|
Tianlong Suspension Bridge
Tianlong (; lit. "heavenly dragon") is a flying dragon in Chinese mythology, a star in Chinese astrology, and a proper name. Word The term ''tianlong'' combines ''tian'' "heaven" and ''long'' "dragon". Since ''tian'' literally means "heaven; the heavens; sky" or figuratively "Heaven; God; gods", ''tianlong'' can denote "heavenly dragon; celestial dragon" or "holy dragon; divine dragon". Tianlong is homophonous with another name in Chinese folklore. Tianlong "Heavenly Deaf" (with the character ''long'' "deaf" combining the "ear radical" and a ''long'' phonetic element) and ''Diya'' "Earthly Dumb" are legendary attendants to Wenchang Wang , the patron deity of literature. Meanings From originally denoting "heavenly dragon", ''Tianlong'' semantically developed meanings as Buddhist "heavenly Nāgas" or "Devas and Nāgas", "centipede", and "proper names" of stars, people, and places. Dragons Among Chinese classic texts, ''tian'' "heaven" and ''long'' "dragon" were first used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon Gods - Project Gutenberg EText 15250
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as winged, horned, and capable of breathing fire. Dragons in eastern cultures are usually depicted as wingless, four-legged, serpentine creatures with above-average intelligence. Commonalities between dragons' traits are often a hybridization of feline, reptilian and avian features. Scholars believe huge extinct or migrating crocodiles bear the closest resemblance, especially when encountered in forested or swampy areas, and are most likely the template of modern Oriental dragon imagery. Etymology The word ''dragon'' entered the English language in the early 13th century from Old French ''dragon'', which in turn comes from la, draconem (nominative ) meaning "huge serpent, dragon", from Ancient Greek , (genitive , ) "serpent, giant s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanyu Da Cidian
The ''Hanyu Da Cidian'' () is the most inclusive available Chinese dictionary. Lexicographically comparable to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', it has diachronic coverage of the Chinese language, and traces usage over three millennia from Chinese classic texts to modern slang. The chief editor Luo Zhufeng (1911–1996), along with a team of over 300 scholars and lexicographers, started the enormous task of compilation in 1979. Publication of the thirteen volumes began with first volume in 1986 and ended with the appendix and index volume in 1994. In 1994, the dictionary also won the National Book Award of China. The ''Hanyu Da Cidian'' includes over 23,000 head Chinese character entries, defines some 370,000 words, and gives 1,500,000 citations. The head entries, which are collated by a novel 200 radical system, are given in traditional Chinese characters while simplified Chinese characters are noted. Definitions and explanations are in simplified, excepting classical quo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpius
Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation that pre-dates the Greeks; it is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. Its old astronomical symbol is (♏︎). Notable features Stars Scorpius contains many bright stars, including Antares (α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; δ Sco (Dschubba, "the forehead"); θ Sco (Sargas, of unknown origin); ν Sco (Jabbah); ξ Sco; π Sco (Fang); σ Sco (Alniyat); and τ Sco (Paikauhale). Marking the tip of the scorpion's curved tail are λ Sco (Shaula) and υ Sco (Lesath), whose names both mean "sting." Given their proximity to one another, λ Sco and υ Sco are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes. The constellation' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Room (Chinese Constellation)
The Room mansion (房宿, pinyin: Fáng Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellation Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" (Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic t ...s. It is one of the eastern mansions of the Azure Dragon. Asterisms {{DEFAULTSORT:Room (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bencao Gangmu
The ''Bencao gangmu'', known in English as the ''Compendium of Materia Medica'' or ''Great Pharmacopoeia'', is an encyclopedic gathering of medicine, natural history, and Chinese herbology compiled and edited by Li Shizhen and published in the late 16th century, during the Ming dynasty. Its first draft was completed in 1578 and printed in Nanjing in 1596. The ''Compendium'' lists the '' materia medica'' of traditional Chinese medicine known at the time, including plants, animals, and minerals that were believed to have medicinal properties. Over the centuries it was reprinted, translated, and cited widely. In the twentieth century was adopted as a basis for Traditional Chinese Medicine. Li compiled his entries not only from hundreds of earlier works in the ''bencao'' medical tradition, but from literary and historical texts. He reasoned that a poem might have better value that a medical work and that a tale of the strange could illustrate a drug's effects. Name The title, tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
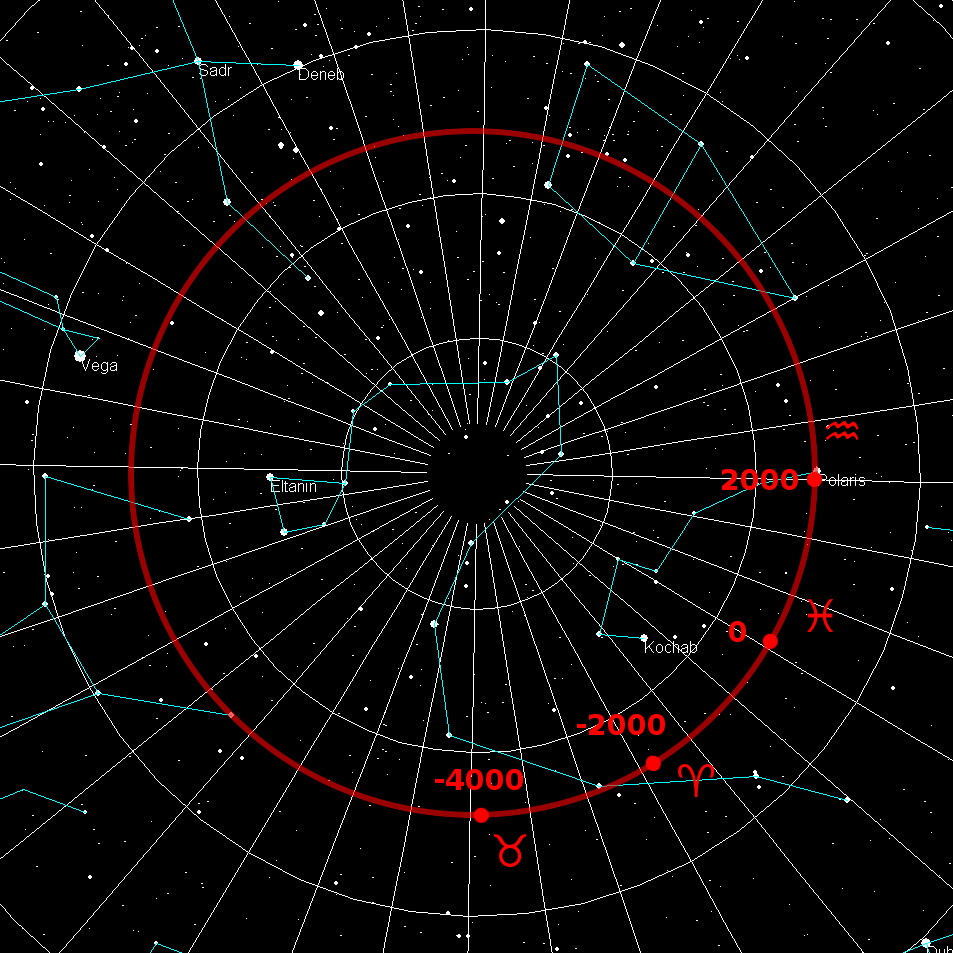
North Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out circles on the celestial sphere, with a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Constellation
Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" (Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic tradition. The Song dynasty (13th-century) Suzhou planisphere shows a total of 283 asterisms, comprising a total of 1,565 individual stars. The asterisms are divided into four groups, the Twenty-Eight Mansions (, ''Èrshíbā Xiù'') along the ecliptic, and the Three Enclosures of the northern sky. The southern sky was added as a fifth group in the late Ming Dynasty based on European star charts, comprising an additional 23 asterisms. The Three Enclosures (, ''Sān Yuán'') include the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which is centered on the north celestial pole and includes those stars which could be seen year-round,Needham, J.Astronomy in Ancient and Medieval China. ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London''. Series A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draco (constellation)
Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. It was one of the 48 Lists of constellations, constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. The north pole of the ecliptic is in Draco. Draco is circumpolar star, circumpolar from northern latitudes. There it is never setting and therefore can be seen all year. Features Stars Thuban (α Draconis) was the northern pole star from 3942 BC, when it moved farther north than Theta Boötis, until 1793 BC. The Egyptian Pyramids were designed to have one side facing north, with an entrance passage geometrically aligned so that Thuban would be visible at night. Due to the effects of Axial precession (astronomy), precession, it would again be the pole star around the year AD 21000. It is a blue-white giant star of magnitude 3.7, 309 light-years from Earth. The traditional name of Alpha Draconis, Thuban, means "head of the serpent". T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panlong (mythology)
Panlong (; lit. "coiled dragon") is an aquatic dragon resembling a ''jiaolong'' 蛟龍 "river dragon; crocodile" in Chinese mythology, an ancient motif in Chinese art, and a proper name. Word The Chinese compound ''panlong'' combines ''pan'' "coiling; curling; curving; bending; winding; twisting" and ''long'' or "dragon". ''Longpan'' "dragon coiling", the reverse of ''panlong'', is a literary metaphor for "person of unrecognized talent" (see the ''Fayan'' below). ''Panlong'' "coiled dragon" can be written or , using ''pan'' 's homophonous variant Chinese character ''pan'' or "tray; plate; dish". Another example of this graphic interchangeability is ''panrao'' or "twine round; surround; fill". Two Classical Chinese ''panlong'' idioms are ''panlongpi'' ("coiling dragon habit") "gambling addiction" (alluding to 5th-century gambler Liu Yi or Liu Panlong of Eastern Jin ) and ''panlong-wohu'' (lit. "coiling dragon crouching tiger") "talented people remaining concealed" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Xiong (author)
Yang Xiong (; 53 BCE–18 CE) was a Chinese philosopher, poet, and politician of the Western Han dynasty known for his philosophical writings and ''fu'' poetry compositions. Life and career Like a number of the other well-known writers of the Han dynasty, Yang was from Shu (modern Sichuan province), specifically the area of Pi (modern Pi County, Sichuan). Yang claimed that his family had moved south from the state of Jin during its civil infighting in the 6th century BCE. As a youth Yang was an admirer and imitator of his elder Shu compatriot Sima Xiangru and the "grand ''fu''" style of the early Han period. His ability and success in ''fu'' composition earned him a summons to the imperial capital at Chang'an to serve as an "Expectant Official", responsible for composing poems and ''fu'' for the emperor.Ho (1986): 912. Yang's position required him to praise the virtue and glory of Emperor Cheng of Han and the grandeur of imperial outings, but he was disturbed by the wast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |