|
Tibetan Annals
The ''Tibetan Annals'', or ''Old Tibetan Annals'' (''OTA''), are composed of two manuscripts written in Old Tibetan language found in the early 20th century in the "hidden library", the Mogao Grottoes near Dunhuang in northwestern Gansu province, Western China, which is believed to have been sealed in the 11th century CE. They form Tibet's earliest extant history. The two manuscripts are known as the "civil" and "military" versions of the Annals. The "civil" version is designated in the British Library in London and in the Bibliothèque Nationale in Paris are originally from the same original roll, 4.34 metres long and 0.258 metres wide. The "civil" version covers the years 650–748 with some gaps.Dotson 2009, p. 15 The "military" version is designated Or.8212/187 is also held at the British Library. This version is much shorter and covers the years 743–765 with some gaps. Discovery An enormous number of early manuscripts in a variety of languages were collected by A. Stei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelliot Tibétain 1288 (Tibetan Annals) Page 1
Paul Eugène Pelliot (28 May 187826 October 1945) was a French Sinologist and Orientalist best known for his explorations of Central Asia and his discovery of many important Chinese texts such as the Dunhuang manuscripts. Early life and career Paul Pelliot was born on 28 May 1878 in Paris, France, and initially intended to pursue a career as a foreign diplomat. Accordingly, he studied English as a secondary school student at La Sorbonne, then studied Mandarin Chinese at the École des Langues Orientales Vivantes (School of Living Oriental Languages). Pelliot was a gifted student, and completed the school's three-year Mandarin course in only two years. His rapid progress and accomplishments attracted the attention of the Sinologist Édouard Chavannes, the chair of Chinese at the Collège de France, who befriended Pelliot and began mentoring him. Chavannes also introduced Pelliot to the Collège's Sanskrit chair, Sylvain Lévi. Pelliot began studying under the two men, who e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunhuang Cave 16
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major stop on the ancient Silk Road and is best known for the nearby Mogao Caves. Dunhuang is situated in an oasis containing Crescent Lake and Mingsha Shan (, meaning "Singing-Sand Mountain"), named after the sound of the wind whipping off the dunes, the singing sand phenomenon. Dunhuang commands a strategic position at the crossroads of the ancient Southern Silk Route and the main road leading from India via Lhasa to Mongolia and Southern Siberia, and also controls the entrance to the narrow Hexi Corridor, which leads straight to the heart of the north Chinese plains and the ancient capitals of Chang'an (today known as Xi'an) and Luoyang. Administratively, the county-level city of Dunhuang is part of the prefecture-level city of Jiuquan. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Literature
Tibetan literature generally refers to literature written in the Tibetan language or arising out of Tibetan culture. Historically, Tibetan has served as a trans-regional literary language that has been used, at different times, from Tibet to Mongolia, Russia, and present-day Bhutan, Nepal, India, and Pakistan. Today, the term Tibetan literature can also be applied to any work by an ethnic Tibetan person or arising out of Tibetan folk culture; contemporary Tibetan writers sometimes use Chinese, English, or other languages to compose their work. Terminology Today, the term "Tibetan literature" can also be applied to any work by an ethnic Tibetan person. However, who is a "Tibetan" and who speaks "the Tibetan language" are contested. For instance, Chinese ethnologists have argued that the Baima language is independent from Tibetan, however, the state classifies them as Tibetans for fear of being seen as attacking the unity of Tibetan identity. Similarly, the Tibetan languages are in fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Tibet
While the Tibetan plateau has been inhabited since pre-historic times, most of Tibet's history went unrecorded until the introduction of Tibetan Buddhism around the 6th century. Tibetan texts refer to the kingdom of Zhangzhung (c. 500 BCE – 625 CE) as the precursor of later Tibetan kingdoms and the originators of the Bon religion. While mythical accounts of early rulers of the Yarlung Dynasty exist, historical accounts begin with the introduction of Buddhism from India in the 6th century and the appearance of envoys from the unified Tibetan Empire in the 7th century. Following the dissolution of the empire and a period of fragmentation in the 9th-10th centuries, a Buddhist revival in the 10th–12th centuries saw the development of three of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. After a period of control by the Mongol Empire and Yuan dynasty, Tibet became effectively independent in the 14th century and was ruled by a succession of noble houses for the next 300 years. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui settlers. Since Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large. The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, with the financial support of Charles Scribner, as a printing press to serve the Princeton community in 1905. Its distinctive building was constructed in 1911 on William Street in Princeton. Its first book was a new 1912 edition of John Witherspoon's ''Lectures on Moral Philosophy.'' History Princeton University Press was founded in 1905 by a recent Princeton graduate, Whitney Darrow, with financial support from another Princetonian, Charles Scribner II. Darrow and Scribner purchased the equipment and assumed the operations of two already existing local publishers, that of the ''Princeton Alumni Weekly'' and the Princeton Press. The new press printed both local newspapers, university documents, ''The Daily Princetonian'', and later added book publishing to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general officer of the Tang military system. The event involved military activity and direct deaths from battle, but also significant associated population loss from famine, and population dislocations. The event is also known, especially in Chinese historiography, either as the An–Shi Rebellion or as the An–Shi Disturbances (). The use of the term ''luàn'' ("chaos") indicates the extreme social instability and population loss which eventually resulted, far beyond the initial consequences of the rebellion. Traditionally, Chinese family names have begun with the family name first. In this case the family name of the initial rebel leader is An. The term ''Ān-Shǐ'' is used to recognize that the rebellion continued after An Lushan's death, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
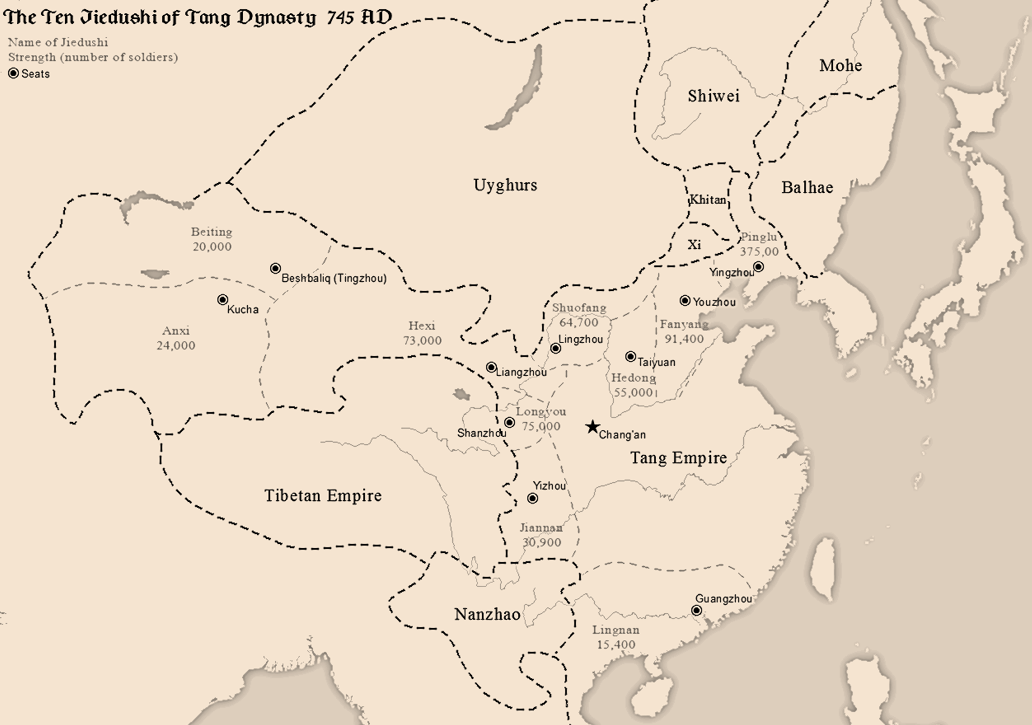
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin Shi Huang of the Qin dynasty, China's first emperor, held his imperial court, and constructed his massive mausoleum guarded by the Terracotta Army. From its capital at Xianyang, the Qin dynasty ruled a larger area than either of the preceding dynasties. The imperial city of Chang'an during the Han dynasty was located northwest of today's Xi'an. During the Tang dynasty, the area that came to be known as Chang'an included the area inside the Ming Xi'an fortification, plus some small areas to its east and west, and a substantial part of its southern suburbs. Thus, Tang Chang'an was eight times the size of the Ming Xi'an, which was reconstructed upon the site of the former imperial quarters of the Sui and Tang city. During its heyday, Chang'an w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Wencheng
Princess Wencheng (; ) was a member of a minor branch of the royal clan of the Tang Dynasty who married King Songtsen Gampo of the Tibetan Empire in 641. She is also known by the name Gyasa or "Chinese wife" in Tibet. Some Tibetan historians consider both Princess Wencheng and Songtsen Gampo's other wife Bhrikuti to be physical manifestations of the bodhisattva Tara. Chinese accounts of Princess Wencheng Life According to Chinese accounts, in the spring of 634 on an official state visit to Imperial China, Tibetan King Songtsen Gampo fell in love at first sight and had relentlessly pursued the princess's hand by sending envoys and tributes but was refused. Allegedly, in 635/636, royal Tibetan forces were deployed, attacking and defeating the peoples of Tuyuhun who strategically lived near the Lake of Koko Nor in present-day Qinghai, impeding a trade route into Imperial China. News of Tibetan King Songtsen Gampo's attack on Songzhou quickly spread from the ground to the Roy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songtsen Gampo
Songtsen Gampo (; 569–649? 650), also Songzan Ganbu (), was the 33rd Tibetan king and founder of the Tibetan Empire, and is traditionally credited with the introduction of Buddhism to Tibet, influenced by his Nepali consort Bhrikuti, of Nepal's Licchavi (kingdom), Licchavi dynasty, as well as with the unification of what had previously been several Tibetan kingdoms. He is also regarded as responsible for the creation of the Tibetan script and therefore the establishment of Classical Tibetan, the language spoken in his region at the time, as the literary language of Tibet. His mother, the queen, is identified as Driza Thökar (). The date of his birth and of when he took the throne are not certain. In Tibetan accounts, it is generally accepted that he was born in an Ox year of the Tibetan calendar, which means one of the following dates: 557, 569, 581, 593, 605 or 617 CE. He is thought to have ascended the throne at age thirteen (twelve by Western reckoning), by this reckoning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Tibetan Chronicle
The ''Old Tibetan Chronicle'' is a collection of narrative accounts and songs relating to Tibet's Yarlung dynasty and the Tibetan Empire. The three manuscripts that comprise the only extant copies of the Chronicle are among the Dunhuang Manuscripts found in the early 20th century in the so-called "hidden library" at the Mogao Grottoes near Dunhuang, which is believed to have been sealed in the 11th century CE. The ''Chronicle'', together with the Old Tibetan Annals comprise Tibet's earliest extant history. Discovery An enormous number of early manuscripts in a variety of languages were collected by Aurel Stein and Paul Pelliot at the famous sealed-up Library Cave (no. 17) of the Mogao Grottoes at Dunhuang and sent back to London and Paris respectively. The ''Dunhuang manuscripts'' in the Tibetan language include the Old Tibetan Chronicle, which was probably compiled in the early 9th century, and the Old Tibetan Annals, which have been described as "the first and single most i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_page_1.jpg)


.png)