|
Thérèse Raquin
''Thérèse Raquin'' () is an early novel by French writer Émile Zola. It appeared in serial form from August–October 1867 in the magazine ''L'Artiste'', and was published in book form later that year. Although it was Zola's third novel, it was the one that earned him fame and notoriety. The plot, with its focus on adultery and murder, was considered scandalous and described as "putrid literature" in a review in ''Le Figaro''. The novel tells the story of a young woman, Thérèse Raquin, who is coerced by an overbearing aunt into a loveless marriage with her first cousin Camille. He is sickly and egocentric and when the opportunity arises, Thérèse enters into a turbulent, sordid affair with Camille's friend, Laurent. Despite their numerous trysts, Thérèse and Laurent are convinced they can only be truly happy if they are married. To do that, they must kill Camille, and so they carry out the murderous deed. The plan worksthey wed two years after his deathbut they are so h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, ; ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of Naturalism (literature), naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of Naturalism (theatre), theatrical naturalism. He was a major figure in the political liberalization of France and in the exoneration of the falsely accused and convicted army officer Alfred Dreyfus, which is encapsulated in his renowned newspaper opinion headlined ''J'Accuse...!'' Zola was nominated for the first and second Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Prizes in Literature in 1901 and 1902. Early life Zola was born in Paris in 1840 to François Zola (originally Francesco Zolla) and Émilie Aubert. His father was an Italian engineer with some Greeks, Greek ancestry, who was born in Venice in 1795, and engineered the Zola Dam in Aix-en-Provence; his mother was French. The family moved to Aix-en-Provence in the Provence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haberdasher
__NOTOC__ In British English, a haberdasher is a business or person who sells small articles for sewing, dressmaking and knitting, such as buttons, ribbons, and zippers; in the United States, the term refers instead to a men's clothing store that sells suits, shirts, neckties, men's dress shoes, and other items. Sewing supplies and accessories The sewing articles are called ''haberdashery'' in British English. The corresponding term is ''notions'' in American English, where ''haberdashery'' is the name for the shop itself, though it is largely an archaism now. In Britain, haberdashery shops, or haberdashers, were a mainstay of high street retail until recent decades, but are now uncommon, due to the decline in home dressmaking, knitting and other textile skills and hobbies, and the rise of internet shopping. They were very often drapers as well, the term for sellers of cloth. Etymology and usage The word ''haberdasher'' appears in Chaucer's '' Canterbury Tales'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Ulbach
Louis Ulbach (7 March 182216 April 1889) was a French novelist, essayist and journalist. He published seventy-six volumes, wrote three plays, and wrote numerous articles and political or biographical pamphlets. His romantic novels were compared to the works of Émile Zola and Alphonse Daudet. He edited the ''Revue de Paris'' and published ''La Cloche'', which was suppressed in 1869 for its hostility to the Second French Empire. He was imprisoned twice for his publication of ''La Cloche''. He was a leader in the movement for perpetual copyright to authors. In 1877, he was awarded the cross of the Legion of Honour. Personal life Ulbach was born at Troyes in the department of Aube. He was described as a genial, intelligent, witty, and interesting man who was a notable conversationalist. He was a member of Jules Simon's salon with Edmond François Valentin About and other Frenchmen to discuss literary, political, and other current events. He was a popular leader within literary ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Bête Humaine
(English: ''The Beast Within'' or ''The Beast in Man'' or ''The Monomaniac'') is an 1890 novel by Émile Zola. It is the seventeenth book in Zola's '' Les Rougon-Macquart'' series. The story focuses on the lives and violent passions of railway workers who operate the line between Paris and Le Havre in the late 1860s. The novel is a tense psychological thriller and has been adapted multiple times for radio, television, and film. Characters * Jacques Lantier: an engine driver who is the family link to the ''Les Rougon-Macquart'' series. He is the son of Gervaise Macquart ('' L'Assommoir''), brother of Étienne Lantier ('' Germinal'') and Claude Lantier ('' L'Œuvre''), and half-brother of the eponymous Nana. * Roubaud: deputy stationmaster at Le Havre * Séverine: Roubaud's wife * Judge Grandmorin: a prominent wealthy manformer director of the railway company and judge in the French judicial systemand a notorious womanizer * Phasie: Lantier's sickly aunt who lives in an isolated h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
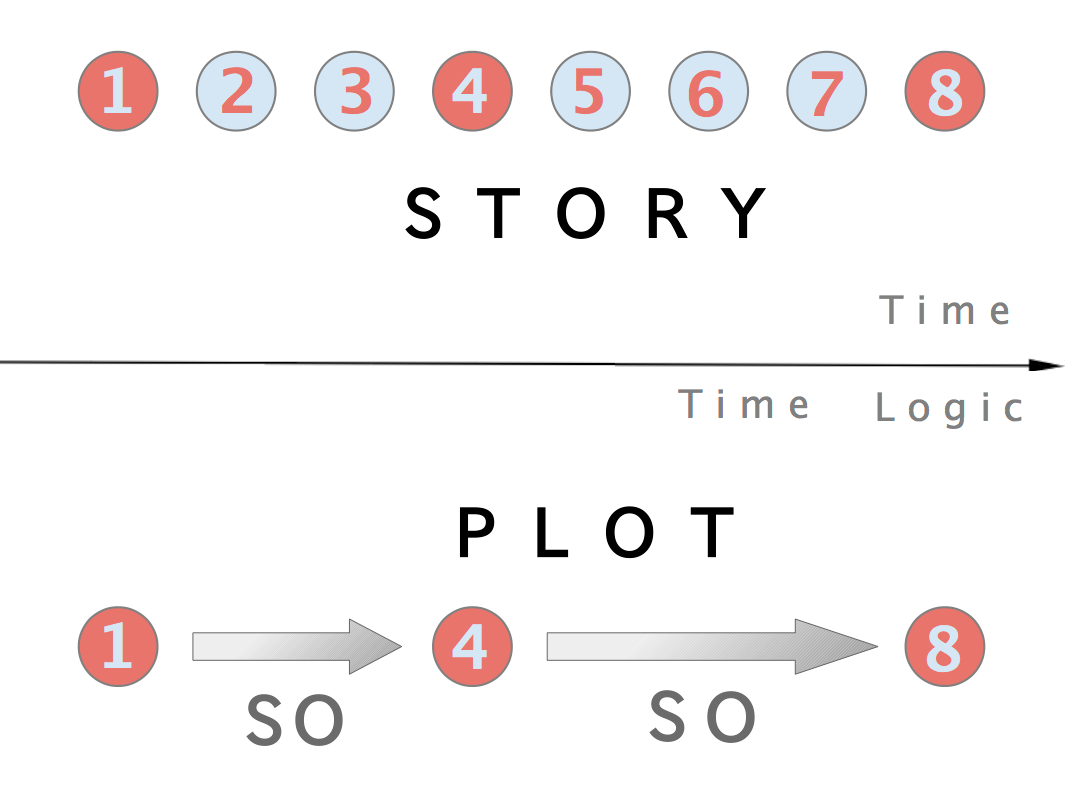
Plot (narrative)
In a literary work, film, or other narrative, the plot is the mapping of events in which each one (except the final) affects at least one other through the principle of Causality, cause-and-effect. The causal events of a plot can be thought of as a selective collection of events from a narrative, all linked by the connector "and so". Simple plots, such as in a traditional ballad, can be linearly sequenced, but plots can form complex interwoven structures, with each part sometimes referred to as a subplot. Plot is similar in meaning to the term ''storyline''. In the narrative sense, the term highlights important points which have consequences within the story, according to American science fiction writer Ansen Dibell. The Premise (narrative), premise sets up the plot, the Character (arts), characters take part in events, while the Setting (narrative), setting is not only part of, but also influences, the final story. An can convolute the plot based on a misunderstanding. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melancholia
Melancholia or melancholy (from ',Burton, Bk. I, p. 147 meaning black bile) is a concept found throughout ancient, medieval, and premodern medicine in Europe that describes a condition characterized by markedly depressed mood, bodily complaints, and sometimes hallucinations and delusions. Melancholy was regarded as one of the four temperaments matching the four humours. Until the 18th century, doctors and other scholars classified melancholic conditions as such by their perceived common causean excess of a notional fluid known as "black bile", which was commonly linked to the spleen. Hippocrates and other ancient physicians described melancholia as a distinct disease with mental and physical symptoms, including persistent fears and despondencies, poor appetite, abulia, sleeplessness, irritability, and agitation. Later, fixed delusions were added by Galen and other physicians to the list of symptoms. In the Middle Ages, the understanding of melancholia shifted to a religi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
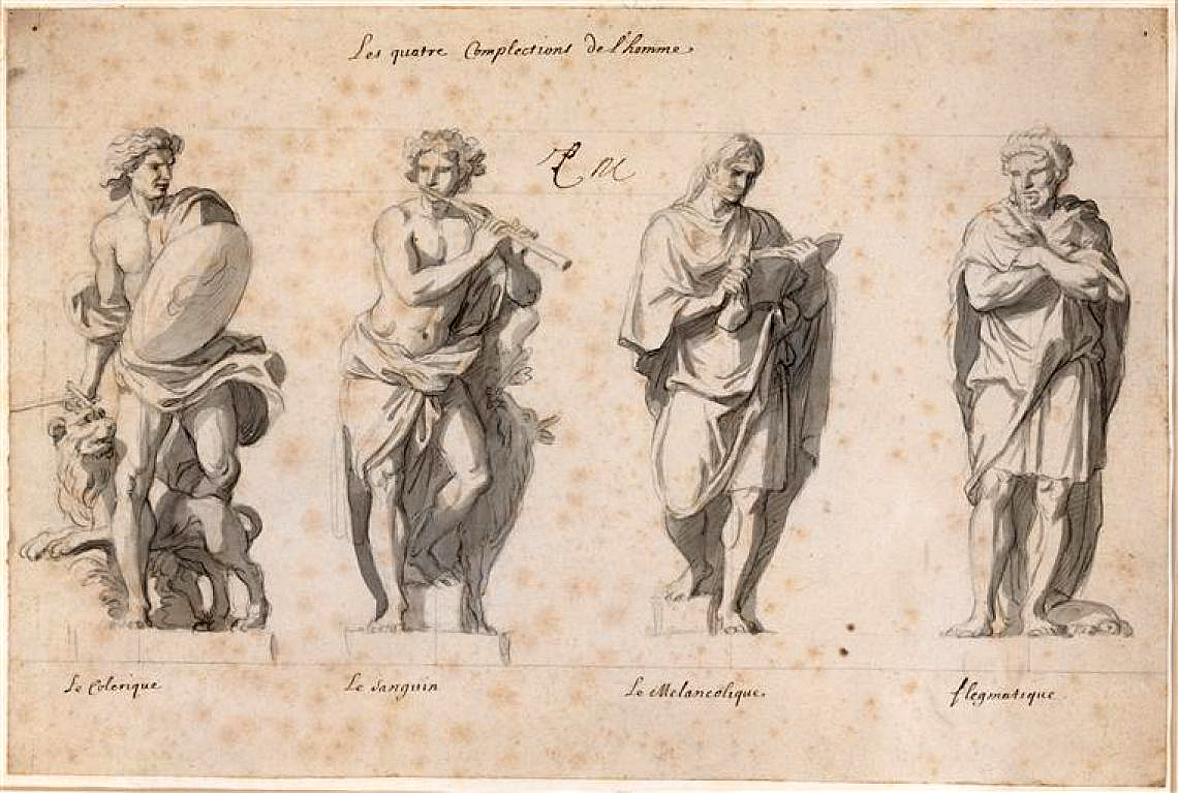
Four Temperaments
The four temperament theory is a proto-psychological theory which suggests that there are four fundamental personality types: sanguine, choleric, melancholic, and phlegmatic. Most formulations include the possibility of mixtures among the types where an individual's personality types overlap and they share two or more temperaments. Greek physician Hippocrates (c. 460 – c. 370 BC) described the four temperaments as part of the ancient medical concept of humourism, that four bodily fluids affect human personality traits and behaviours. Modern medical science does not define a fixed relationship between internal secretions and personality, although some psychological personality type systems use categories similar to the Greek temperaments. The four temperament theory was abandoned after the 1850s. History Temperament theory has its roots in the ancient theory of humourism. It may have originated in Mesopotamia, but it was Greek physician Hippocrates (460–370 BC) (and late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all medical researchers of Ancient history, antiquity, Galen influenced the development of various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and neurology, as well as philosophy and logic. The son of Aelius Nicon, a wealthy Greek architect with scholarly interests, Galen received a comprehensive education that prepared him for a successful career as a physician and philosopher. Born in the ancient city of Pergamon (present-day Bergama, Turkey), Galen traveled extensively, exposing himself to a wide variety of medical theories and discoveries before settling in Ancient Rome, Rome, where he served prominent members of Roman society and eventually was given the position of perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Temperaments
The four temperament theory is a proto-psychological theory which suggests that there are four fundamental personality types: sanguine, choleric, melancholic, and phlegmatic. Most formulations include the possibility of mixtures among the types where an individual's personality types overlap and they share two or more temperaments. Greek physician Hippocrates (c. 460 – c. 370 BC) described the four temperaments as part of the ancient medical concept of humourism, that four bodily fluids affect human personality traits and behaviours. Modern medical science does not define a fixed relationship between internal secretions and personality, although some psychological personality type systems use categories similar to the Greek temperaments. The four temperament theory was abandoned after the 1850s. History Temperament theory has its roots in the ancient theory of humourism. It may have originated in Mesopotamia, but it was Greek physician Hippocrates (460–370 BC) (and late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passage Du Pont-Neuf Par Castelli (Thérèse Raquin, 1883)
Passage, The Passage or Le Passage may refer to: Arts and entertainment Films * ''Passage'' (2008 film), a documentary about Arctic explorers * ''Passage'' (2009 film), a short movie about three sisters * Passage (2020 film), a Canadian documentary film, * ''The Passage'' (1979 film), starring James Mason and Malcolm McDowell * ''The Passage'' (1986 film), a French supernatural thriller film starring Alain Delon * ''The Passage'' (2007 film), by Mark Heller * ''The Passage'' (2011 film), by Roberto Minervini * ''The Passage'' (2018 film), a short film directed by Kitao Sakurai Literature * ''The Passage'' (Palmer novel), a 1930 novel by Vance Palmer * ''Le Passage'', a 1954 French novel by Jean Reverzy * ''Passage'' (Willis novel), a 2001 science fiction novel by Connie Willis * ''Passage'' (Morley novel), a 2007 novel by John David Morley * ''Passage'' (Bujold novel), a 2008 novel by Lois McMaster Bujold *''Le Passage'', a 2009 novel by former French President Valéry G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orléans
Orléans (,"Orleans" (US) and ; ) is a city in north-central France, about 120 kilometres (74 miles) southwest of Paris. It is the prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Loiret and of the Regions of France, region of Centre-Val de Loire. Orléans is located on the river Loire nestled in the heart of the Loire Valley, classified as a Loire Valley, World Heritage Site, where the river curves south towards the Massif Central. In 2020, the city had 117,026 inhabitants within its municipal boundaries. Orléans is the center of Orléans Métropole that has a population of 290,346. The larger Functional area (France), metropolitan area has a population of 454,208, the 20th largest in France. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protagonist
A protagonist () is the main character of a story. The protagonist makes key decisions that affect the plot, primarily influencing the story and propelling it forward, and is often the character who faces the most significant obstacles. If a story contains a subplot, or is a narrative made up of several stories, then each subplot may have its own protagonist. The protagonist is the character whose fate is most closely followed by the reader or audience, and who is opposed by the antagonist. The antagonist provides obstacles and complications and creates conflicts that test the protagonist, revealing the strengths and weaknesses of the protagonist's character, and having the protagonist develop as a result. A particularly noble, virtuous, or accomplished protagonist is commonly called a ''hero,'' though the terms are not synonyms. Etymology The term ''protagonist'' comes , combined of (, 'first') and (, 'actor, competitor'), which stems from (, 'contest') via (, 'I conten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |