|
Thorsellia Kandunguensis
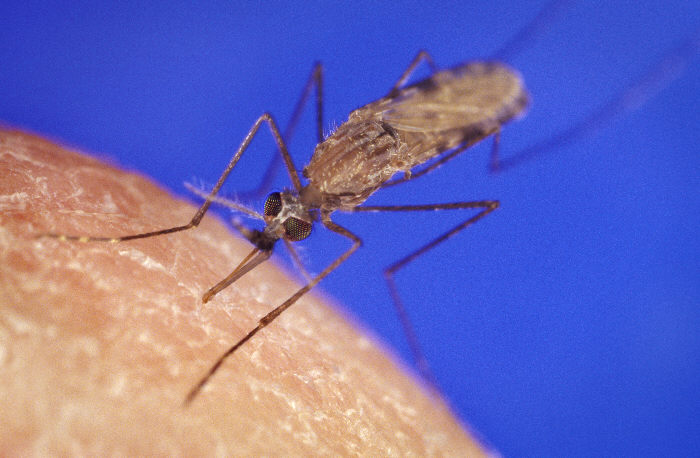
Thorselliaceae is a family of bacteria belonging to the class Gammaproteobacteria and it was first described in February 2015. It is not assigned to an order. The family consists of four species in two genera. The bacteria are Gram-negative and rod shaped, approximately 1 μm wide and 2 μm long. They are facultative anaerobes and motile. Thorselliaceae bacteria have been found around the world associated with vector mosquitoes, mainly with vectors of malaria. The first described species was ''Thorsellia anophelis''. It was isolated from the midgut of the malaria mosquito '' Anopheles arabiensis'' from Kenya. This new bacterium was given its name after the Swedish researcher Walborg Thorsell who worked with mosquitoes and insecticides against mosquitoes for many years. ''Thorsellia'' bacteria have now been found in mosquito species that are the major vectors of malaria in Africa, Asia and South America. The bacteria have also been found in the waters where the malaria m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorsellia Anophelis
Thorselliaceae is a family of bacteria belonging to the class Gammaproteobacteria and it was first described in February 2015. It is not assigned to an order. The family consists of four species in two genera. The bacteria are Gram-negative and rod shaped, approximately 1 μm wide and 2 μm long. They are facultative anaerobes and motile. Thorselliaceae bacteria have been found around the world associated with vector mosquitoes, mainly with vectors of malaria. The first described species was ''Thorsellia anophelis''. It was isolated from the midgut of the malaria mosquito '' Anopheles arabiensis'' from Kenya. This new bacterium was given its name after the Swedish researcher Walborg Thorsell who worked with mosquitoes and insecticides against mosquitoes for many years. ''Thorsellia'' bacteria have now been found in mosquito species that are the major vectors of malaria in Africa, Asia and South America. The bacteria have also been found in the waters where the malaria m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walborg Thorsell
Walborg Susanna Thorsell (12 February 1919 – January 2016) was a Swedish scientist who performed research mainly on mosquitoes and mosquito repellents. Education Thorsell defended her thesis for her doctorate in veterinary medicine at the Swedish Veterinarian Institute in 1967, and was a docent in experimental parasitology. Research Thorsell started her studies on mosquitoes while working at the Swedish National Defence Research Institute (FOA). At that time claims circulated, from both the United States and the Soviet Union, that the other part was conducting experiments with malaria mosquitos in relations to biological warfare. The Swedish military therefore felt it necessary to develop a mosquito repellent, especially for malaria mosquitoes, to be used by Swedish soldiers. The existing repellents were either not efficient enough or had unwanted side effects, so Thorsell and her group of researchers at FOA began looking for a better agent. The substance ''diethylami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria Parasites
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue (often the liver) before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect (mosquitoes in majority cases), continuing the life cycle. ''Plasmodium'' is a member of the phylum Apicomplexa, a large group of parasitic eukaryotes. Within Apicomplexa, ''Plasmodium'' is in the order Haemosporida and family Plasmodiidae. Over 200 species of ''Plasmodium'' have been described, many of which have been subdivided into 14 subgenera based on parasite morphology and host range. Evolutionary relationships among different ''Plasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory. Transformation is one of three processes that lead to horizontal gene transfer, in which exogenous genetic material passes from one bacterium to another, the other two being conjugation (transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of foreign DNA by a bacteriophage virus into the host bacterium). In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and uptake is completely dependent on the recipient bacterium. As of 2014 about 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
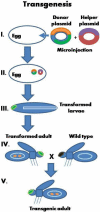
Paratransgenesis
Paratransgenesis is a technique that attempts to eliminate a pathogen from vector populations through transgenesis of a symbiont of the vector. The goal of this technique is to control vector-borne diseases. The first step is to identify proteins that prevent the vector species from transmitting the pathogen. The genes coding for these proteins are then introduced into the symbiont, so that they can be expressed in the vector. The final step in the strategy is to introduce these transgenic symbionts into vector populations in the wild. One use of this technique is to prevent mortality for humans from insect-borne diseases. Preventive methods and current controls against vector-borne diseases depend on insecticides, even though some mosquito breeds may be resistant to them. There are other ways to fully eliminate them. “Paratransgenesis focuses on utilizing genetically modified insect symbionts to express molecules within the vector that are deleterious to pathogens they trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anopheles Darlingi
''Anopheles darlingi'', the American malaria mosquito, is a species of mosquito in the family Culicidae. ''A. darlingi'' is one of the major species of mosquito known to be responsible for malaria in the Amazonian regions. It has a wide range of geographic distribution that stretches from Mexico and Argentina but it has also been found to populate in areas affected by deforestation and environment changes due to humans. Breeding The breeding patterns of ''A. darlingi'' are affected heavily by the precipitation seen in their environment. Due to the fact that mosquitoes rely on the surfaces of stagnant water or areas with regular flooding as breeding grounds for their eggs and larvae, the annual density of the ''A. darlingi'' population is dependent upon the availability of larval habitats. During the wet season, riverine areas are often abundant with mosquitoes and densities are higher in these after the peak of rainfall. Oppositely, in drier inland areas that are usually further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maureen Coetzee
Maureen Coetzee is a medical entomologist, specialising in African malaria vector mosquitoes for over 40 years. She is currently a Distinguished Professor in the Wits Research Institute for Malaria, School of Pathology at the University of the Witwatersrand. She is a member of the Academy of Science of South Africa. She is a consultant in the World Health Organization 's Global Malaria Programme. She obtained her Doctorate from the University of the Witwatersrand. A subgenus of the Aedes mosquito, ''Coetzeemyia'', was named after her. Also a genus of bacteria strongly associated with malaria mosquitoes, '' Coetzeea'', was named after her. Professor Coetzee has published over 190 peer-reviewed scholarly articles. Awards and honors * The Kwame Nkrumah Science Award, (2011) References External links Maureen Coetzeeon ResearchGate ResearchGate is a European commercial social networking site for scientists and researchers to share papers, ask and answer questions, and find coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, trouble speaking, memory problems, and problems with hearing. Causes of encephalitis include viruses such as herpes simplex virus and rabies virus as well as bacteria, fungi, or parasites. Other causes include autoimmune diseases and certain medications. In many cases the cause remains unknown. Risk factors include a weak immune system. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and supported by blood tests, medical imaging, and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. Certain types are preventable with vaccines. Treatment may include antiviral medications (such as acyclovir), anticonvulsants, and corticosteroids. Treatment generally takes place in hospital. Some people require artificial respiration. Once the immediate problem is under co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Nile Virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes West Nile fever. It is a member of the family ''Flaviviridae'', from the genus ''Flavivirus'', which also contains the Zika virus, dengue virus, and yellow fever virus. The virus is primarily transmitted by mosquitoes, mostly species of ''Culex''. The primary hosts of WNV are birds, so that the virus remains within a "bird–mosquito–bird" transmission cycle. The virus is genetically related to the Japanese encephalitis family of viruses. Humans and horses both exhibit disease symptoms from the virus, and symptoms rarely occur in other animals. Identification of the human disease was first made in 1937 in Uganda and in the latter half of the 20th century spread to many other parts of the world. Structure Like most other flaviviruses, WNV is an enveloped virus with icosahedral symmetry. Electron microscope studies reveal a 45–50 nm virion covered with a relatively smooth protein shell; this structure i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culex
''Culex'' is a genus of mosquitoes, several species of which serve as vectors of one or more important diseases of birds, humans, and other animals. The diseases they vector include arbovirus infections such as West Nile virus, Japanese encephalitis, or St. Louis encephalitis, but also filariasis and avian malaria. They occur worldwide except for the extreme northern parts of the temperate zone, and are the most common form of mosquito encountered in some major U.S. cities, such as Los Angeles. Etymology In naming this genus, Carl Linnaeus appropriated the nonspecific Latin term for a midge or gnat: '. Description Depending on the species, the adult ''Culex'' mosquito may measure from . The adult morphology is typical of flies in the suborder Nematocera with the head, thorax, and abdomen clearly defined and the two forewings held horizontally over the abdomen when at rest. As in all Diptera capable of flight, the second pair of wings is reduced and modified into tiny, incon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anopheles
''Anopheles'' () is a genus of mosquito first described and named by J. W. Meigen in 1818. About 460 species are recognised; while over 100 can transmit human malaria, only 30–40 commonly transmit parasites of the genus ''Plasmodium'', which cause malaria in humans in endemic areas. '' Anopheles gambiae'' is one of the best known, because of its predominant role in the transmission of the most dangerous malaria parasite species (to humans) – '' Plasmodium falciparum''. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word 'useless', derived from , 'not', 'un-' and 'profit'. Mosquitoes in other genera (''Aedes'', ''Culex'', '' Culiseta'', '' Haemagogus'', and ''Ochlerotatus'') can also serve as vectors of disease agents, but not human malaria. Evolution The ancestors of ''Drosophila'' and the mosquitoes diverged . The culicine and ''Anopheles'' clades of mosquitoes diverged between and . The Old and New World ''Anopheles'' species subsequently diverged between and . '' Anophel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |