|
Timia
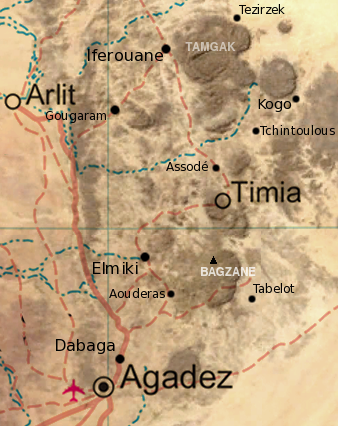
Timia is a small town and commune in northern Niger, situated at an oasis in the Aïr Mountains, Agadez Region, Arlit Department. Visitors come to the Tuareg people, Tuareg town to see a seasonal waterfall, a former French fort and the nearby ruined town of Assodé. As of 2011, the commune had a total population of 13,588 people. Timia lies south of Iferouane and north of Agadez. The main town lies around 3 km from a stone guelta oasis, which holds water year round. It is also known for its fruit trees, an unusual sight in the Saharan regions of northern Niger. Gallery Image:Timia_valley.JPG, The valleys of Timia Image:Timia_Oasis.JPG, The Oasis of Timia Image:Timia_Valley_Floor.JPG , In the valley Image:Well_in_Timia.jpg , Well in Timia References Oases of Niger Tuareg Agadez Region Communes of Niger {{Niger-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aïr Mountains
The Aïr Mountains or Aïr Massif ( tmh, Ayăr; Hausa: Eastern ''Azbin'', Western ''Abzin'') is a triangular massif, located in northern Niger, within the Sahara. Part of the West Saharan montane xeric woodlands ecoregion, they rise to more than and extend over . Lying in the midst of desert north of the 17th parallel, the Aïr plateau, with an average altitude between , forms an island of Sahel climate which supports a wide variety of life, many pastoral and farming communities, and dramatic geological and archaeological sites. There are notable archaeological excavations in the region that illustrate the prehistoric past of this region. The endangered African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus'') once existed in this region, but may now be extirpated due to human population pressures in this region. Geology The Precambrian to Cenozoic Aïr Mountains consist of peralkaline granite intrusions which appear dark in colour (unusual since most granitic masses are light-ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agadez Region
Agadez Region is one of the seven regions of Niger. At , it covers more than half of Niger's land area, and is the largest region in the country, as well as the largest African state subdivision. The capital of the department is Agadez. History The region is a centre for palaeontology, with numerous dinosaur skeletons being found here, including the ''Ouranosaurus nigeriensis''. Cave painting and the remains of ancient human settlements are also located here. Tuareg peoples began migrating to the region from the mid-8th century. From the mid-15th century to the early 20th, much of the region was under the control of the Sultanate of Agadez, except for a period when the area came under the rule of the Songhai Empire in the 1500s. The region suffered with the advent of French colonialism as power shifted away to the southwest; Tuareg disaffection with French rule resulted in the Kaocen revolt in 1916–17. This process continued following Niger's independence in 1960; local Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlit Department
Arlit is a department of the Agadez Region in Niger. Its capital lies at the city of Arlit. As of 2012, the department had a total population of 105,025 people. Communes It is divided administratively into the following communes: *Arlit * Dannet * Gougaram *Iferouane *Imouraren *Timia Timia is a small town and commune in northern Niger, situated at an oasis in the Aïr Mountains, Agadez Region, Arlit Department. Visitors come to the Tuareg town to see a seasonal waterfall, a former French fort and the nearby ruined town of A ... References Departments of Niger Agadez Region {{Niger-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of Niger
The Departments of Niger are subdivided into communes. As of 2005, in the seven Regions and one Capital Area, there were 36 ''départements'', divided into 265 ''communes'', 122 ''cantons'' and 81 ''groupements''. The latter two categories cover all areas not covered by ''Urban Communes'' (population over 10000) or ''Rural Communes'' (population under 10000), and are governed by the Department, whereas Communes have (since 1999) elected councils and mayors. Additional semi-autonomous sub-divisions include ''Sultanates'', ''Provinces'' and ''Tribes'' (''tribus''). The Nigerien government estimates there are an additional 17000 Villages administered by ''Rural Communes'', while there are over 100 ''Quartiers'' (boroughs or neighborhoods) administered by ''Urban Communes''. The territorial reorganisation of Niger's local administration, known informally as the ''Decentralisation process'', was carried out through a series of laws from 1998 - 2005. Most important are: * The Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guelta
A guelta ( ar, قلتة, also transliterated qalta or galta; Berber: agelmam) is a pocket of water that forms in drainage canals or wadis in the Sahara. The size and duration will depend on the location and conditions. It may last year-round through the dry season if fed by a source such as a spring. When a river (wadi) dries up, there may be pockets of water remaining along its course (c.f. oxbow lake). In Western Sahara, gueltas correspond to oases. Some examples include Guelta d'Archei in Chad and Timia in Niger. References See also *Billabong Billabong ( ) is an Australian term for an oxbow lake, an isolated pond left behind after a river changes course. Billabongs are usually formed when the path of a creek or river changes, leaving the former branch with a dead end. As a result ... - term for a similar type of body of water in Australia Aquatic ecology Bodies of water Geomorphology Oases Wadis Wetlands {{geomorph-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iferouane
Iferouane (french: link=no, Iférouane), also spelled Iferouan, is an oasis town and commune in northern Niger, in Agadez Department. It is located northeast of Arlit in the northern Aïr, in the Ighazar valley near the Tamgak Range. Iferouane is also the location of the headquarters of the Aïr and Ténéré Natural Reserves, a World Heritage Site covering more than . The Project for the Conservation and Management of the Natural Resources of the Aïr-Ténéré, a joint venture between the government of Niger, the World Conservation Union (IUCN), and the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), is also based in Iferouane. The town has one airport: Iferouane Airport . History The Foureau-Lamy Mission, a French military expedition led by Fernand Foreau and Amédée-François Lamy, spent a number of months at Iferouane in 1899. The expedition stopped at Iferouane on 24 February 1899 to acquire additional pack animals, their number having dwindled from 1,004 to 585, and depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuareg People
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern Algeria, Niger, Mali, and Burkina Faso. Traditionally nomadic pastoralists, small groups of Tuareg are also found in northern Nigeria. The Tuareg speak languages of the same name (also known as ''Tamasheq''), which belong to the Berber branch of the Afroasiatic family. The Tuaregs have been called the "blue people" for the indigo dye coloured clothes they traditionally wear and which stains their skin. They are a semi-nomadic people who practice Islam, and are descended from the indigenous Berber communities of Northern Africa, which have been described as a mosaic of local Northern African (Taforalt), Middle Eastern, European (Early European Farmers), and Sub-Saharan African-related ancestries, prior to the Arab expansion. Tuareg peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern Algeria, Niger, Mali, and Burkina Faso. Traditionally nomadic pastoralists, small groups of Tuareg are also found in northern Nigeria. The Tuareg speak languages of the same name (also known as ''Tamasheq''), which belong to the Berber branch of the Afroasiatic family. The Tuaregs have been called the "blue people" for the indigo dye coloured clothes they traditionally wear and which stains their skin. They are a semi-nomadic people who practice Islam, and are descended from the indigenous Berber communities of Northern Africa, which have been described as a mosaic of local Northern African (Taforalt), Middle Eastern, European (Early European Farmers), and Sub-Saharan African-related ancestries, prior to the Arab expansion. Tuareg peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.” The location of oases has been of critical importance for trade and transportation routes in desert areas; caravans must travel via oases so that supplies of water and food can be replenished. Thus, political or military control of an oasis has in many cases meant control of trade on a particular route. For example, the oases of Awjila, Ghadames and Kufra, situated in modern-day Libya, have at various times been vital to both north–south and east–west Trans-Saharan trade, trade in the Sahara Desert. The location of oases also informed the Darb El Arba'īn trade route from Sudan to Egypt, as well as the caravan route from the Niger River to Tangier, Morocco. The Silk Road “traced its course from water hole to water hole, relying on oasis communities such as Turpan in China and Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niger
) , official_languages = , languages_type = National languagesRépublique du Niger, "Loi n° 2001-037 du 31 décembre 2001 fixant les modalités de promotion et de développement des langues nationales." L'aménagement linguistique dans le monde (accessed 21 September 2016) , languages = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2012 , religion = , demonym = Nigerien , capital = , coordinates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Niger
Niger is divided into eight regions (French: ''régions;'' singular''région)'', each of which is named after its capital. Current regions *Additionally, the national capital, Niamey, comprises a special capital district. Current administrative structure Each of Niger's regions are subdivided into departments and communes. As of 2005, there were 36 ''départements'', divided into 265 communes, 122 cantons and 81 ''groupements''. The latter two categories cover all areas not covered by urban communes (population over 10000) or rural communes (total population 13 million), and are governed by the department, whereas communes have had elected councils and mayors since 1999. Additional semi-autonomous subdivisions include sultanates, provinces and tributaries (''tribus''). The Nigerien government estimates there are an additional 17000 villages administered by rural communes, while there are a number of ''quartiers'' (boroughs or neighborhoods) administered by urban communes. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek ''Towns of ancient Greece#Military settlements, phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the ancient Roman, Roman castellum or English language, English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
