|
Thyrotomy
:''Thyrotomy may also refer to the cutting or biopsy the thyroid gland.'' Thyrotomy (also called thyroidotomy, median laryngotomy, laryngofissure or thyrofissure) is an incision of the larynx through the thyroid cartilage. See also * Laryngotomy *Cricothyrotomy *Tracheotomy * List of surgeries by type References * ''Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary ''Dorland's'' is the brand name of a family of medical reference works (including dictionaries, spellers and word books, and spell-check software) in various media spanning printed books, CD-ROMs, and online content. The flagship products are ''Do ...'' Larynx surgery Otorhinolaryngology {{Surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy (also called cricothyroidotomy) is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, or massive facial trauma. Cricothyrotomy is nearly always performed as a last resort in cases where other means of tracheal intubation are impossible or impractical. Compared with tracheotomy, cricothyrotomy is quicker and easier to perform, does not require manipulation of the cervical spine, and is associated with fewer complications. However, while cricothyrotomy may be life-saving in extreme circumstances, this technique is only intended to be a temporizing measure until a definitive airway can be established. Indications A cricothyrotomy is often used as an airway of last resort given the numerous other airway options available including standard tracheal intubation and rapid sequence induction which are the common means of establishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngotomy
Surgical airway management (bronchotomy or laryngotomy) is the medical procedure ensuring an open airway between a patient’s lungs and the outside world. Surgical methods for airway management rely on making a surgical incision below the glottis in order to achieve direct access to the lower respiratory tract, bypassing the upper respiratory tract. Surgical airway management is often performed as a last resort in cases where orotracheal and nasotracheal intubation are impossible or contraindicated. Surgical airway management is also used when a person will need a mechanical ventilator for a longer period. The surgical creation of a permanent opening in the larynx is referred to as laryngostomy. Surgical airway management is a primary consideration in anaesthesia, emergency medicine and intensive care medicine. Surgical methods for airway management include cricothyrotomy and tracheostomy History Asclepiades of Bithynia is credited with being the first person who proposed broncho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube or tracheostomy tube to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek words: the root ''tom-'' (from Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth," refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening, and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Surgeries By Type
Many surgical procedure names can be broken into parts to indicate the meaning. For example, in gastrectomy, "ectomy" is a suffix meaning the removal of a part of the body. "Gastro-" means stomach. Thus, ''gastrectomy'' refers to the surgical removal of the stomach (or sections thereof). "Otomy" means cutting into a part of the body; a ''gastrotomy'' would be cutting into, but not necessarily removing, the stomach. And also "pharyngo" means pharynx, "laryngo" means larynx, "esophag" means esophagus. Thus, "pharyngolaryngoesophagectomy" refers to the surgical removal of the three. The field of minimally invasive surgery has spawned another set of words, such as ''arthroscopic'' or ''laparoscopic'' surgery. These take the same form as above; an arthroscope is a device which allows the inside of the joint to be seen. List of common surgery terms Prefixes * ''mono-'' : one, from the Greek μόνος, ''monos'', "only, single" * ''angio-'' : related to a blood vessel, from the Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
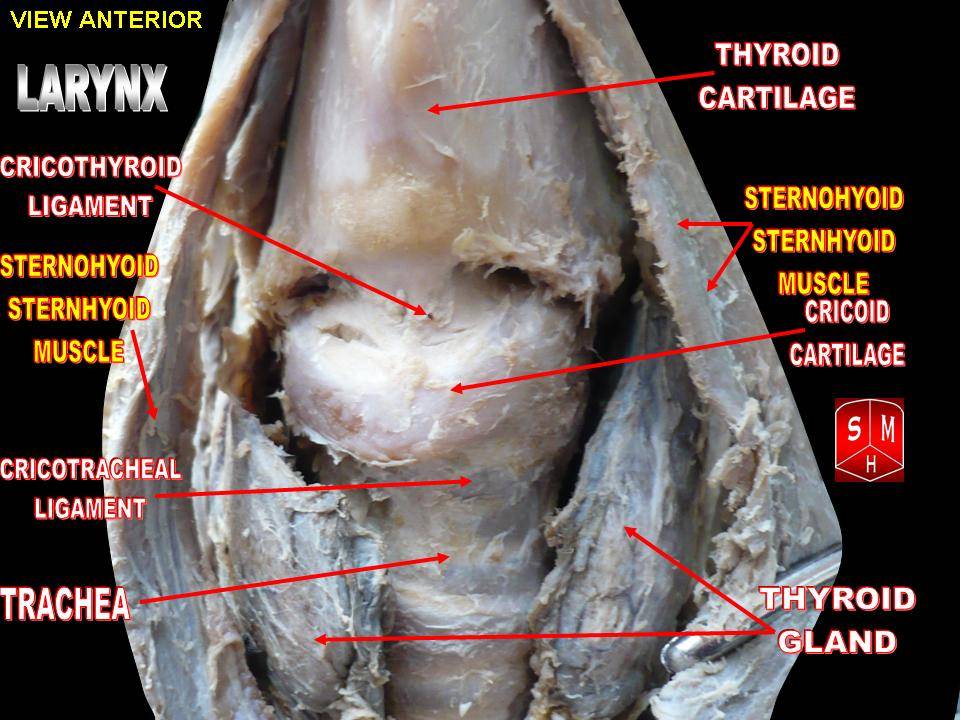
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobe (anatomy), lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of Connective tissue, tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical Thyroid follicular cell#Location, thyroid follicle, lined with thyroid follicular cell, follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a follicular lumen, lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormonestriiodothyronine, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroid hormone, thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the basal metabolic rate, metabolic rate and protein biosynthesis, protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Cartilage
The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the ''laryngeal skeleton'', the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx (only the cricoid cartilage encircles it). Structure The thyroid cartilage is a hyaline cartilage structure that sits in front of the larynx and above the thyroid gland. The cartilage is composed of two halves, which meet in the middle at a peak called the laryngeal prominence, also called the Adam's apple. In the midline above the prominence is the superior thyroid notch. A counterpart notch at the bottom of the cartilage is called the inferior thyroid notch. The two halves of the cartilage that make out the outer surfaces extend obliquely to cover the sides of the trachea. The posterior edge of each half articulates with the cricoid cartilage inferiorly at a joint called the cricothyroid joint. The most posterior part of the cartilage also has two projection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary
''Dorland's'' is the brand name of a family of medical reference works (including dictionaries, spellers and word books, and spell-check software) in various media spanning printed books, CD-ROMs, and online content. The flagship products are ''Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary'' (currently in its 33rd edition) and ''Dorland's Pocket Medical Dictionary'' (currently in its 30th edition). The principal dictionary was first published in 1890 as the ''American Illustrated Medical Dictionary'', including 770 pages. The pocket edition, called the ''American Pocket Medical Dictionary'', was first published in 1898, consisting of just over 500 pages. With the death of the editor William Alexander Newman Dorland, AM, MD in 1956, the dictionaries were retitled to incorporate his name, which was how they had generally come to be known. The illustrated dictionary had grown to 2144 pages for the 33rd edition. The dictionaries were historically published by Saunders. List of products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx Surgery
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |