|
Tirumalai (Jain Complex)
Tirumalai (lit. "the holy mountain"; also later Arhasugiri, lit. "the excellent mountain of the Arha ; Tamil Engunavirai-Tirumalai, lit. "the holy mountain of the Arhar" is a Jain temple and cave complex dating from at least the 9th century CE that is located northwest of Polur in Tamil Nadu, southeast India. The complex includes 3 Jain caves, 2 Jain temples and a sculpture of Tirthankara Neminatha thought to date from the 12th century CE that is the tallest Jain image in Tamil Nadu. Arahanthgiri Jain Math is also present near Tirumalai complex. History Tirumalai has been an important Jain center since ancient times. It is believed that 8,000 Jain monks who accompanied Bhadrabahu did the penance and attained nirvana here. The footprints of four great saints - Vrishabhsenachrya, Samanatabhadracharya, Varadattachrya munivar and Sri Vadeepa Simhasuri are also present here. An inscription dating back to 1024 CE is present mentioning the name Kunthavai Jinalaya temple. This inscr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahāvīra, Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the Jain cosmology, cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''Ahimsa in Jainism, ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''Achourya, asteya'' (not stealing), ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirumalai Jain Temple - Terrocotta Sculpture '', 2003 Indian Tamil film starring Vijay
{{Disambig ...
Tirumalai may refer to: Geography *Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, Andhra Pradesh, India * Tirumalai, a mountain and Jain site near Polur, Tamil Nadu, India See also *''Thirumalai ''Thirumalai'' is a 2003 Indian Tamil-language masala film written and directed by Ramana. The film stars Vijay and Jyothika, with Manoj K. Jayan, Avinash (in his Tamil debut), Vivek, Raghuvaran, Kausalya and Karunas in supporting roles. Prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
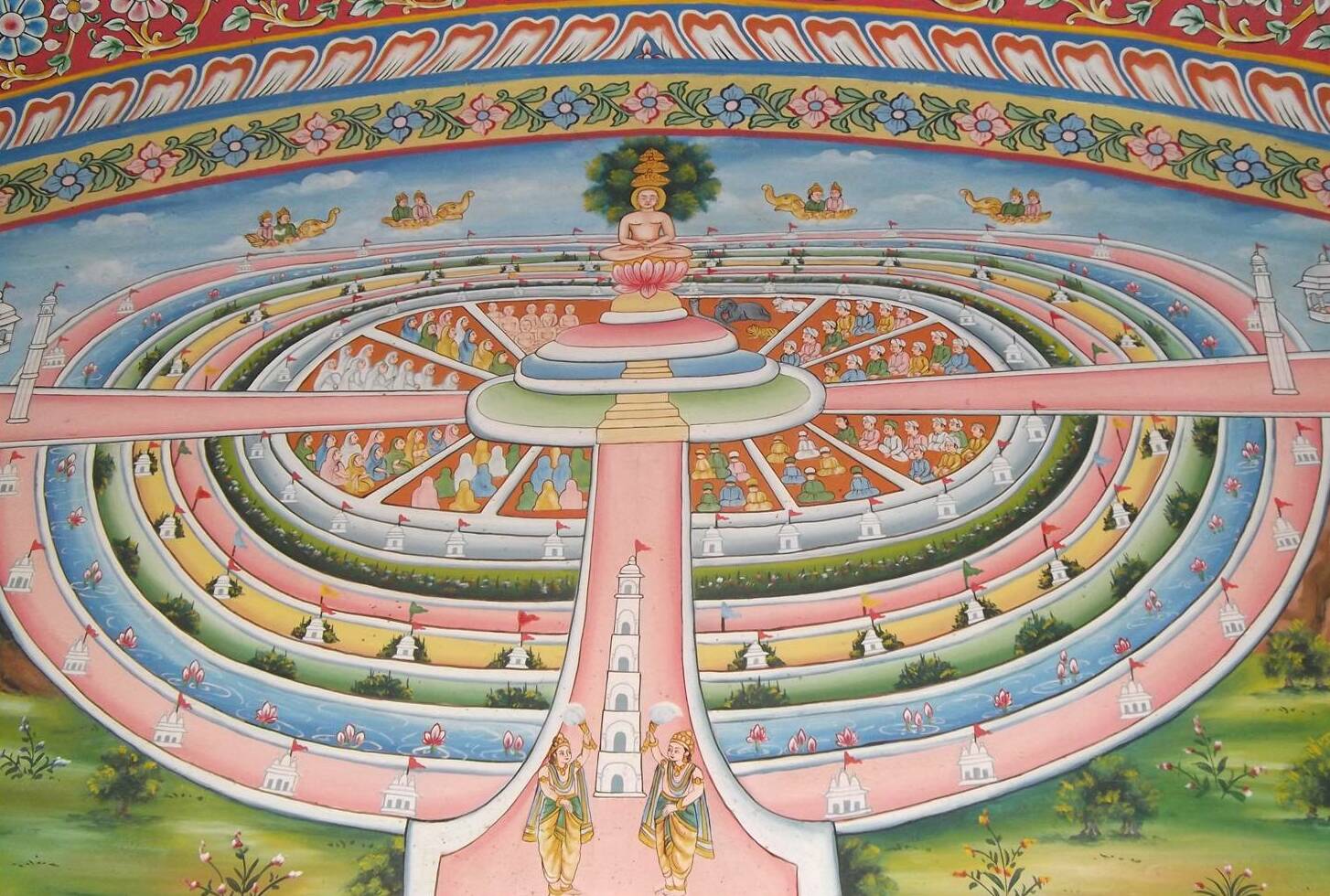
Samavasarana
In Jainism, Samavasarana or Samosharana ("Refuge to All") is the divine preaching hall of the Tirthankara, stated to have more than 20,000 stairs in it. The word ''samavasarana'' is derived from two words, ''sama'', meaning general and ''avasara'', meaning opportunity. It is an important feature in Jain art. The Samavasarana seems to have replaced the original Jain stupa as an object of worship. Samavasarana Hall In samavasarana hall, the ''tirthankara'' sits on a throne without touching it (about two inches above it). Around the tirthankara sit the ''ganadharas'' (chief disciples). Living beings sit in the following order: *In the first hall, ascetics *In the second hall, one class of deva ladies *In the third hall, ''aryikas'' (nuns) and laywomen *In the next three halls, three other classes of deva ladies *In the next four halls, the four classes of devas (heavenly beings) *Men, in the eleventh hall *Animals, in the last hall According to Jain texts, there would be four w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parshvanatha
''Parshvanatha'' (), also known as ''Parshva'' () and ''Parasnath'', was the 23rd of 24 ''Tirthankaras'' (supreme preacher of dharma) of Jainism. He is the only Tirthankara who gained the title of ''Kalīkālkalpataru (Kalpavriksha in this "Kali Yuga").'' Parshvanatha is one of the earliest ''Tirthankaras'' who are acknowledged as historical figures. He was the earliest exponent of Karma philosophy in recorded history. The Jain sources place him between the 9th and 8th centuries BCE whereas historians consider that he lived in the 8th or 7th century BCE. Parshvanatha was born 273 years before Mahavira. He was the spiritual successor of 22nd tirthankara Neminatha. He is popularly seen as a propagator and reviver of Jainism. Parshvanatha attained moksha on Mount Sammeda ( Madhuban, Jharkhand) popular as Parasnath hill in the Ganges basin, an important Jain pilgrimage site. His iconography is notable for the serpent hood over his head, and his worship often includes Dharanendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirumalai 3365 '', 2003 Indian Tamil film starring Vijay
{{Disambig ...
Tirumalai may refer to: Geography *Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, Andhra Pradesh, India * Tirumalai, a mountain and Jain site near Polur, Tamil Nadu, India See also *''Thirumalai ''Thirumalai'' is a 2003 Indian Tamil-language masala film written and directed by Ramana. The film stars Vijay and Jyothika, with Manoj K. Jayan, Avinash (in his Tamil debut), Vivek, Raghuvaran, Kausalya and Karunas in supporting roles. Prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parshvanath
''Parshvanatha'' (), also known as ''Parshva'' () and ''Parasnath'', was the 23rd of 24 ''Tirthankaras'' (supreme preacher of dharma) of Jainism. He is the only Tirthankara who gained the title of ''Kalīkālkalpataru (Kalpavriksha in this "Kali Yuga").'' Parshvanatha is one of the earliest ''Tirthankaras'' who are acknowledged as historical figures. He was the earliest exponent of Karma philosophy in recorded history. The Jain sources place him between the 9th and 8th centuries BCE whereas historians consider that he lived in the 8th or 7th century BCE. Parshvanatha was born 273 years before Mahavira. He was the spiritual successor of 22nd tirthankara Neminatha. He is popularly seen as a propagator and reviver of Jainism. Parshvanatha attained moksha on Mount Sammeda ( Madhuban, Jharkhand) popular as Parasnath hill in the Ganges basin, an important Jain pilgrimage site. His iconography is notable for the serpent hood over his head, and his worship often includes Dharanendra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahavir
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6th century BCE into a royal Kshatriya Jain family in ancient India. His mother's name was Trishala and his father's name was Siddhartha. They were lay devotees of Parshvanatha. Mahavira abandoned all worldly possessions at the age of about 30 and left home in pursuit of spiritual awakening, becoming an ascetic. Mahavira practiced intense meditation and severe austerities for twelve and a half years, after which he attained '' Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). He preached for 30 years and attained Moksha (liberation) in the 6th century BCE, although the year varies by sect. Historically, Mahavira, who revived and preached Jainism in ancient India, was an older contemporary of Gautama Buddha. Jains celebrate ''Mahavir Janma Kalyanak'' every ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahavira
Mahavira (Sanskrit: महावीर) also known as Vardhaman, was the 24th ''tirthankara'' (supreme preacher) of Jainism. He was the spiritual successor of the 23rd ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha. Mahavira was born in the early part of the 6th century BCE into a royal Kshatriya Jain family in ancient India. His mother's name was Trishala and his father's name was Siddhartha. They were lay devotees of Parshvanatha. Mahavira abandoned all worldly possessions at the age of about 30 and left home in pursuit of spiritual awakening, becoming an ascetic. Mahavira practiced intense meditation and severe austerities for twelve and a half years, after which he attained '' Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). He preached for 30 years and attained Moksha (liberation) in the 6th century BCE, although the year varies by sect. Historically, Mahavira, who revived and preached Jainism in ancient India, was an older contemporary of Gautama Buddha. Jains celebrate ''Mahavir Janma Kalyanak'' every ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chola Dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamils, Tamil thalassocratic Tamil Dynasties, empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE during the reign of Ashoka of the Maurya Empire. As one of the Three Crowned Kings of Tamilakam, along with the Chera dynasty, Chera and Pandya dynasty, Pandya, the dynasty continued to govern over varying territories until the 13th century CE. The Chola Empire was at its peak under the Medieval Cholas in the mid-9th century CE. The heartland of the Cholas was the fertile valley of the Kaveri River. They ruled a significantly larger area at the height of their power from the later half of the 9th century till the beginning of the 13th century. They unified peninsular India south of the Tungabhadra River, and held the territory as one state for three centuries between 907 and 1215 CE.K. A. Nilakanta Sastri, ''A Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kundavai Pirāttiyār
Kundavai Pirattiyar commonly known mononymously as Kundavai, was a princess of the Chola empire who lived in the tenth century in South India.''Lalit kalā, Issue 15, page 34'' She was the daughter of Parantaka II and Vanavan Mahadevi.''Early Chola art, page 183''''A Topographical List of Inscriptions in the Tamil Nadu and Kerala States: Thanjavur District, page 180''''Worshiping Śiva in medieval India: ritual in an oscillating universe, page 5'' She was born in Tirukoilur and was the elder sister of Chola emperor Rajaraja I. She had title as ''Ilaiyapirātti Kundavai Nachiyar''. However when her husband Vallavaraiyan Vandiyadevan was crowned king in his hometown Bana Kingdom, she did not accept the offer to become queen of the kingdom and remained as the princess of Tanjore. Life Kundavai (also transliterated as Kundhavai or Kunthavai) was born in 945 CE. She was the only daughter of the Chola king Parantaka II and queen Vanavan Mahadevi. She had an elder brother – Adith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Temple
A Jain temple, Derasar (Gujarati: દેરાસર) or Basadi (Kannada: ಬಸದಿ) is the place of worship for Jains, the followers of Jainism. Jain architecture is essentially restricted to temples and monasteries, and Jain buildings generally reflect the prevailing style of the place and time they were built. Jain temple architecture is generally close to Hindu temple architecture, and in ancient times Buddhist architecture. Normally the same builders and carvers worked for all religions, and regional and period styles are generally similar. For over 1,000 years, the basic layout of a Hindu or most Jain temples has consisted of a small garbhagriha or sanctuary for the main murti or cult images, over which the high superstructure rises, then one or more larger mandapa halls. Māru-Gurjara architecture or the "Solanki style" is, a particular temple style from Gujarat and Rajasthan (both regions with a strong Jain presence) that originated in both Hindu and Jain temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirumalai Jaintemple 4 '', 2003 Indian Tamil film starring Vijay
{{Disambig ...
Tirumalai may refer to: Geography *Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, Andhra Pradesh, India * Tirumalai, a mountain and Jain site near Polur, Tamil Nadu, India See also *''Thirumalai ''Thirumalai'' is a 2003 Indian Tamil-language masala film written and directed by Ramana. The film stars Vijay and Jyothika, with Manoj K. Jayan, Avinash (in his Tamil debut), Vivek, Raghuvaran, Kausalya and Karunas in supporting roles. Prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)


