|
Tiberius Claudius Nero (praetor 42 BC)
Tiberius Claudius Nero (c. 82 – 33 BC) was a Roman politician, senator, and praetor who lived in the last century of the Roman Republic. He was notable for being the first husband of Livia, before she divorced him to marry the future emperor Augustus, and the biological father of the second Roman emperor Tiberius. Ancestry Nero was a member of the republican Claudia gens of Rome. He was a descendant of the censor Appius Claudius Caecus. Nero was the son of Tiberius Claudius Nero and his mother was a descendant of the Claudian gens. Nero had a sister called Claudia, who married the prefect Quintus Volusius. Political career Under Julius Caesar Nero had served as a quaestor to Julius Caesar in 48 BC, commanding his fleet in the Alexandrian War. Having achieved victory over the Egyptian navy, he was rewarded with a priesthood. Julius Caesar had sent Nero to create Roman colonies in Gaul and in other provinces. Assassination of Julius Caesar Despite his service with Jul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetor
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the ''praetura'' (praetorship), are described by the adjective: the ''praetoria potestas'' (praetorian power), the ''praetorium imperium'' (praetorian authority), and the ''praetorium ius'' (praetorian law), the legal precedents established by the ''praetores'' (praetors). ''Praetorium'', as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his '' castra'', the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship. History of the title The status of the ''praetor'' in the early republic is unclear. The traditional account from Livy claims that the praetorship was created by the Sextian-Licinian Rogatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
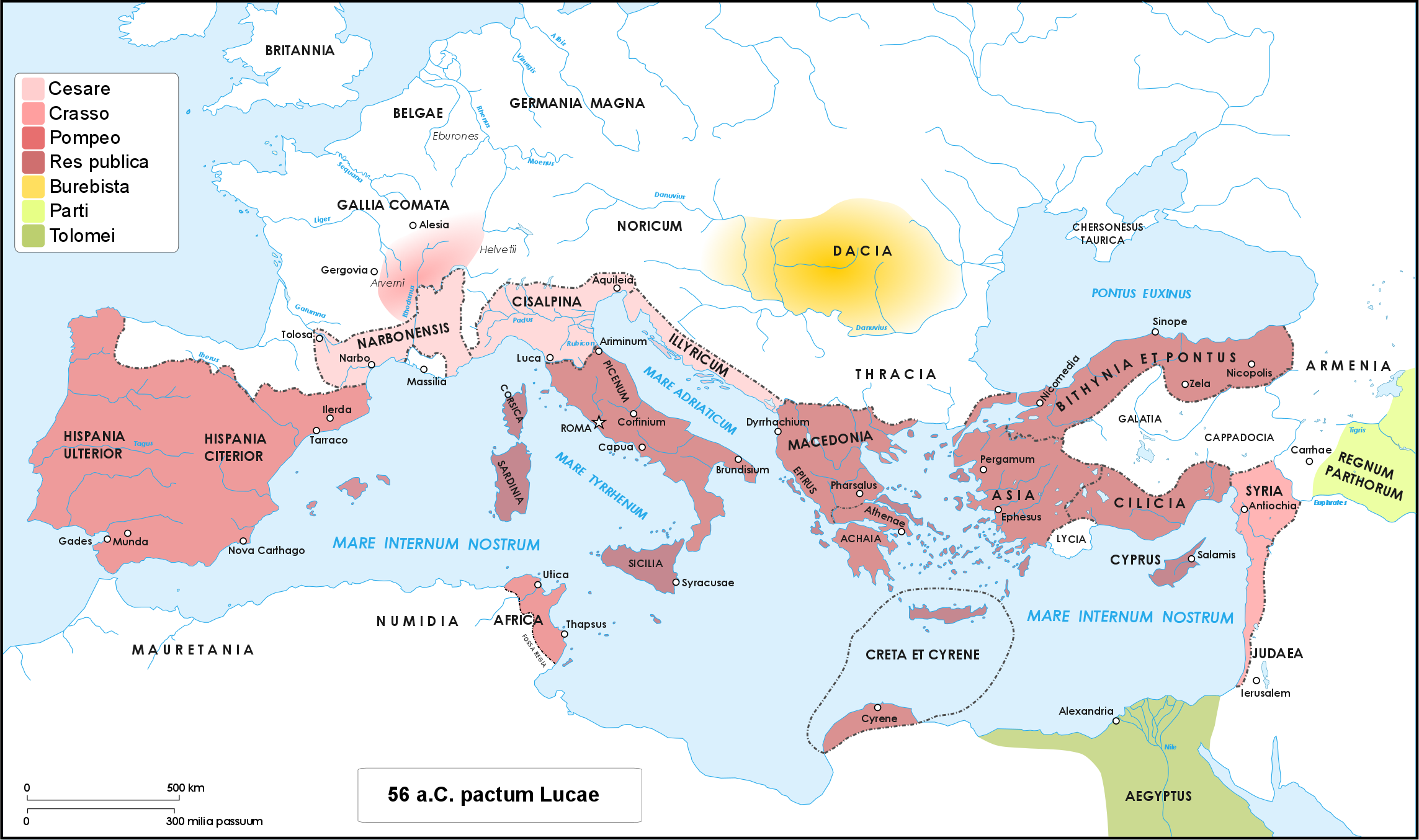
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's administrative limits as of 2022. Its province-level municipality is the third-most populous metropolitan city in Italy with a population of 3,115,320 residents, and its metropolitan area stretches beyond the boundaries of the city wall for approximately 20 miles. Founded by Greeks in the first millennium BC, Naples is one of the oldest continuously inhabited urban areas in the world. In the eighth century BC, a colony known as Parthenope ( grc, Παρθενόπη) was established on the Pizzofalcone hill. In the sixth century BC, it was refounded as Neápolis. The city was an important part of Magna Graecia, played a major role in the merging of Greek and Roman society, and was a significant cultural centre under the Romans. Naples served a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestrina
Palestrina (ancient ''Praeneste''; grc, Πραίνεστος, ''Prainestos'') is a modern Italian city and ''comune'' (municipality) with a population of about 22,000, in Lazio, about east of Rome. It is connected to the latter by the Via Prenestina. It is built upon the ruins of the ancient city of Praeneste. Palestrina is the birthplace of composer Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina. Geography Palestrina is sited on a spur of the Monti Prenestini, a mountain range in the central Apennines. Modern Palestrina borders the following municipalities: Artena, Castel San Pietro Romano, Cave, Gallicano nel Lazio, Labico, Rocca di Cave, Rocca Priora, Rome, San Cesareo, Valmontone, Zagarolo. History Ancient Praeneste Ancient mythology connected the origin of Praeneste to Ulysses, or to other fabled characters such as Caeculus, Telegonus, Erulus or ''Praenestus''. The name probably derives from the word ''Praenesteus'', referring to its overlooking location. Early burials show that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perusia
The ancient Perusia, now Perugia, first appears in history as one of the 12 confederate cities of Etruria. It is first mentioned in the account of the war of 310 or 309 BC between the Etruscans and the Romans. It took, however, an important part in the rebellion of 295 BC and was reduced, with Vulsinii and Arretium ( Arezzo), to seek for peace in the following year. It seems the city was in the Antonii's clientela since this period, as it was said by historians during imperial times. In 216 BC and 205 BC it assisted Rome in the Hannibalic war, but afterward it is not mentioned until 41–40 BC, when Lucius Antonius took refuge there and was reduced by Octavian after a long siege, known as the Perusine War. Some of the refugees ran away towards Gaul to escape Octavian. A local history said they were the founders of Perouges en Dauphiné Province (France). A number of lead bullets used by slingers have been found in and around the city. The city was burnt, we are told, with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Antonius (brother Of Mark Antony)
Lucius Antonius (1st century BC) was the younger brother and supporter of Mark Antony, a Roman politician. He was nicknamed Pietas as a young man. Biography Early life Lucius was a son of Marcus Antonius Creticus, son of the rhetorician Marcus Antonius Orator executed by Gaius Marius' supporters in 86 BC, and Julia, a third cousin of Julius Caesar. Together with his older brothers Mark Antony and Gaius Antonius, he spent his early years roaming through Rome in bad company. Plutarch refers to the untamed life of the youths and their friends, frequenting gambling houses and drinking too much. Career Lucius was always a strong supporter of Mark Antony. In 44 BC, the year of Antony's consulship and Julius Caesar's assassination, Lucius, as tribune of the plebs, brought forward a law authorizing Caesar to nominate the chief magistrates during his absence from Rome. After the murder of Caesar, he supported his brother Marcus. He proposed an agrarian law in favor of the people and Caesa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autocratic Roman Empire. Antony was a relative and supporter of Julius Caesar, and served as one of his generals during the conquest of Gaul and the Civil War. Antony was appointed administrator of Italy while Caesar eliminated political opponents in Greece, North Africa, and Spain. After Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, Antony joined forces with Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, another of Caesar's generals, and Octavian, Caesar's great-nephew and adopted son, forming a three-man dictatorship known to historians as the Second Triumvirate. The Triumvirs defeated Caesar's killers, the ''Liberatores'', at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BC, and divided the government of the Republic between themselves. Antony was assigned Rome's eastern provinces, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Triumvirate
The Second Triumvirate was an extraordinary commission and magistracy created for Mark Antony, Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, and Octavian to give them practically absolute power. It was formally constituted by law on 27 November 43 BC with a term of five years; it was renewed in 37 BC for another five years before expiring in 32 BC. Constituted by the ''lex Titia'', the triumvirs were given broad powers to make or repeal legislation, issue judicial punishments without due process or right of appeal, and appoint all other magistrates. The triumvirs also split the Roman world into three sets of provinces. The triumvirate, formed in the aftermath of a conflict between Antony and the senate, emerged as a force to reassert Caesarian control over the western provinces and wage war on the ''liberatores'' led by the men who assassinated Julius Caesar. After proscriptions, purging the senatorial and equestrian orders, and a brutal civil war, the ''liberatores'' were defea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Münzer
Friedrich Münzer (22 April 1868 – 20 October 1942) was a German classical scholar noted for the development of prosopography, particularly for his demonstrations of how family relationships in ancient Rome connected to political struggles. He died in Theresienstadt concentration camp. Biography He was born at Oppeln, Silesia (now Opole, Poland), into a Jewish merchant family, went to Leipzig University and then in 1887 to Berlin University, where he wrote his thesis ''De Gente Valeria'' under the supervision of Otto Hirschfeld. In 1893 he traveled to Rome, where Georg Wissowa recruited him to write biographical articles for the '' Realencyclopädie der classischen Altertumswissenschaft''. From there he went to Athens and participated in excavations on the Acropolis. He also met Clara Engels there; they were married two years later, on 4 September 1897. Meanwhile, Münzer had been appointed as an unsalaried lecturer at University of Basel in 1896; he and Clara were supported by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetor
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the ''praetura'' (praetorship), are described by the adjective: the ''praetoria potestas'' (praetorian power), the ''praetorium imperium'' (praetorian authority), and the ''praetorium ius'' (praetorian law), the legal precedents established by the ''praetores'' (praetors). ''Praetorium'', as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his '' castra'', the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship. History of the title The status of the ''praetor'' in the early republic is unclear. The traditional account from Livy claims that the praetorship was created by the Sextian-Licinian Rogatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |