. The internal thyroarytenoid is the portion of the thyroarytenoid that vibrates to produce sound. Notably the only muscle capable of separating the vocal cords for normal breathing is the posterior cricoarytenoid. If this muscle is incapacitated on both sides, the inability to pull the vocal cords apart (abduct) will cause difficulty breathing. Bilateral injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve would cause this condition. It is also worth noting that all muscles are innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus except the cricothyroid muscle, which is innervated by the external laryngeal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (a branch of the vagus). Additionally, intrinsic laryngeal muscles present a constitutive Ca2+-buffering profile that predicts their better ability to handle calcium changes in comparison to other muscles. This profile is in agreement with their function as very fast muscles with a well-developed capacity for prolonged work. Studies suggests that mechanisms involved in the prompt sequestering of Ca2+ (sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-reuptake proteins, plasma membrane pumps, and cytosolic Ca2+-buffering proteins) are particularly elevated in laryngeal muscles, indicating their importance for the myofiber function and protection against disease, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Furthermore, different levels of Orai1 in rat intrinsic laryngeal muscles and extraocular muscles over the limb muscle suggests a role for store operated calcium entry channels in those muscles' functional properties and signaling mechanisms.Extrinsic
The extrinsic laryngeal muscles support and position the larynx within the mid-cervical cereal region. Extrinsic laryngeal muscles * Sternothyroid muscles depress the larynx. (Innervated by ansa cervicalis) *Omohyoid muscle
The omohyoid muscle is a muscle that depresses the hyoid. It is located in the front of the neck, and consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon. The omohyoid muscle is proximally attached to the scapula and distally attached to th ...
s depress the larynx. (Ansa cervicalis)
* Sternohyoid muscles depress the larynx. (Ansa cervicalis)
* Inferior constrictor muscles. (CN X)
* Thyrohyoid muscles elevates the larynx. (C1)
* Digastric elevates the larynx. (CN V3, CN VII)
* Stylohyoid elevates the larynx. (CN VII)
* Mylohyoid elevates the larynx. (CN V3)
* Geniohyoid elevates the larynx. (C1)
* Hyoglossus elevates the larynx. (CN XII)
* Genioglossus elevates the larynx. (CN XII)
Nerve supply
The larynx isinnervate
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
d by branches of the vagus nerve on each side. Sensory innervation to the glottis and laryngeal vestibule is by the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. The external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve innervates the cricothyroid muscle. Motor innervation to all other muscles of the larynx and sensory innervation to the subglottis is by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. While the sensory input described above is (general) visceral sensation (diffuse, poorly localized), the vocal cords also receives general somatic sensory innervation (proprioceptive and touch) by the superior laryngeal nerve.
Injury to the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve causes weakened phonation because the vocal cords cannot be tightened. Injury to one of the recurrent laryngeal nerves produces hoarseness, if both are damaged the voice may or may not be preserved, but breathing becomes difficult.
Development
In newborn infants, the larynx is initially at the level of the C2–C3 vertebrae, and is further forward and higher relative to its position in the adult body. The larynx descends as the child grows.Laryngeal cavity
The laryngeal cavity (cavity of the larynx) extends from the laryngeal inlet downwards to the lower border of thecricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
where it is continuous with that of the trachea.
It is divided into two parts by the projection of the vocal folds, between which is a narrow triangular opening, the rima glottidis.
The portion of the cavity of the larynx above the vocal folds is called the laryngeal vestibule
The portion of the cavity of the larynx above the vestibular fold is called the laryngeal vestibule; it is wide and triangular in shape, its base or anterior wall presenting, however, about its center the backward projection of the tubercle of the ...
; it is wide and triangular in shape, its base or anterior wall presenting, however, about its center the backward projection of the tubercle of the epiglottis.
It contains the vestibular folds, and between these and the vocal folds are the laryngeal ventricle
The laryngeal ventricle, (also called the ventricle of the larynx, laryngeal sinus, or Morgagni's sinus)pitch and volume are manipulated. The strength of expiration from the lungs also contributes to loudness.
Manipulation of the larynx is used to generate a source sound with a particular fundamental frequency, or pitch. This source sound is altered as it travels through the vocal tract, configured differently based on the position of the tongue, lips,
 The most important role of the larynx is its protective function, the prevention of foreign objects from entering the lungs by
The most important role of the larynx is its protective function, the prevention of foreign objects from entering the lungs by
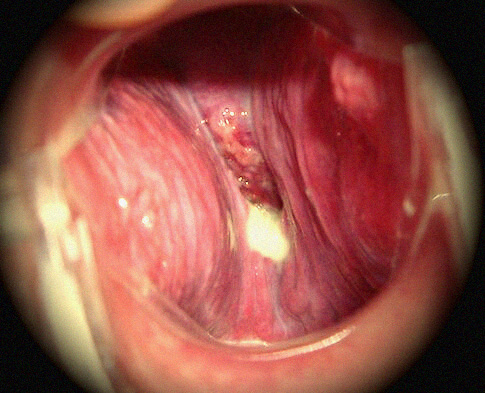 There are several things that can cause a larynx to not function properly. Some symptoms are hoarseness, loss of voice, pain in the throat or ears, and breathing difficulties.
*
There are several things that can cause a larynx to not function properly. Some symptoms are hoarseness, loss of voice, pain in the throat or ears, and breathing difficulties.
*
 Pioneering work on the structure and evolution of the larynx was carried out in the 1920s by the British comparative anatomist Victor Negus, culminating in his monumental work ''The Mechanism of the Larynx'' (1929). Negus, however, pointed out that the descent of the larynx reflected the reshaping and descent of the human tongue into the pharynx. This process is not complete until age six to eight years. Some researchers, such as Philip Lieberman,
Pioneering work on the structure and evolution of the larynx was carried out in the 1920s by the British comparative anatomist Victor Negus, culminating in his monumental work ''The Mechanism of the Larynx'' (1929). Negus, however, pointed out that the descent of the larynx reflected the reshaping and descent of the human tongue into the pharynx. This process is not complete until age six to eight years. Some researchers, such as Philip Lieberman,
File:Slide14rom.JPG, Larynx. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
File:Slide36uru.JPG, Larynx. Deep dissection. Posterior view.
mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
, and pharynx. The process of altering a source sound as it passes through the filter of the vocal tract creates the many different vowel and consonant sounds of the world's languages as well as tone, certain realizations of stress and other types of linguistic prosody. The larynx also has a similar function to the lungs in creating pressure differences required for sound production; a constricted larynx can be raised or lowered affecting the volume of the oral cavity as necessary in glottalic consonants.
The vocal cords can be held close together (by adducting the arytenoid cartilages) so that they vibrate (see phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
). The muscles attached to the arytenoid cartilages control the degree of opening. Vocal cord length and tension can be controlled by rocking the thyroid cartilage forward and backward on the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
(either directly by contracting the cricothyroids or indirectly by changing the vertical position of the larynx), by manipulating the tension of the muscles within the vocal cords, and by moving the arytenoids forward or backward. This causes the pitch produced during phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
to rise or fall. In most males the vocal cords are longer and have a greater mass than most females' vocal cords, producing a lower pitch.
The vocal apparatus consists of two pairs of folds, the vestibular folds (false vocal cords) and the true vocal cords. The vestibular folds are covered by respiratory epithelium, while the vocal cords are covered by stratified squamous epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural i ...
. The vestibular folds are not responsible for sound production, but rather for resonance. The exceptions to this are found in Tibetan chanting and Kargyraa, a style of Tuvan throat singing. Both make use of the vestibular folds to create an undertone. These false vocal cords do not contain muscle, while the true vocal cords do have skeletal muscle.
Other
 The most important role of the larynx is its protective function, the prevention of foreign objects from entering the lungs by
The most important role of the larynx is its protective function, the prevention of foreign objects from entering the lungs by coughing
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three phas ...
and other reflexive actions. A cough is initiated by a deep inhalation through the vocal cords, followed by the elevation of the larynx and the tight adduction (closing) of the vocal cords. The forced expiration that follows, assisted by tissue recoil and the muscles of expiration, blows the vocal cords apart, and the high pressure expels the irritating object out of the throat. Throat clearing is less violent than coughing, but is a similar increased respiratory effort countered by the tightening of the laryngeal musculature. Both coughing and throat clearing are predictable and necessary actions because they clear the respiratory passageway, but both place the vocal cords under significant strain.
Another important role of the larynx is abdominal fixation, a kind of Valsalva maneuver in which the lungs are filled with air in order to stiffen the thorax so that forces applied for lifting can be translated down to the legs. This is achieved by a deep inhalation followed by the adduction of the vocal cords. Grunting while lifting heavy objects is the result of some air escaping through the adducted vocal cords ready for phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the defini ...
.
Abduction of the vocal cords is important during physical exertion. The vocal cords are separated by about during normal respiration, but this width is doubled during forced respiration.
During swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing i ...
, elevation of the posterior portion of the tongue levers (inverts) the epiglottis over the glottis' opening to prevent swallowed material from entering the larynx which leads to the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s, and provides a path for a food or liquid bolus to "slide" into the esophagus; the hyo-laryngeal complex is also pulled upwards to assist this process. Stimulation of the larynx by aspirated food or liquid produces a strong cough reflex
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus.
Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs ...
to protect the lungs.
In addition, intrinsic laryngeal muscles are spared from some muscle wasting disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, may facilitate the development of novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of muscle wasting in a variety of clinical scenarios. ILM have a calcium regulation system profile suggestive of a better ability to handle calcium changes in comparison to other muscles, and this may provide a mechanistic insight for their unique pathophysiological properties
Clinical significance
Disorders
 There are several things that can cause a larynx to not function properly. Some symptoms are hoarseness, loss of voice, pain in the throat or ears, and breathing difficulties.
*
There are several things that can cause a larynx to not function properly. Some symptoms are hoarseness, loss of voice, pain in the throat or ears, and breathing difficulties.
* Acute laryngitis
Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx (voice box). Symptoms often include a hoarse voice and may include fever, cough, pain in the front of the neck, and trouble swallowing. Typically, these last under two weeks.
Laryngitis is categorised ...
is the sudden inflammation and swelling of the larynx. It is caused by the common cold or by excessive shouting. It is not serious. Chronic laryngitis
Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx (voice box). Symptoms often include a hoarse voice and may include fever, cough, pain in the front of the neck, and trouble swallowing. Typically, these last under two weeks.
Laryngitis is categoris ...
is caused by smoking, dust, frequent yelling, or prolonged exposure to polluted air. It is much more serious than acute laryngitis.
* Presbylarynx The presbylarynx is a condition in which age-related atrophy of the soft tissues of the larynx results in weak voice and restricted vocal range and stamina. In other words, it is the loss of vocal fold tone and elasticity due to aging which affect ...
is a condition in which age-related atrophy of the soft tissues of the larynx results in weak voice and restricted vocal range and stamina. Bowing of the anterior portion of the vocal colds is found on laryngoscopy.
* Ulcers may be caused by the prolonged presence of an endotracheal tube.
* Polyps and vocal cord nodules are small bumps caused by prolonged exposure to tobacco smoke and vocal misuse, respectively.
* Two related types of cancer of the larynx, namely squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
and verrucous carcinoma, are strongly associated with repeated exposure to cigarette smoke and alcohol.
* Vocal cord paresis is weakness of one or both vocal cords that can greatly impact daily life.
* Idiopathic laryngeal spasm.
* Laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition in which acid from the stomach irritates and burns the larynx. Similar damage can occur with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
* Laryngomalacia is a very common condition of infancy, in which the soft, immature cartilage of the upper larynx collapses inward during inhalation, causing airway obstruction.
* Laryngeal perichondritis, the inflammation of the perichondrium of laryngeal cartilages, causing airway obstruction.
* Laryngeal paralysis
Laryngeal paralysis in animals is a condition in which the nerves and muscles that control the movements of one or both arytenoid cartilages of the larynx cease to function, and instead of opening during aspiration and closing during swallowing, th ...
is a condition seen in some mammals (including dogs) in which the larynx no longer opens as wide as required for the passage of air, and impedes respiration. In mild cases it can lead to exaggerated or "raspy" breathing or panting, and in serious cases can pose a considerable need for treatment.
* Duchenne muscular dystrophy, intrinsic laryngeal muscles (ILM) are spared from the lack of dystrophin and may serve as a useful model to study the mechanisms of muscle sparing in neuromuscular diseases. Dystrophic ILM presented a significant increase in the expression of calcium-binding proteins Calcium-binding proteins are proteins that participate in calcium cell signalling pathways by binding to Ca2+, the calcium ion that plays an important role in many cellular processes. Calcium-binding proteins have specific domains that bind to calc ...
. The increase of calcium-binding proteins in dystrophic ILM may permit better maintenance of calcium homeostasis, with the consequent absence of myonecrosis. The results further support the concept that abnormal calcium buffering is involved in these neuromuscular diseases.
Treatments
Patients who have lost the use of their larynx are typically prescribed the use of an electrolarynx device. Larynxtransplants
Transplant or Transplantation may refer to:
Sciences
*Transplanting a plant from one location to another
*Organ transplantation, moving an organ from one body to another
*Transplant thought experiment, an experiment similar to Trolley problem
*Tra ...
are a rare procedure. The world's first successful operation took place in 1998 at the Cleveland Clinic, and the second took place in October 2010 at the University of California Davis Medical Center in Sacramento.
Other animals
 Pioneering work on the structure and evolution of the larynx was carried out in the 1920s by the British comparative anatomist Victor Negus, culminating in his monumental work ''The Mechanism of the Larynx'' (1929). Negus, however, pointed out that the descent of the larynx reflected the reshaping and descent of the human tongue into the pharynx. This process is not complete until age six to eight years. Some researchers, such as Philip Lieberman,
Pioneering work on the structure and evolution of the larynx was carried out in the 1920s by the British comparative anatomist Victor Negus, culminating in his monumental work ''The Mechanism of the Larynx'' (1929). Negus, however, pointed out that the descent of the larynx reflected the reshaping and descent of the human tongue into the pharynx. This process is not complete until age six to eight years. Some researchers, such as Philip Lieberman, Dennis Klatt
Dennis H. Klatt (March 31, 1938 – December 30, 1988) was an American researcher in speech and hearing science. Klatt was the pioneer of computerized speech synthesis and created an interface which allowed for speech for non-expert users for the ...
, Bart de Boer
Bart is a masculine given name, usually a diminutive of Bartholomew, sometimes of Barton, Bartolomeo, etc.
Bart is a Dutch and Ashkenazi Jewish surname, and derives from the name ''Bartholomäus'', a German form of the biblical name ''Bartholo ...
and Kenneth Stevens using computer-modeling techniques have suggested that the species-specific human tongue allows the vocal tract (the airway above the larynx) to assume the shapes necessary to produce speech sounds that enhance the robustness of human speech. Sounds such as the vowels of the words and , and (in phonetic notation), have been shown to be less subject to confusion in classic studies such as the 1950 Peterson and Barney investigation of the possibilities for computerized speech recognition.
In contrast, though other species have low larynges, their tongues remain anchored in their mouths and their vocal tracts cannot produce the range of speech sounds of humans. The ability to lower the larynx transiently in some species extends the length of their vocal tract, which as Fitch showed creates the acoustic illusion that they are larger. Research at Haskins Laboratories in the 1960s showed that speech allows humans to achieve a vocal communication rate that exceeds the fusion frequency of the auditory system by fusing sounds together into syllables and words. The additional speech sounds that the human tongue enables us to produce, particularly allow humans to unconsciously infer the length of the vocal tract of the person who is talking, a critical element in recovering the phonemes that make up a word.
Non-mammals
Most tetrapod species possess a larynx, but its structure is typically simpler than that found in mammals. The cartilages surrounding the larynx are apparently a remnant of the original gill arches in fish, and are a common feature, but not all are always present. For example, the thyroid cartilage is found only in mammals. Similarly, only mammals possess a true epiglottis, although a flap of non-cartilagenousmucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
is found in a similar position in many other groups. In modern amphibians, the laryngeal skeleton is considerably reduced; frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" '' Triadobatrachus'' is ...
s have only the cricoid and arytenoid cartilages, while salamanders possess only the arytenoids.
An example of a frog that possesses a larynx is túngara frog. While larynx is the main sound producing organ in túngara frogs, it serves a higher significance due to its contribution to mating call, which consist of two components: ‘whine’ and ‘chuck’. While ‘whine’ induces female phonotaxis and allows species recognition, ‘chuck’ increases mating attractiveness. In particular, túngara frog produces ‘chuck’ by vibrating the fibrous mass attached to the larynx.
Vocal folds are found only in mammals, and a few lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
s. As a result, many reptiles and amphibians are essentially voiceless; frogs use ridges in the trachea to modulate sound, while bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s have a separate sound-producing organ, the syrinx
In classical Greek mythology, Syrinx (Greek Σύριγξ) was a nymph and a follower of Artemis, known for her chastity. Pursued by the amorous god Pan, she ran to a river's edge and asked for assistance from the river nymphs. In answer, sh ...
.
History
The ancient Greek physicianGalen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be on ...
first described the larynx, describing it as the "first and supremely most important instrument of the voice".
Additional images
See also
* Articulatory phonetics * Electrolarynx * Histology of the vocal cords *Origin of speech
The origin of speech refers to the general problem of the origin of language in the context of the physiological development of the human speech organs such as the tongue, lips, and vocal organs used to produce phonological units in all spok ...
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * {{Authority control Human head and neck Human voice Phonetics Human throat Respiratory system Speech organs