|
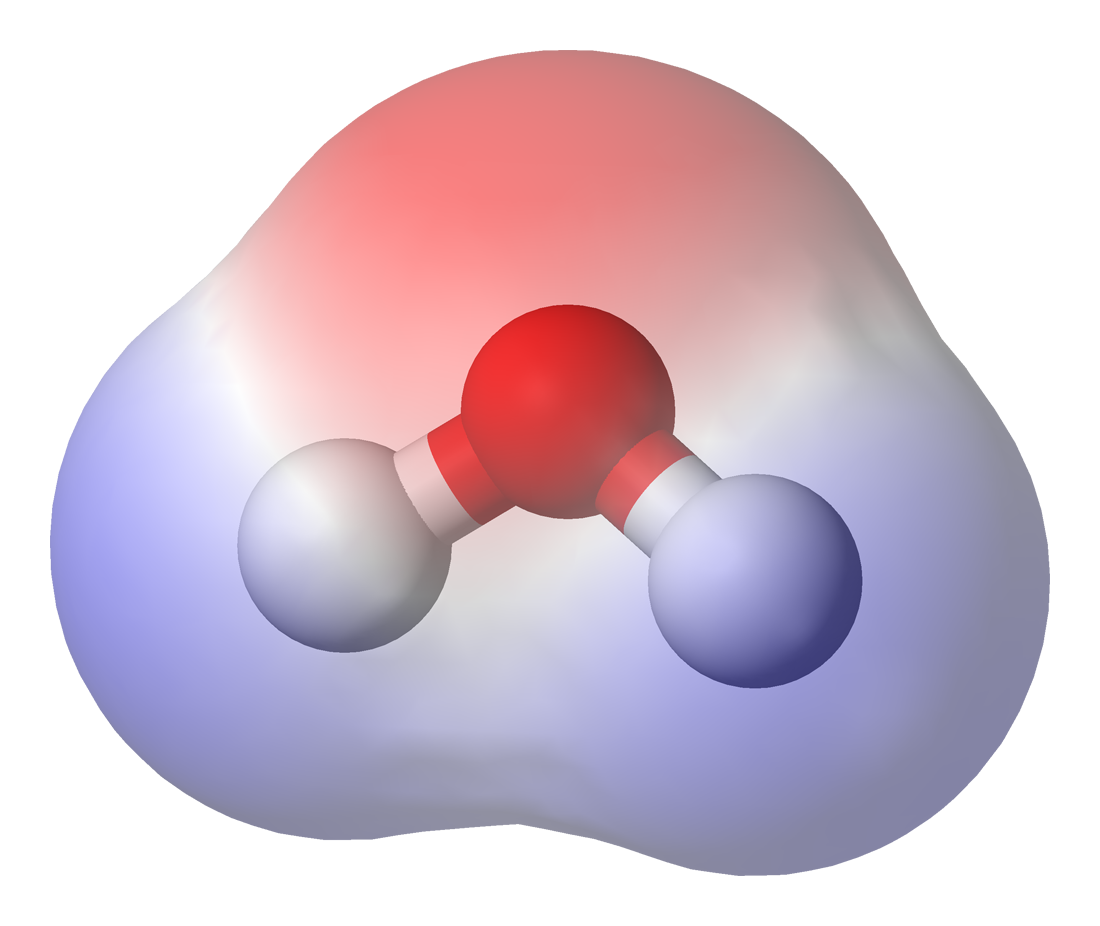
Thorium Monoxide
Thorium monoxide (thorium(II) oxide), is the binary oxide of thorium having chemical formula ThO. The covalent bond in this diatomic molecule is highly polar. The effective electric between the two atoms has been calculated to be about 80 gigavolts per centimeter, one of the largest known internal effective electric fields. Simple combustion of thorium in air produces thorium dioxide. However, laser ablation Laser ablation or photoablation (also called laser blasting) is the process of removing material from a solid (or occasionally liquid) surface by irradiating it with a laser beam. At low laser flux, the material is heated by the absorbed laser ... of thorium in the presence of oxygen gives the monoxide. Additionally, exposure of a thin film of thorium to low-pressure oxygen at medium temperature forms a rapidly growing layer of thorium monoxide under a more-stable surface coating of the dioxide. At extremely high temperatures, thorium dioxide can convert to the mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ullmann's Encyclopedia Of Industrial Chemistry
''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' is a major reference work related to industrial chemistry by Chemist Fritz Ullmann, first published in 1914, and exclusively in German as "Enzyklopädie der Technischen Chemie" until 1984. History Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry is a major reference work related to industrial chemistry by chemist Fritz Ullmann. Its 1st edition was published in German by Fritz Ullmann in 1914. The 4th edition, published 1972 to 1984, already contained 25 volumes. The 5th edition, published 1985 to 1996, was the first version available in English. In 1997, the first online version was published. 2014 marked its centenary. As of 2016, Ullmann's Encyclopedia was in its 7th edition, in 40 volumes including one index volume and more than 1,050 articles (200 more than the 6th edition), approx. 30,000 pages, 22,000 images, 8,000 tables, 19,000 references and 85,000 indices. Editions * 1914–1922: 1st edition in 12 volumes, which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face-centered Cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one lattice point. Each atom at a lattice point is then shared equally between eight adjacent cubes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Compound
In materials chemistry, a binary phase or binary compound is a chemical compound containing two different elements. Some binary phase compounds are molecular, e.g. carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). More typically binary phase refers to extended solids. Famous examples zinc sulfide, which contains zinc and sulfur, and tungsten carbide, which contains tungsten and carbon. Phases with higher degrees of complexity feature more elements, e.g. three elements in ternary phases, four elements in quaternary phase In materials chemistry, a quaternary phase is a chemical compound containing four elements. Some compounds can be molecular or ionic, examples being chlorodifluoromethane () sodium bicarbonate (). More typically quaternary phase refers to exten ...s. References Chemical compounds {{chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of a equation or reaction) Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high melting point. Thorium is an electropositive actinide whose chemistry is dominated by the +4 oxidation state; it is quite reactive and can ignite in air when finely divided. All known thorium isotopes are unstable. The most stable isotope, 232Th, has a half-life of 14.05 billion years, or about the age of the universe; it decays very slowly via alpha decay, starting a decay chain named the thorium series that ends at stable 208 Pb. On Earth, thorium and uranium are the only significantly radioactive elements that still occur naturally in large quantities as primordial elements. Thorium is estimated to be over three times as abundant as uranium in the Earth's crust, and is chiefly refined from monazite sands as a by-product of extracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term ''covalent bond'' dates from 1939. The prefix ''co-'' means ''jointly, associated in action, partnered to a lesser degree, '' etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share " valence", such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatomic Molecule
Diatomic molecules () are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen () or oxygen (), then it is said to be homonuclear. Otherwise, if a diatomic molecule consists of two different atoms, such as carbon monoxide () or nitric oxide (), the molecule is said to be heteronuclear. The bond in a homonuclear diatomic molecule is non-polar. The only chemical elements that form stable homonuclear diatomic molecules at standard temperature and pressure (STP) (or typical laboratory conditions of 1 bar and 25 °C) are the gases hydrogen (), nitrogen (), oxygen (), fluorine (), and chlorine (). The noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon) are also gases at STP, but they are monatomic. The homonuclear diatomic gases and noble gases together are called "elemental gases" or "molecular gases", to distinguish them from other gases that are chemical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While the activation energy must be overcome to initiate combustion (e.g., using a lit match to light a fire), the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining. Combustion is often a complicated sequence of elementary radical reactions. Solid fuels, such as wood and coal, first undergo endothermic pyrolysis to produce gaseous fuels whose combustion then supplies the heat required to produce more of them. Combustion is often hot enough that incandescent light in the form of either glowing or a flame is produced. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorium Dioxide
Thorium dioxide (ThO2), also called thorium(IV) oxide, is a crystalline solid, often white or yellow in colour. Also known as thoria, it is produced mainly as a by-product of lanthanide and uranium production. Thorianite is the name of the mineralogical form of thorium dioxide. It is moderately rare and crystallizes in an isometric system. The melting point of thorium oxide is 3300 °C – the highest of all known oxides. Only a few elements (including tungsten and carbon) and a few compounds (including tantalum carbide) have higher melting points. All thorium compounds, including the dioxide, are radioactive because there are no stable isotopes of thorium. Structure and reactions Thoria exists as two polymorphs. One has a fluorite crystal structure. This is uncommon among binary dioxides. (Other binary oxides with fluorite structure include cerium dioxide, uranium dioxide and plutonium dioxide.) The band gap of thoria is about 6 eV. A tetragonal form of thoria is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Ablation
Laser ablation or photoablation (also called laser blasting) is the process of removing material from a solid (or occasionally liquid) surface by irradiating it with a laser beam. At low laser flux, the material is heated by the absorbed laser energy and evaporates or sublimates. At high laser flux, the material is typically converted to a plasma. Usually, laser ablation refers to removing material with a pulsed laser, but it is possible to ablate material with a continuous wave laser beam if the laser intensity is high enough. While relatively long laser pulses (e.g. nanosecond pulses) can heat and thermally alter or damage the processed material, ultrashort laser pulses (e.g. femtoseconds) cause only minimal material damage during processing due to the ultrashort light-matter interaction and are therefore also suitable for micromaterial processing. Excimer lasers of deep ultra-violet light are mainly used in photoablation; the wavelength of laser used in photoablation is ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comproportionation
Comproportionation or synproportionation is a chemical reaction where two reactants containing the same element but with different oxidation numbers, form a compound having an intermediate oxidation number. It is the opposite of disproportionation.Shriver, D. F.; Atkins, P. W.; Overton, T. L.; Rourke, J. P.; Weller, M. T.; Armstrong, F. A. “Inorganic Chemistry” W. H. Freeman, New York, 2006. . Frost diagrams The tendency of two species to disproportionate or comproportionate can be determined by examining the Frost diagram of the oxidation states; if a species' value of Δ''G''/''F'' is lower than the line joining the two oxidation numbers on either side of it, then it is more stable and if in a solution, these two species will undergo comproportionation. A Frost Diagram is another way of displaying the reduction potentials for the various oxidation states of a given element, X. It shows nE against the oxidation number N: here, E is the reduction potential for the X(N)/X(0) c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |