|
Tokharian
The Tocharian (sometimes ''Tokharian'') languages ( or ), also known as ''Arśi-Kuči'', Agnean-Kuchean or Kuchean-Agnean, are an extinct branch of the Indo-European language family spoken by inhabitants of the Tarim Basin, the Tocharians. The languages are known from manuscripts dating from the 5th to the 8th century AD, which were found in oasis cities on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (now part of Xinjiang in Northwest China) and the Lop Desert. The discovery of these languages in the early 20th century contradicted the formerly prevalent idea of an east–west division of the Indo-European language family as centum and satem languages, and prompted reinvigorated study of the Indo-European family. Scholars studying these manuscripts in the early 20th century identified their authors with the ''Tokharoi'', a name used in ancient sources for people of Bactria (Tokharistan). Although this identification is now believed to be mistaken, "Tocharian" remains the usual term for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tocharians
The Tocharians, or Tokharians ( US: or ; UK: ), were speakers of Tocharian languages, Indo-European languages known from around 7600 documents from around 400 to 1200 AD, found on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (modern Xinjiang, China).. "Our knowledge of the Tocharian languages derives essentially from c. 7600 documents found across about thirty sites in the eastern half of the greater Tarim Basin (Fig. 1). The documents date from c. 400 to 1200 CE" The name "Tocharian" was given to these languages in the early 20th century by scholars who identified their speakers with a people known in ancient Greek sources as the ''Tókharoi'' (Latin ''Tochari''), who inhabited Bactria from the 2nd century BC. This identification is generally considered erroneous, but the name "Tocharian" remains the most common term for the languages and their speakers. Their actual ethnic name is unknown, although they may have referred to themselves as ''Agni'', '' Kuči'' and ''Krorän'', or ''Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources. In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan came under the rule of the Chinese Empire, administered by the Protectorate General to Pacify the West. Today, Tokharistan is fragmented between Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Afghanistan. Names of Tokharistan Several languages have used variations of the word "Tokhara" to designate the region: * Tokharistan may appear in ancient India sources as the Kingdom of Tushara, to the northwest of India. "Tushara" is the Sanskrit word for "snowy" "frigid", and is known to have been used to designate the country of Tukhara. In Sanskrit, it became तुखार (Tukhāra). * In ancient Greek, the name was Tokharoi ( grc, Τόχαροι ) or Thaguroi. * Tochari for Latin historians. * The name "Tokhara" appeared in the 4th century CE, in Buddhist texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
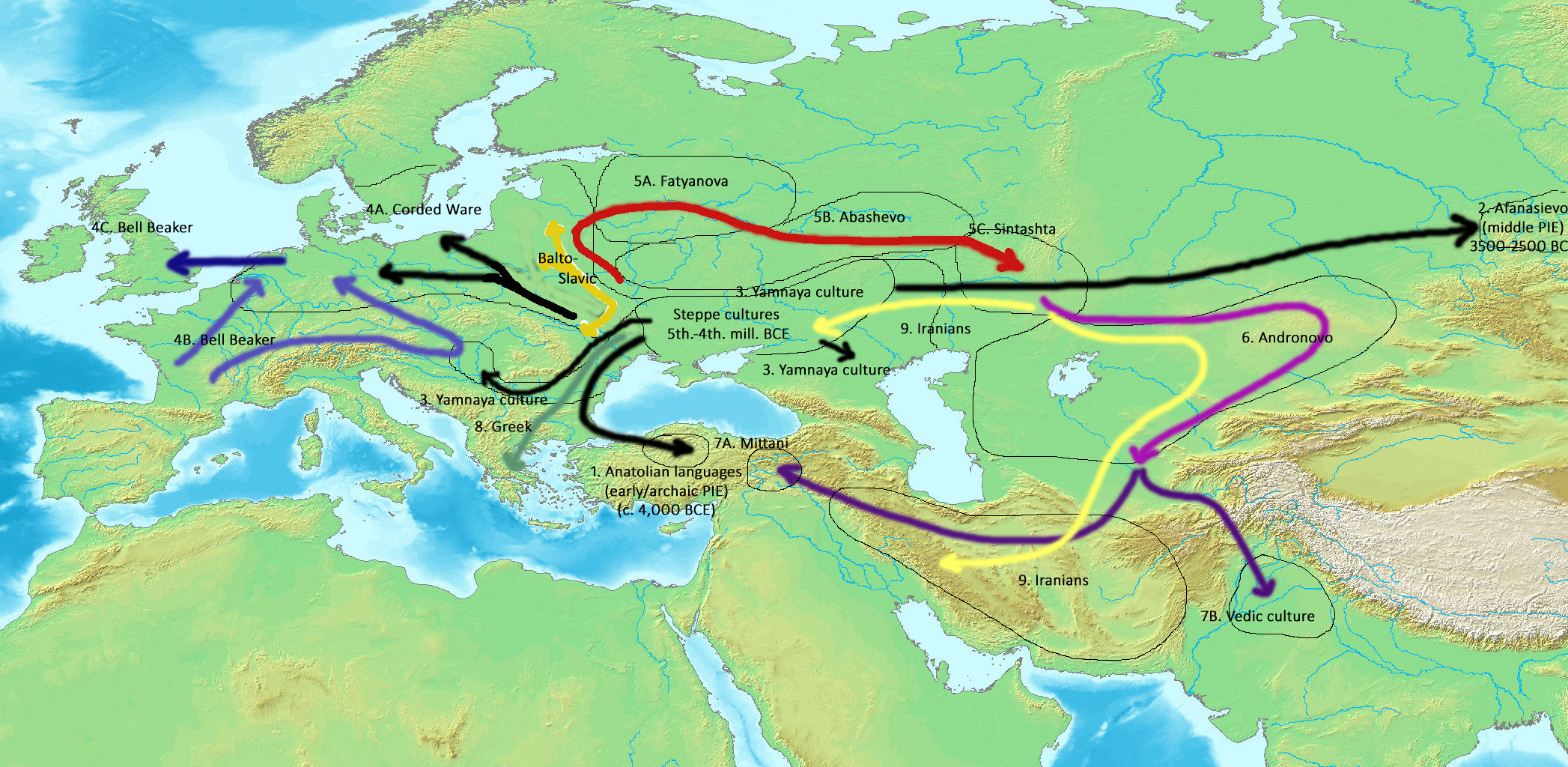
Indo-European Migrations
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially explaining how these languages came to be spoken across a large area of Eurasia, from India and Iran, to Europe. While there can be no direct evidence of prehistoric languages, a synthesis of linguistics, archaeology, anthropology and genetics establish both the existence of Proto-Indo-European and the spread of its daughter dialects through migrations of large populations of its speakers, as well as the recruitment of new speakers through emulation of conquering elites. Comparative linguistics describes the similarities between various languages and the laws of systematic change, which allow the reconstruction of ancestral speech (see Indo-European studies). Archaeology traces the spread of artifacts, habitations, and burial sites presumed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Tocharian
Proto-Tocharian, also spelled Proto-Tokharian ( or ), is the reconstructed proto-language of the extinct Tocharian branch of the Indo-European languages. Proto-Tocharian is the unattested reconstructed ancestor of an Indo-European eponymous extinct branch, known from manuscripts dating from the 5th to the 8th century AD, which were on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin and the Lop Desert. The discovery of this language family in the early 20th century contradicted the formerly prevalent idea of an east–west division of the Indo-European language family on the centum–satem isogloss, and prompted reinvigorated study of the family. The documents record two closely related languages, called Tocharian A (also ''East Tocharian'', ''Agnean'' or ''Turfanian'') and Tocharian B (''West Tocharian'' or ''Kuchean''). The subject matter of the texts suggests that Tocharian A was more archaic and used as a Buddhist liturgical language, while Tocharian B was more actively spoken in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuchean Language
Kuchean (also known as Tocharian B or West Tocharian) was a Western member of Tocharian branch of Indo-European languages, extinct from ninth century. Once spoken in the Tarim Basin in Central Asia. Tocharian B shows an internal chronological development; three linguistic stages have been detected. The oldest stage is attested only in Kucha. There are also the middle ('classicalʼ), and the late stage. Nomenclature Acorrding to Peyrot, the self-designation for the language was ''kuśi'' 'Kuča'. In scholarly works, it is known as West Tocharian or Kuchean. Overview According to scholar Michael Peyrot, Tocharian B is dated between the 5th and 10th centuries AD, and was spread from Kuča to Yānqi and Turfan. Paul Widmer, following Tamai's and Adams's studies, situates Tocharian B roughly between 400 CE to 1200 CE, its oldest layer dating from ca. 400 to 600 CE, around "Kucha and environs". Documentation According to J. H. W. Penney, Tocharian B is reported to be documented as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the largest province-level division of China by area and the 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang borders the countries of Mongolia, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions, both administered by China, are claimed by India. Xinjiang also borders the Tibet Autonomous Region and the provinces of Gansu and Qinghai. The most well-known route of the historic Silk Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydrological Processes 20.10 (2006): 2207–2216.online 426 KB) Located in China's Xinjiang region, it is sometimes used synonymously to refer to the southern half of the province, or Southern Xinjiang, Nanjiang (), as opposed to the northern half of the province known as Dzungaria or Beijiang. Its northern boundary is the Tian Shan mountain range and its southern boundary is the Kunlun Mountains on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau. The Taklamakan Desert dominates much of the basin. The historical Uyghur name for the Tarim Basin is Altishahr (Uyghur language, Traditional spelling: 六城 or ), which means 'six cities' in Uyghur language, Uyghur. Geography and relation to Xinjiang Xinjiang consists of two main geographically, historically, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afanasievo Culture
The Afanasievo culture, or Afanasevo culture (Afanasevan culture) (russian: Афанасьевская культура ''Afanas'yevskaya'' kul'tura), is the earliest known archaeological culture of south Siberia, occupying the Minusinsk Basin and the Altai Mountains during the eneolithic era, 3300 to 2500 BCE. It is named after a nearby mountain, Gora Afanasieva () in what is now Bogradsky District, Khakassia, Russia. David W. Anthony believes that the Afanasevan population was descended from people who migrated c. 3700–3300 BCE across the Eurasian Steppe from the pre-Yamnaya Repin culture of the Don-Volga region. Because of its geographical location and dating, Anthony and earlier scholars such as Leo Klejn, J. P. Mallory and Victor H. Mair have linked the Afanasevans to the Proto-Tocharian language. Dating Conventional archaeological understanding tended to date at around 2000–2500 BC. However radiocarbon gave dates as early as 3705 BC on wooden tools and 2874 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and introduced Proto-Indo-Aryan language. The Indo-Aryan language speakers are found across South Asia. History Proto-Indo-Iranians The introduction of the Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent was the result of a migration of Indo-Aryan people from Central Asia into the northern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka). These migrations started approximately 1,800 BCE, after the invention of the war chariot, and also brought Indo-Aryan languages into the Levant and possibly Inner Asia. Another group of the Indo-Aryans migrated further westward and founded the Mitanni kingdom in northern Syria; (c. 1500–1300 BC) the other group were the Vedic people. Christopher I. Beckwith su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontic Steppes
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to: The Black Sea Places * The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores * Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores * The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from north of the Black Sea as far east as the Caspian Sea * The Pontic Mountains, a range of mountains in northern Turkey, close to the southern coast of the Black Sea Languages and peoples * Pontic Greeks, all Greek peoples from the shores of the Black Sea and Pontus * Pontic Greek, a form of the Greek language originally spoken by the Pontic Greeks (see above) * ''Pontic'', as opposed to ''Caspian'' (which refers to the possibly related Nakho-Dagestanian or Northeast Caucasian languages), is sometimes used as a synonym for the Northwest Caucasian language family. * Pontic languages, the hypothetical language family linking the Northwest Caucasian and Indo-European languages, and Proto-Pontic, the Pontic proto-language, is the reconstructed comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamnaya Culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура literal translation, lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural (river), Ural rivers (the Pontic steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BCE. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaelogical excavations near Siversky Donets in 1901—1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: (romanized, romanization: ) is a Russian adjective that means 'related to pits ()', as these people used to bury their dead in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. The people of the Yamnaya culture were likely the result of a genetic admixture between the descendants of Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG)The Eastern European hunter-gatherers were themselves mostly descended from ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.png)