|
Tokamak (other)
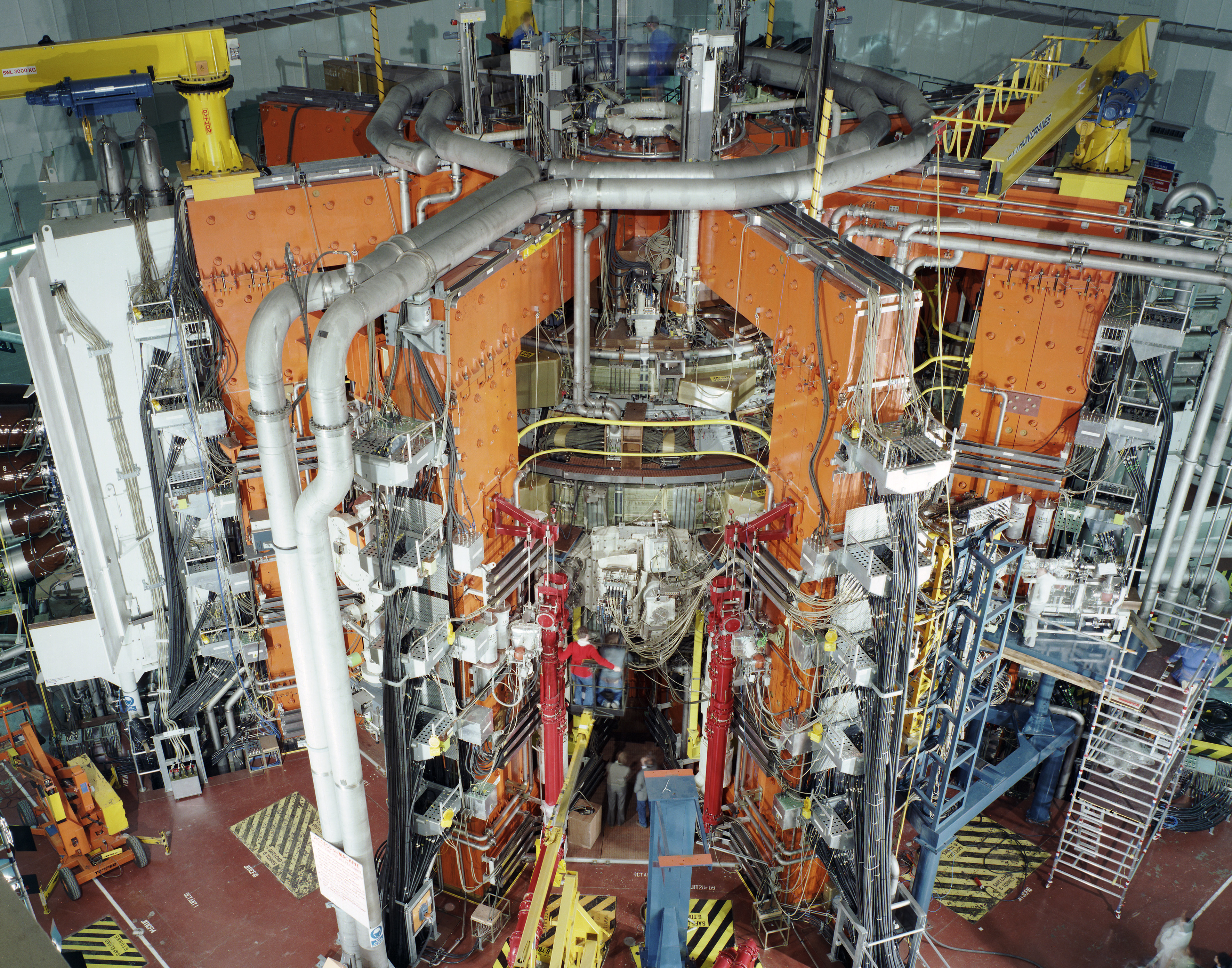
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in 1954, and for over a decade this technology existed only in the USSR. In 1968 the electronic plasma tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 TOCAMAC Fusion Chamber N0689
Seventeen or 17 may refer to: *17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18 * one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017 Literature Magazines *Seventeen (American magazine), ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine *Seventeen (Japanese magazine), ''Seventeen'' (Japanese magazine), a Japanese magazine Novels *Seventeen (Tarkington novel), ''Seventeen'' (Tarkington novel), a 1916 novel by Booth Tarkington *''Seventeen'' (''Sebuntiin''), a 1961 novel by Kenzaburō Ōe *Seventeen (Serafin novel), ''Seventeen'' (Serafin novel), a 2004 novel by Shan Serafin Stage and screen Film *Seventeen (1916 film), ''Seventeen'' (1916 film), an American silent comedy film *''Number Seventeen'', a 1932 film directed by Alfred Hitchcock *Seventeen (1940 film), ''Seventeen'' (1940 film), an American comedy film *''Eric Soya's '17''' (Danish: ''Sytten''), a 1965 Danish comedy film *Seventeen (1985 film), ''Seventeen'' (1985 film), a documentary film *17 Again (film), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of . The Helsinki urban area, city's urban area has a population of , making it by far the List of urban areas in Finland by population, most populous urban area in Finland as well as the country's most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research; while Tampere in the Pirkanmaa region, located to the north from Helsinki, is the second largest urban area in Finland. Helsinki is located north of Tallinn, Estonia, east of Stockholm, Sweden, and west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has History of Helsinki, close historical ties with these three cities. Together with the cities of Espoo, Vantaa, and Kauniainen (and surrounding commuter towns, including the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactor Pressure Vessel
A reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in a nuclear power plant is the pressure vessel containing the nuclear reactor coolant, core shroud, and the reactor core. Classification of nuclear power reactors Russian Soviet era RBMK reactors have each fuel assembly enclosed in an individual 8 cm diameter pipe rather than having a pressure vessel. Whilst most power reactors do have a pressure vessel, they are generally classified by the type of coolant rather than by the configuration of the vessel used to contain the coolant. The classifications are: *Light-water reactor - Includes the pressurized water reactor and the boiling water reactor. Most nuclear power reactors are of this type. *Graphite-moderated reactor - Includes the Chernobyl reactor (RBMK), which has a highly unusual reactor configuration compared to the vast majority of nuclear power plants in Russia and around the world. *Gas cooled thermal reactor - Includes the Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor, the gas cooled fast breeder re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion, nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an Inertial confinement fusion, inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma (physics), plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Factor (plasma Physics)
In a toroidal fusion power reactor, the magnetic fields confining the plasma are formed in a helical shape, winding around the interior of the reactor. The safety factor, labeled q or q(r), is the ratio of the times a particular magnetic field line travels around a toroidal confinement area's "long way" (toroidally) to the "short way" (poloidally). The term "safety" refers to the resulting stability of the plasma; plasmas that rotate around the torus poloidally about the same number of times as toroidally are inherently less susceptible to certain instabilities. The term is most commonly used when referring to tokamak devices. Although the same considerations apply in stellarators, by convention the inverse value is used, the rotational transform, or i. The concept was first developed by Martin David Kruskal and Vitaly Shafranov, who noticed that the plasma in pinch effect reactors would be stable if q was larger than 1. Macroscopically, this implies that the wavelength of the pot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellarator
A stellarator is a plasma device that relies primarily on external magnets to confine a plasma. Scientists researching magnetic confinement fusion aim to use stellarator devices as a vessel for nuclear fusion reactions. The name refers to the possibility of harnessing the power source of the stars, such as the Sun. It is one of the earliest fusion power devices, along with the z-pinch and magnetic mirror. The stellarator was invented by American scientist Lyman Spitzer of Princeton University in 1951, and much of its early development was carried out by his team at what became the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL). Lyman's Model A began operation in 1953 and demonstrated plasma confinement. Larger models followed, but these demonstrated poor performance, losing plasma at rates far worse than theoretical predictions. By the early 1960s, any hope of quickly producing a commercial machine faded, and attention turned to studying the fundamental theory of high-energy plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-pinch
In fusion power research, the Z-pinch (zeta pinch) is a type of plasma confinement system that uses an electric current in the plasma to generate a magnetic field that compresses it (see pinch). These systems were originally referred to simply as pinch or Bennett pinch (after Willard Harrison Bennett), but the introduction of the θ-pinch (theta pinch) concept led to the need for clearer, more precise terminology. The name refers to the direction of the current in the devices, the Z-axis on a normal three-dimensional graph. Any machine that causes a pinch effect due to current running in that direction is correctly referred to as a Z-pinch system, and this encompasses a wide variety of devices used for an equally wide variety of purposes. Early uses focused on fusion research in donut-shaped tubes with the Z-axis running down the inside the tube, while modern devices are generally cylindrical and used to generate high-intensity x-ray sources for the study of nuclear weapons an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek word ''ἕλιξ'', "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called ''helicoid''. Properties and types The ''pitch'' of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. A ''conic helix'', also known as a ''conic spiral'', may be defined as a spiral on a conic surface, with the distance to the apex an expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field Line
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Equilibria And Stability
The stability of a plasma is an important consideration in the study of plasma physics. When a system containing a plasma is at equilibrium, it is possible for certain parts of the plasma to be disturbed by small perturbative forces acting on it. The stability of the system determines if the perturbations will grow, oscillate, or be damped out. In many cases, a plasma can be treated as a fluid and its stability analyzed with magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). MHD theory is the simplest representation of a plasma, so MHD stability is a necessity for stable devices to be used for nuclear fusion, specifically magnetic fusion energy. There are, however, other types of instabilities, such as velocity-space instabilities in magnetic mirrors and systems with beams. There are also rare cases of systems, e.g. the field-reversed configuration, predicted by MHD to be unstable, but which are observed to be stable, probably due to kinetic effects. Plasma instabilities Plasma instabilities can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herald Of The Russian Academy Of Sciences
Established in 1931, the ''Herald of the Russian Academy of Sciences'' (''Vestnik Rossiiskoi Akademii Nauk'') is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal published by MAIK Nauka/Interperiodica and Springer Science+Business Media. It covers major contributions, speeches, and presentations to the Russian Academy of Sciences from both Russian and foreign academics. Subjects encompass natural, technical, and social sciences, as well as education, the environment, the value of scientific knowledge, and researchers' relationship to society. Since April 2018, the editor-in-chief is Alexey Khokhlov (one of the vice-presidents of the Russian Academy of Sciences). Editors-in-chief * acad. V.P. Volgin (1931—1935, 1945–1951) * acad. N.P. Gorbunov (1936—1937) * acad. V. L. Komarov (1937—1945) * acad . S. I. Vavilov (1945, acting) * acad. A. N. Nesmeyanov (1951—1953) * acad. K. V. Ostrovityanov (1953—1963) * acad. V. A. Kirillin (1963—1965) * acad. N. M. Sissakian (196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evgeny Velikhov
Evgeny Pavlovich Velikhov (born on February 2, 1935; in Russian: ''Евгений Павлович Велихов'') is a physicist and scientific leader in the Russian Federation. His scientific interests include plasma physics, lasers, controlled nuclear fusion, power engineering, and magnetohydrodynamics ( high-power pulsed MHD generators). He is the author of over 1500 scientific publications and a number of inventions and discoveries. He currently holds the post of president of the Kurchatov Institute (named after Igor Kurchatov) and first Secretary (head) of the Civic Chamber of the Russian Federation. He is a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences and has been the vice-president of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. Career Evgeny Velikhov graduated from the Department of Physics at M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU) in 1958, where he specialized in theoretical physics. From 1958 until 1961, he studied at graduate school. After completing his gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |