|
Time-saving Bias
Time-saving bias is a concept that describes people's tendency to misestimate the time that could be saved (or lost) when increasing (or decreasing) speed. In general, people underestimate the time that could be saved when increasing from a relatively low speed - e.g., or - and overestimate the time that could be saved when increasing from a relatively high speed - e.g., or . People also underestimate the time that could be lost when decreasing from a low speed and overestimate the time that could be lost when decreasing from a high speed. Examples In one study, participants were asked to judge which of two road improvement plans would be more efficient in reducing mean journey time. Respondents preferred a plan that would increase the mean speed from more than a plan that would increase the mean speed from , although the latter actually saves more time. In another study, drivers were asked to indicate how much time they felt could be saved when increasing from either a low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance travelled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as the duration of the time interval approaches zero. Speed is not the same as velocity. Speed has the dimensions of distance divided by time. The SI unit of speed is the metre per second (m/s), but the most common unit of speed in everyday usage is the kilometre per hour (km/h) or, in the US and the UK, miles per hour (mph). For air and marine travel, the knot is commonly used. The fastest possible speed at which energy or information can travel, according to special relativity, is the speed of light in a vacuum ''c'' = metres per second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship between given quantities. The plural of ''formula'' can be either ''formulas'' (from the most common English plural noun form) or, under the influence of scientific Latin, ''formulae'' (from the original Latin). In mathematics In mathematics, a formula generally refers to an identity which equates one mathematical expression to another, with the most important ones being mathematical theorems. Syntactically, a formula (often referred to as a ''well-formed formula'') is an entity which is constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language. For example, determining the volume of a sphere requires a significant amount of integral calculus or its geometrical analogue, the method of exhaustion. However, having done t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curvilinear Coordinates
In geometry, curvilinear coordinates are a coordinate system for Euclidean space in which the coordinate lines may be curved. These coordinates may be derived from a set of Cartesian coordinates by using a transformation that is locally invertible (a one-to-one map) at each point. This means that one can convert a point given in a Cartesian coordinate system to its curvilinear coordinates and back. The name ''curvilinear coordinates'', coined by the French mathematician Lamé, derives from the fact that the coordinate surfaces of the curvilinear systems are curved. Well-known examples of curvilinear coordinate systems in three-dimensional Euclidean space (R3) are cylindrical and spherical coordinates. A Cartesian coordinate surface in this space is a coordinate plane; for example ''z'' = 0 defines the ''x''-''y'' plane. In the same space, the coordinate surface ''r'' = 1 in spherical coordinates is the surface of a unit sphere, which is curved. The formalism of curvilinear c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristic
A heuristic (; ), or heuristic technique, is any approach to problem solving or self-discovery that employs a practical method that is not guaranteed to be optimal, perfect, or rational, but is nevertheless sufficient for reaching an immediate, short-term goal or approximation. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Examples that employ heuristics include using trial and error, a rule of thumb or an educated guess. Heuristics are the strategies derived from previous experiences with similar problems. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstract issues. When an individual applies a heuristic in practice, it generally performs as expected. However it can alternatively cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
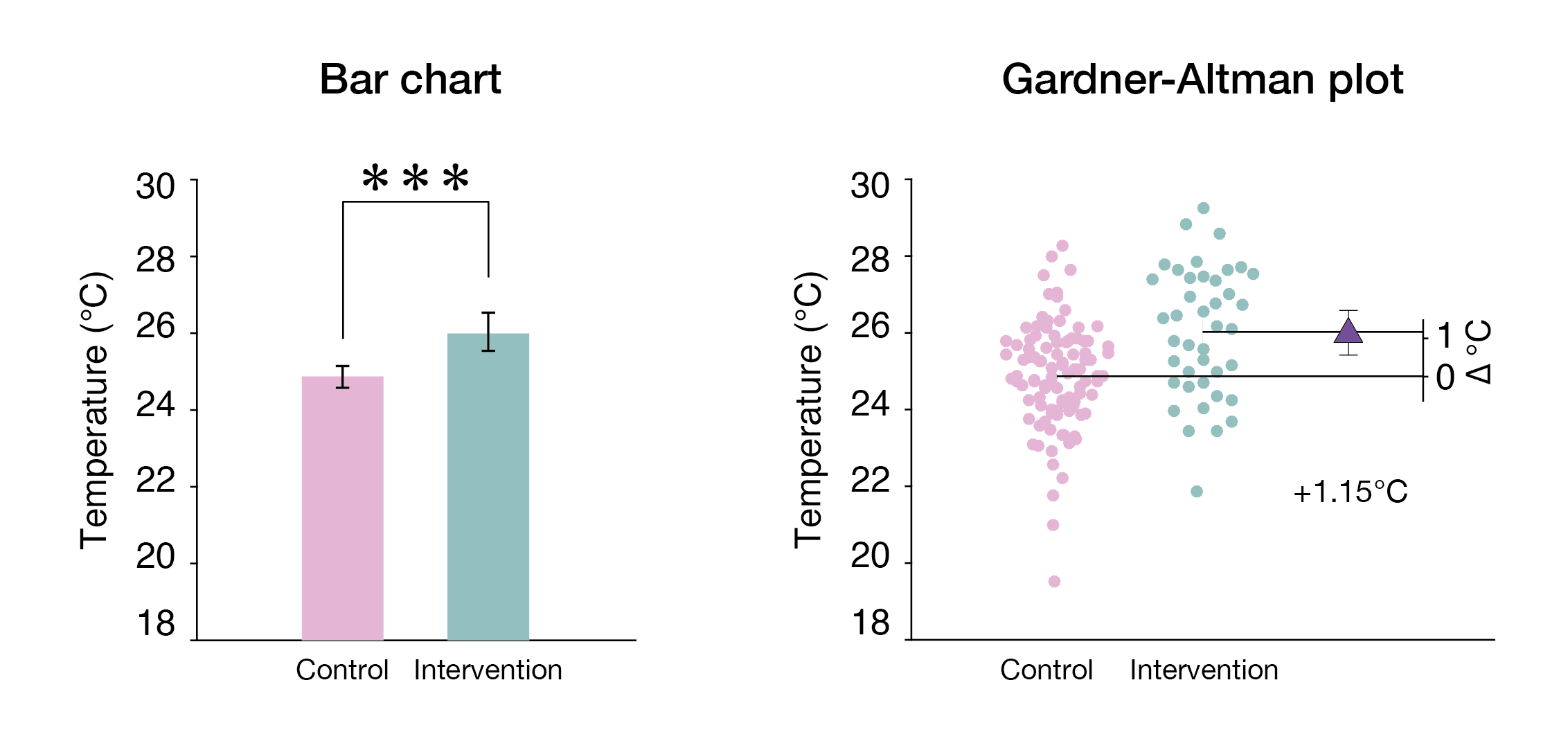
Estimation Statistics
Estimation statistics, or simply estimation, is a data analysis framework that uses a combination of effect sizes, confidence intervals, precision planning, and meta-analysis to plan experiments, analyze data and interpret results. It complements hypothesis testing approaches such as null hypothesis significance testing (NHST), by going beyond the question is an effect present or not, and provides information about how large an effect is. Estimation statistics is sometimes referred to as ''the new statistics''. The primary aim of estimation methods is to report an effect size (a point estimate) along with its confidence interval, the latter of which is related to the precision of the estimate. The confidence interval summarizes a range of likely values of the underlying population effect. Proponents of estimation see reporting a ''P'' value as an unhelpful distraction from the important business of reporting an effect size with its confidence intervals, and believe that estimat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production process, i.e. output per unit of input, typically over a specific period of time. The most common example is the (aggregate) labour productivity measure, one example of which is GDP per worker. There are many different definitions of productivity (including those that are not defined as ratios of output to input) and the choice among them depends on the purpose of the productivity measurement and/or data availability. The key source of difference between various productivity measures is also usually related (directly or indirectly) to how the outputs and the inputs are aggregated to obtain such a ratio-type measure of productivity. Productivity is a crucial factor in the production performance of firms and nations. Increasing national productivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cognitive Biases
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm and/or rationality in judgment. They are often studied in psychology, sociology and behavioral economics. Although the reality of most of these biases is confirmed by reproducible research, there are often controversies about how to classify these biases or how to explain them. Several theoretical causes are known for some cognitive biases, which provides a classification of biases by their common generative mechanism (such as noisy information-processingMartin Hilbert (2012) "Toward a synthesis of cognitive biases: How noisy information processing can bias human decision making"'. Psychological Bulletin, 138(2), 211–237; free access to the study here: https://www.martinhilbert.net/toward-a-synthesis-of-cognitive-biases/). Gerd Gigerenzer has criticized the framing of cognitive biases as errors in judgment, and favors interpreting them as arising from rational deviations from logical thought. Explanations include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdahl's Law
In computer architecture, Amdahl's law (or Amdahl's argument) is a formula which gives the theoretical speedup in latency of the execution of a task at fixed workload that can be expected of a system whose resources are improved. It states that "the overall performance improvement gained by optimizing a single part of a system is limited by the fraction of time that the improved part is actually used". It is named after computer scientist Gene Amdahl, and was presented at the American Federation of Information Processing Societies (AFIPS) Spring Joint Computer Conference in 1967. Amdahl's law is often used in parallel computing to predict the theoretical speedup when using multiple processors. For example, if a program needs 20 hours to complete using a single thread, but a one-hour portion of the program cannot be parallelized, therefore only the remaining 19 hours' () execution time can be parallelized, then regardless of how many threads are devoted to a parallelized execution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Biases
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the objective input, may dictate their behavior in the world. Thus, cognitive biases may sometimes lead to perceptual distortion, inaccurate judgment, illogical interpretation, or what is broadly called irrationality. Although it may seem like such misperceptions would be aberrations, biases can help humans find commonalities and shortcuts to assist in the navigation of common situations in life. Some cognitive biases are presumably adaptive. Cognitive biases may lead to more effective actions in a given context. Furthermore, allowing cognitive biases enables faster decisions which can be desirable when timeliness is more valuable than accuracy, as illustrated in heuristics. Other cognitive biases are a "by-product" of human processing limitations, resulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |