|
Thorp T211
The T-211 is a light aircraft designed in the US by John Thorp in 1945. It is a low-wing monoplane of conventional layout with fixed tricycle undercarriage and a sliding canopy. John Thorp developed the Sky Scooter with lessons learned from developing the Lockheed Little Dipper project in 1944. It bears some family resemblance to the Piper Cherokee, a design that Thorp later contributed to significantly. Development Thorp constructed eight prototypes, and had the design certified by the FAA, but was unable to find a foothold in the Cessna-dominated post-war US market. The original prototypes were powered by a 65 hp Lycoming engine. Novel features of the Sky Skooter include an all movable horizontal stabilizer and externally ribbed wings and tailplane. The wings were corrugated to impart stiffness, each wing needing only three internal ribs. This feature simplified construction, reduced the number of rivits (and weight), and helped control the spanwise flow of air over the wing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homebuilt
Homebuilt machines are machines built outside of specialised workshops or factories. This can include different things such as kit cars or homebuilt computers, but normally it pertains to homebuilt aircraft, also known as amateur-built aircraft or kit planes. Homebuilt aircraft or kit cars are constructed by amateurs. Homebuilt computers have been built at home for a long time, starting with the Victorian era pioneer Charles Babbage in the 1820s. A century later, Konrad Zuse built his own machine when electromechanical relay technology was widely available. The hobby took off with the early development of microprocessors and, since then, many enthusiasts have constructed their own computers. A homebuilt vehicle is a wider concept than a kit car. A homebuilt vehicle is a motor vehicle (car, truck or motorcycle) built by an individual instead of a manufacturer. These machines may be constructed "from scratch", from plans, or from assembly kits. Outside of the United States (for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AD Aerospace
AD Aerospace are involved in Aircraft Video Surveillance and form part of the Mythra Group of companies. Headquartered in Hazel Grove, Cheshire, UK at purpose-built premises, making Flight Deck Entry/Cockpit Door Surveillance Systems (FDEVSS/CDSS), Cabin Surveillance Systems and Cargo Surveillance Systems, as well as Ground Manoeuvring and In Flight Entertainment (IFE) systems utilising external cameras. External Camera systems have proved popular with Airbus Helicopters (formerly Eurocopter) and was chosen for the H175/EC175 helicopter. AD Aerospace also offer a VIP Cabin Surveillance Solution which is an option for 1st Class pods or Business Class cabins comprising a HD-SDI covert camera in the passenger cabin and monitor at the cabin attendant's seat. AD Aerospace achieved Boeing approved supplier status as early as 2001 with an order to fit a video smoke verification system to the entire Swiss Air fleet. This was carried out in response to the Peggy's Cove disaster a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorp T-18
The Thorp T-18 is an American, two-place, all-metal, plans-built, homebuilt aircraft designed in 1963 by John Thorp.Bayerl, Robby; Martin Berkemeier; et al: ''World Directory of Leisure Aviation 2011–12'', page 98. WDLA UK, Lancaster UK, 2011. Tacke, Willi; Marino Boric; et al: ''World Directory of Light Aviation 2015–16'', page 105. Flying Pages Europe SARL, 2015. The aircraft was originally designed as an open cockpit aircraft, powered by a military surplus Lycoming O-290G ground power unit engine, but evolved into a fully bubble canopied aircraft powered by engines of up to . Design and development The T-18 was designed to be easily constructed from sheets of aluminum, and use the modified Lycoming O-290G powerplant. It was originally designed with an open cockpit and with the cylinder heads protruding through the engine cowling in the interest of simplicity. Even as originally designed, the cruising speed was quite high. The design showed great potential for high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McCauley Propeller Systems
McCauley Propeller Systems is an American aircraft propeller manufacturer, founded in Dayton, Ohio in 1938 by Ernest G. McCauley.Artifact note"McCauley Industrial Corp. Propeller, fixed-pitch, two-blade, metal,"NASM inventory number A19580112000, ''National Air and Space Museum'' (NASM), retrieved March 31, 2021 At its peak, it was reportedly the world's largest aircraft propeller manufacturer,Sator, Darwin"7 Key officials to retire early at McCauley,"December 10, 1982 , ''Dayton Daily News'' of Dayton, Ohio, archived at Newspapers.com, retrieved March 31, 2021 or at least the largest manufacturer of general aviation propellers."Dussault, Deinzer: McCauley Names 2 to Top Posts," March 21, 1967, '' |
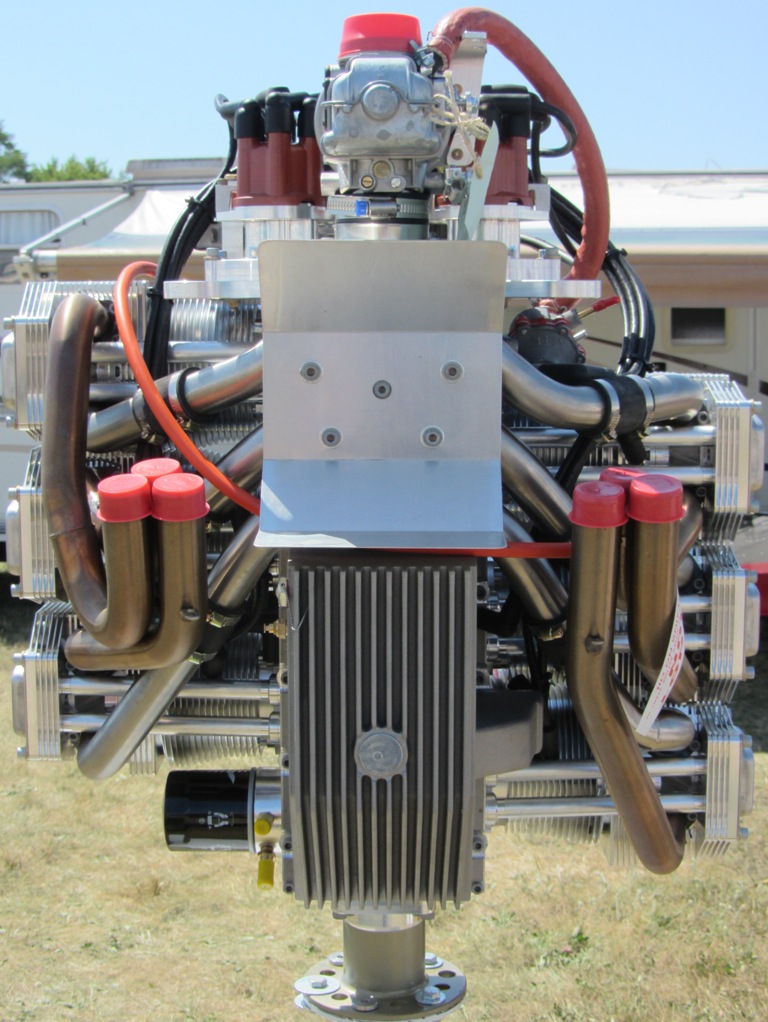
Flat Four
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine, is a four-cylinder piston engine with two banks of cylinders lying on opposite sides of a common crankshaft. The most common type of flat-four engine is the boxer-four engine, each pair of opposed pistons moves inwards and outwards at the same time. A boxer-four engine has perfect primary and secondary balance, however, the two cylinder heads means the design is more expensive to produce than an inline-four engine. Boxer-four engines have been used in cars since 1897, especially by Volkswagen and Subaru. They have also occasionally been used in motorcycles and frequently in aircraft. Cessna and Piper use flat four engines from Lycoming and Continental in the most common civil aircraft in the world - the Cessna 172, and Piper Cherokee, while many ultralight and LSA planes use versions of the Rotax 912. Design Most flat-four engines are designed so that each pair of opposing pistons moves inwards and outw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The two cities and the surrounding towns form one of the United Kingdom's most populous conurbations, the Greater Manchester Built-up Area, which has a population of 2.87 million. The history of Manchester began with the civilian settlement associated with the Roman fort ('' castra'') of ''Mamucium'' or ''Mancunium'', established in about AD 79 on a sandstone bluff near the confluence of the rivers Medlock and Irwell. Historically part of Lancashire, areas of Cheshire south of the River Mersey were incorporated into Manchester in the 20th century, including Wythenshawe in 1931. Throughout the Middle Ages Manchester remained a manorial township, but began to expand "at an astonishing rate" around the turn of the 19th century. Manchest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kit Aircraft
Homebuilt aircraft, also known as amateur-built aircraft or kit planes, are constructed by persons for whom this is not a professional activity. These aircraft may be constructed from "scratch", from plans, or from assembly kits.Armstrong, Kenneth: ''Choosing Your Homebuilt - the one you will finish and fly! Second Edition'', pp. 39–52. Butterfield Press, 1993. Peter M Bowers: ''Guide to Homebuilts - Ninth Edition''. TAB Books, Blue Ridge Summit PA, 1984. Overview In the United States, Brazil, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa, homebuilt aircraft may be licensed Experimental aircraft, Experimental under Federal Aviation Administration, FAA or similar local regulations. With some limitations, the builder(s) of the aircraft must have done it for their own education and recreation rather than for profit. In the U.S., the primary builder can also apply for a repairman's certificate for that airframe. The repairman's certificate allows the holder to perform and sign off on m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Flight Rules
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR). The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) ''Instrument Flying Handbook'' defines IFR as: "Rules and regulations established by the FAA to govern flight under conditions in which flight by outside visual reference is not safe. IFR flight depends upon flying by reference to instruments in the flight deck, and navigation is accomplished by reference to electronic signals." It is also a term used by pilots and controllers to indicate the type of flight plan an aircraft is flying, such as an IFR or VFR flight plan. Basic information Comparison to visual flight rules It is possible and fairly straightforward, in relatively clear weather conditions, to fly an aircraft solely by reference to outside visual cues, such as the horizon to maintain orientation, nearby buildings and terrain features for n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Flight Rules
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e. in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft. If the weather is less than VMC, pilots are required to use instrument flight rules, and operation of the aircraft will be primarily through referencing the instruments rather than visual reference. In a control zone, a VFR flight may obtain a clearance from air traffic control to operate as Special VFR. Requirements VFR require a pilot to be able to see outside the cockpit, to control the aircraft's altitude, navigate, and avoid obstacles and other aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental O-200
The Continental C90 and O-200 are a family of air-cooled, horizontally opposed, four-cylinder, direct-drive aircraft engines of 201 in³ (3.29 L) displacement, producing between 90 and 100 horsepower (67 and 75 kW).''Federal Aviation AdministrationType certificate data sheet no. E-252'' Revision 34. (27 June 2013) Built by Continental Motors these engines are used in many light aircraft designs of the United States, including the early Piper PA-18 Super Cub,''Aircraft specification no. 1A2.'' Revision 37. (Sep. 4, 1996.) Department of Transportation. Federal Aviation Administration. the Champion 7EC,''Aircraft specification no. A-759.'' Revision 67. (Jun. 3, 2005.) Department of Transportation. Federal Aviation Administration. the Alon Aircoupe,''Type certificate date sheet no. A-787.'' Revision 33. (Jul. 14, 2005.) Department of Transportation. Federal Aviation Administration. and the Cessna 150.''Type certificate data sheet no. 3A19.'' Revision 44. (Mar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Certificate
A type certificate signifies the airworthiness of a particular category of aircraft, according to its manufacturing design (''type design''). It confirms that the aircraft of a new type intended for serial production, is in compliance with applicable airworthiness requirements established by the national air law. For up to three seats, primary category aircraft, certification costs around US$1m, US$25m for a general aviation aircraft and hundreds of millions of dollars for a commercial aircraft; certification delays can cost millions of dollars and can decide a program's profitability. Authority A type certificate (TC) is issued to signify the airworthiness of the approved design or "type" of an aircraft to be manufactured. The TC is issued by a regulatory authority, and once issued, the design cannot be changed unless at least part of the process for certification is repeated to cover the changes. The TC reflects a determination made by a regulatory authority that the type desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabiru 3300
The Jabiru 3300 is a lightweight four-stroke, horizontally opposed "flat-six" air-cooled aircraft engine produced by Jabiru Aircraft. The engines are direct drive and fitted with alternators, silencers, vacuum pump drives and dual ignition systems as standard. The engine is used to power homebuilt and ultralight aircraft. History Jabiru Aircraft began as a builder of small two-seater aircraft in Bundaberg, Australia. It turned to producing its own engines when supplies of the Italian-sourced engines previously used dried up. Jabiru engines are designed to be manufactured in small batch quantities, so the firm uses CNC machines to mill major engine parts such as cylinder blocks and heads, rather than using cast items. The 3300 is a modular development of Jabiru's flat-four 2200 engine. In November 2014, the Australian Civil Aviation Safety Authority proposed restricting all Jabiru-powered aircraft to day-visual flight rules only, without passengers or solo students and within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |