|
Titanium Isotope
Naturally occurring titanium (22Ti) is composed of five stable isotopes; 46Ti, 47Ti, 48Ti, 49Ti and 50Ti with 48Ti being the most abundant (73.8% natural abundance). Twenty-one radioisotopes have been characterized, with the most stable being 44Ti with a half-life of 60 years, 45Ti with a half-life of 184.8 minutes, 51Ti with a half-life of 5.76 minutes, and 52Ti with a half-life of 1.7 minutes. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 33 seconds, and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than half a second. The isotopes of titanium range in atomic mass from 38.01 u (38Ti) to 62.99 u (63Ti). The primary decay mode for isotopes lighter than the stable isotopes (lighter than 46Ti) is β+ and the primary mode for the heavier ones (heavier than 50Ti) is β−; their respective decay products are scandium isotopes and the primary products after are vanadium isotopes. List of isotopes , - , rowspan=3, 39Ti , rowspan=3 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titan (mythology), Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll process, Kroll and Hunter process, Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalysis, photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
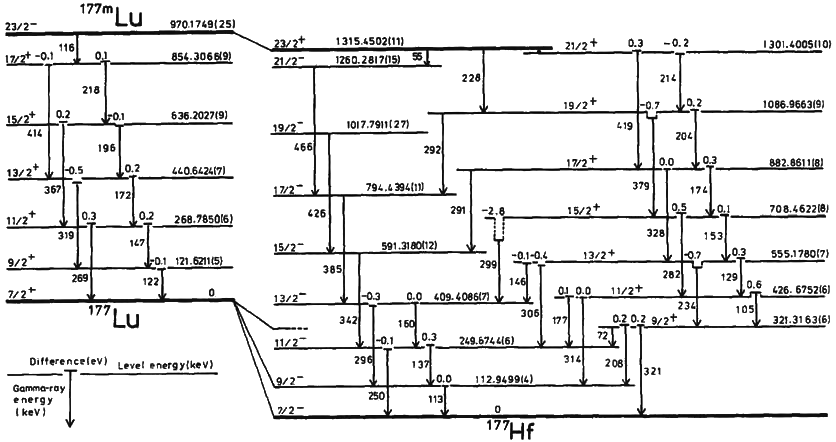
Nuclear Isomer
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by as well as , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Titanium
Naturally occurring titanium (22Ti) is composed of five stable isotopes; 46Ti, 47Ti, 48Ti, 49Ti and 50Ti with 48Ti being the most abundant (73.8% natural abundance). Twenty-one radioisotopes have been characterized, with the most stable being 44Ti with a half-life of 60 years, 45Ti with a half-life of 184.8 minutes, 51Ti with a half-life of 5.76 minutes, and 52Ti with a half-life of 1.7 minutes. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 33 seconds, and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than half a second. The isotopes of titanium range in atomic mass from 38.01 unified atomic mass unit, u (38Ti) to 62.99 u (63Ti). The primary radioactive decay, decay mode for isotopes lighter than the stable isotopes (lighter than 46Ti) is beta decay, β+ and the primary mode for the heavier ones (heavier than 50Ti) is β−; their respective decay products are isotopes of scandium, scandium isotopes and the primary products after are is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 1987A
SN 1987A was a type II supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It occurred approximately from Earth and was the closest observed supernova since Kepler's Supernova. 1987A's light reached Earth on February 23, 1987, and as the earliest supernova discovered that year, was labeled "1987A". Its brightness peaked in May, with an apparent magnitude of about 3. It was the first supernova that modern astronomers were able to study in great detail, and its observations have provided much insight into core-collapse supernovae. SN 1987A provided the first opportunity to confirm by direct observation the radioactive source of the energy for visible light emissions, by detecting predicted gamma-ray line radiation from two of its abundant radioactive nuclei. This proved the radioactive nature of the long-duration post-explosion glow of supernovae. For over thirty years, the expected collapsed neutron star could not be found, but in 2019, indirect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia A
Cassiopeia A (Cas A) () is a supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately away within the Milky Way; given the width of the Orion Arm, it lies in the next-nearest arm outwards, the Perseus Arm, about 30 degrees from the Galactic anticenter. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova now appears approximately across from Earth's perspective. It has been seen in wavelengths of visible light with amateur telescopes down to 234 mm (9.25 in) with filters. It is estimated that light from the supernova itself first reached Earth near the 1690s, although there are no definitively corresponding records from then. Cas A is circumpolar at and above mid-Northern latitudes which had extensive records and basic telescopes. Its likely omission in records is probably due to interstellar dust absorbing optical wavel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequency, frequencies above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Ulrich Villard, Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha particle, alpha rays and beta particle, beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium-4
Helium-4 () is a stable isotope of the element helium. It is by far the more abundant of the two naturally occurring isotopes of helium, making up about 99.99986% of the helium on Earth. Its nucleus is identical to an alpha particle, and consists of two protons and two neutrons. Alpha decay of heavy elements in the Earth's crust is the source of most naturally occurring helium-4 on Earth, produced after the planet cooled and solidified. While it is also produced by nuclear fusion in stars, most helium-4 in the Sun and in the universe is thought to have been produced by the Big Bang, and is referred to as "primordial helium". However, primordial helium-4 is largely absent from the Earth, having escaped during the high-temperature phase of Earth's formation. Helium-4 makes up about one quarter of the ordinary matter in the universe by mass, with almost all of the rest being hydrogen. When liquid helium-4 is cooled to below , it becomes a superfluid, with properties that are ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Particle
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produced in other ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as or indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge (missing its two electrons). Once the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal (electrically neutral) helium atom . Alpha particles have a net spin of zero. Due to the mechanism of their production in standard alpha radioactive decay, alpha particles generally have a kinetic energy of about 5 MeV, and a velocity in the vicinity of 4% of the speed of light. (See discussion below for the limits of these figures in alpha decay.) T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium-40
Calcium (20Ca) has 26 known isotopes, ranging from 35Ca to 60Ca. There are five stable isotopes (40Ca, 42Ca, 43Ca, 44Ca and 46Ca), plus one isotope ( 48Ca) with such a long half-life that for all practical purposes it can be considered stable. The most abundant isotope, 40Ca, as well as the rare 46Ca, are theoretically unstable on energetic grounds, but their decay has not been observed. Calcium also has a cosmogenic isotope, radioactive 41Ca, which has a half-life of 99,400 years. Unlike cosmogenic isotopes that are produced in the atmosphere, 41Ca is produced by neutron activation of 40Ca. Most of its production is in the upper metre of the soil column, where the cosmogenic neutron flux is still sufficiently strong. 41Ca has received much attention in stellar studies because it decays to 41K, a critical indicator of solar system anomalies. The most stable artificial radioisotopes are 45Ca with a half-life of 163 days and 47Ca with a half-life of 4.5 days. All other calcium isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
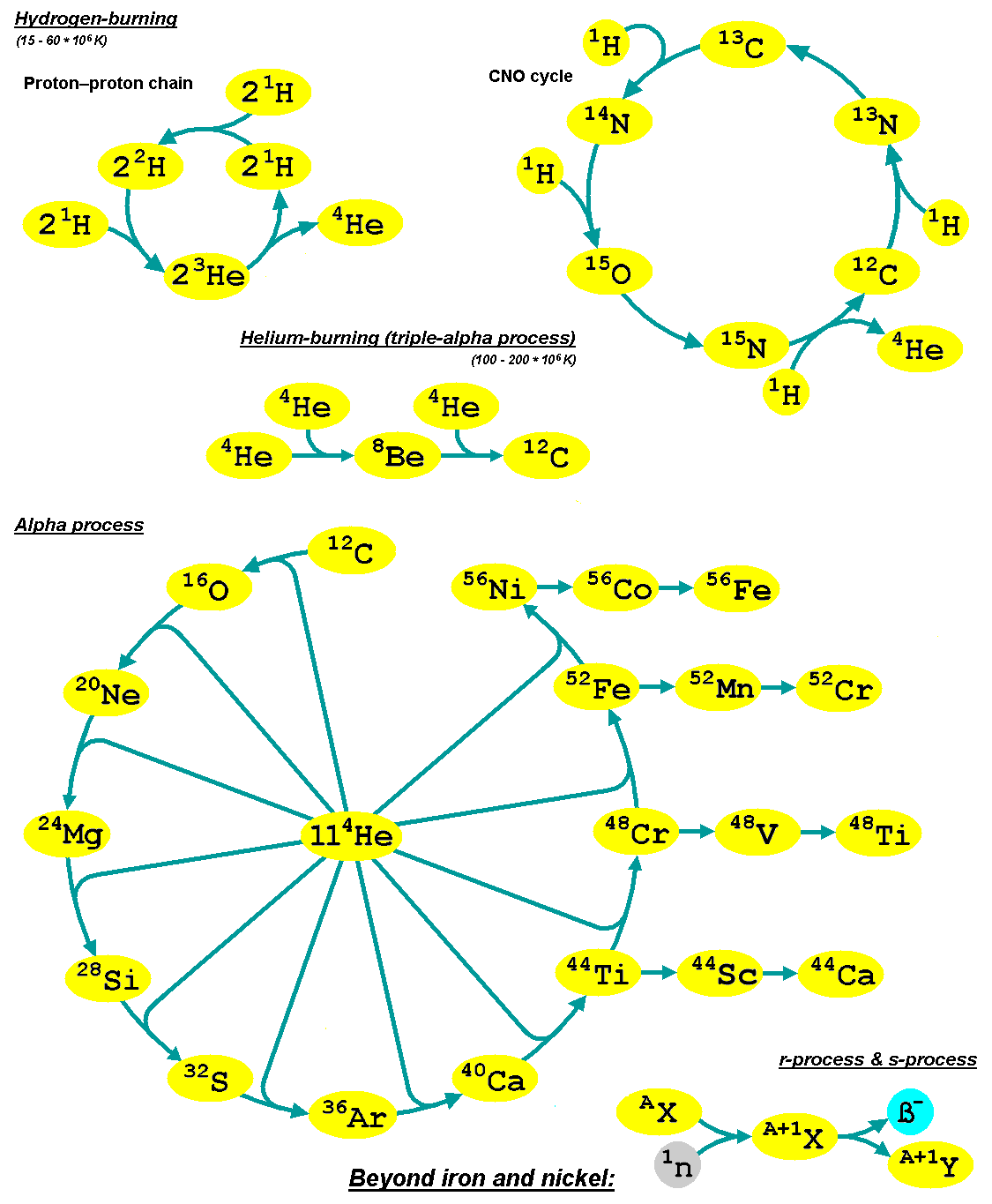
Stellar Nucleosynthesis
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation (nucleosynthesis) of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a predictive theory, it yields accurate estimates of the observed abundances of the elements. It explains why the observed abundances of elements change over time and why some elements and their isotopes are much more abundant than others. The theory was initially proposed by Fred Hoyle in 1946, who later refined it in 1954. Further advances were made, especially to nucleosynthesis by neutron capture of the elements heavier than iron, by Margaret and Geoffrey Burbidge, William Alfred Fowler and Hoyle in their famous 1957 B2FH paper, which became one of the most heavily cited papers in astrophysics history. Stars evolve because of changes in their composition (the abundance of their constituent elements) over their lifespans, first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Process
The alpha process, also known as the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements, the other being the triple-alpha process. The triple-alpha process consumes only helium, and produces carbon. After enough carbon has accumulated, further reactions below take place, listed below. Each step only consumes helium and the product of the previous reaction. :\begin \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \end The energy produced each the reaction, , is primarily in the gamma ray (), with a small amount taken by the byproduct element, as added momentum. It is a common misconception that the above sequence ends at \, _^\mathrm \, (or \, _^\mathrm \,, which is a decay product of \, _^\mathrm \,) because it is the most tightly bound nuclide - i.e., having the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |