|
Thor Agena
Thor-Agena was a series of orbital launch vehicles. The launch vehicles used the Douglas-built Thor first stage and the Lockheed-built Agena second stages. They are thus cousins of the more-famous Thor-Deltas, which founded the Delta rocket family. The first attempted launch of a Thor-Agena was in January 1959. The first successful launch was on 28 February 1959, launching ''Discoverer 1''. It was the first two-stage launch vehicle to place a satellite into orbit. Missions Among other uses, the clandestine CORONA program used Thor-Agena from June 1959 until January 1968 to launch United States military reconnaissance satellites operated by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). During this program, Thor-Agena launch vehicles were used in 145 launch attempts, now known to have been part of satellite surveillance programs. Also, ''Alouette 1,'' Canada's first satellite, was launched on a Thor-Agena B. 1963 Mystery Cloud On 28 February 1963, a Thor-Agena launch vehicle car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, launch pads, supported by a missile launch control center, launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital spaceflight, orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital spaceflight, Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as Solid-propellant rocket, solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, and analyzing national security information from around the world, primarily through the use of human intelligence (HUMINT) and performing covert actions. As a principal member of the United States Intelligence Community (IC), the CIA reports to the Director of National Intelligence and is primarily focused on providing intelligence for the President and Cabinet of the United States. President Harry S. Truman had created the Central Intelligence Group under the direction of a Director of Central Intelligence by presidential directive on January 22, 1946, and this group was transformed into the Central Intelligence Agency by implementation of the National Security Act of 1947. Unlike the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), which is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1959 In Spaceflight
Luna 1 was the first spacecraft to leave the gravitational influence of Earth. Also in 1959, Luna 2 was the first spacecraft to reach the surface of another celestial body, impacting the Moon, and Luna 3 returned the first images of the far side of the Moon The far side of the Moon is the lunar hemisphere that always faces away from Earth, opposite to the Near side of the Moon, near side, because of synchronous rotation in the Moon's orbit. Compared to the near side, the far side's terrain is ru .... Launches January February March April May June July August September October November December Deep Space Rendezvous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-air Retrieval
Mid-air retrieval is a technique used in atmospheric reentry when the reentering vehicle is incapable of a satisfactory unassisted landing. The vehicle is slowed by means of parachutes, and then a specially-equipped aircraft matches the vehicle's trajectory and catches it in mid-air. This is a risky technique, and so is only used when other forms of landing are infeasible. Successful mid-air retrieval requires correct operation of the retrieving aircraft, favourable atmospheric conditions, and successful execution of a tricky manoeuvre, in addition to correct operation of the vehicle itself. These risks can be mitigated somewhat: for example, multiple recovery aircraft can be used. The need for human aviators to perform a manoeuvre which would normally be classed as a stunt may in the future be avoided by advances in unmanned aerial vehicles. Notable uses of the technique: * The first use of midair retrieval was in 1955, with Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar transports being used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar
The Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar (Navy and Marine Corps designation R4Q) was an American military transport aircraft developed from the World War II-era Fairchild C-82 Packet, designed to carry cargo, personnel, litter patients, and mechanized equipment, and to drop cargo and troops by parachute. The first C-119 made its initial flight in November 1947, and by the time production ceased in 1955, more than 1,100 C-119s had been built. Development The Air Force C-119 and Navy R4Q was initially a redesign of the earlier C-82 Packet, built between 1945 and 1948. The Packet provided service to the Air Force's Tactical Air Command and Military Air Transport Service for nearly nine years during which time its design was found to have several serious problems. All of these were addressed in the C-119. In contrast to the C-82, the cockpit was moved forward to fit flush with the nose rather than its previous location over the cargo compartment. This resulted in more usable cargo s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoverer 14
Discoverer 14, also known as Corona 9009, was a spy satellite used in the Corona program managed by Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the Department of Defense and the United States Air Force. On 19 August 1960, usable photographic film images of the Soviet Union taken by the satellite were recovered by a C-119 recovery aircraft. This was the first successful recovery of film from an orbiting satellite and the first mid-air recovery of an object returning from Earth orbit. Background "Discoverer" was the civilian designation and cover for the Corona satellite photo-reconnaissance series of satellites managed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency of the Department of Defense and the U.S. Air Force. The primary goal of the satellites was to replace the U-2 spyplane in surveilling the Sino-Soviet Bloc, determining the disposition and speed of production of Soviet missiles and long-range bombers assets. The Corona program was also used to produce maps and charts for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a public land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first university in the Arizona Territory. The university is part of the Association of American Universities and the Universities Research Association. In the former, it is the only member from the state of Arizona. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity". The University of Arizona is one of three universities governed by the Arizona Board of Regents. , the university enrolled 49,471 students in 19 separate colleges/schools, including the University of Arizona College of Medicine in Tucson and Phoenix and the James E. Rogers College of Law, and is affiliated with two academic medical centers ( Banner – University Medical Center Tucson and Banner – University Medical Center Phoenix). In 2021, University of Arizona acquired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alouette 1
''Alouette 1'' is a deactivated Canadian satellite that studied the ionosphere. Launched in 1962, it was Canada's first satellite, and the first satellite constructed by a country other than the Soviet Union or the United States. Canada was the fourth country to operate a satellite, as the British ''Ariel 1'', constructed in the United States by NASA, preceded ''Alouette 1'' by five months. The name "Alouette" came from the French for "skylark" and the French-Canadian folk song of the same name. A key device on ''Alouette'' were the radio antennas consisting of thin strips of beryllium copper bent into a slight U-shape and then rolled up into small disks in a fashion similar to a measuring tape. When triggered, the rotation of the satellite created enough centrifugal force to pull the disk away from the spacecraft body, and the shaping of the metal caused it to unwind into a long spiral. The result was a stiff circular cross-section antenna known as a "STEM", for "storable tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
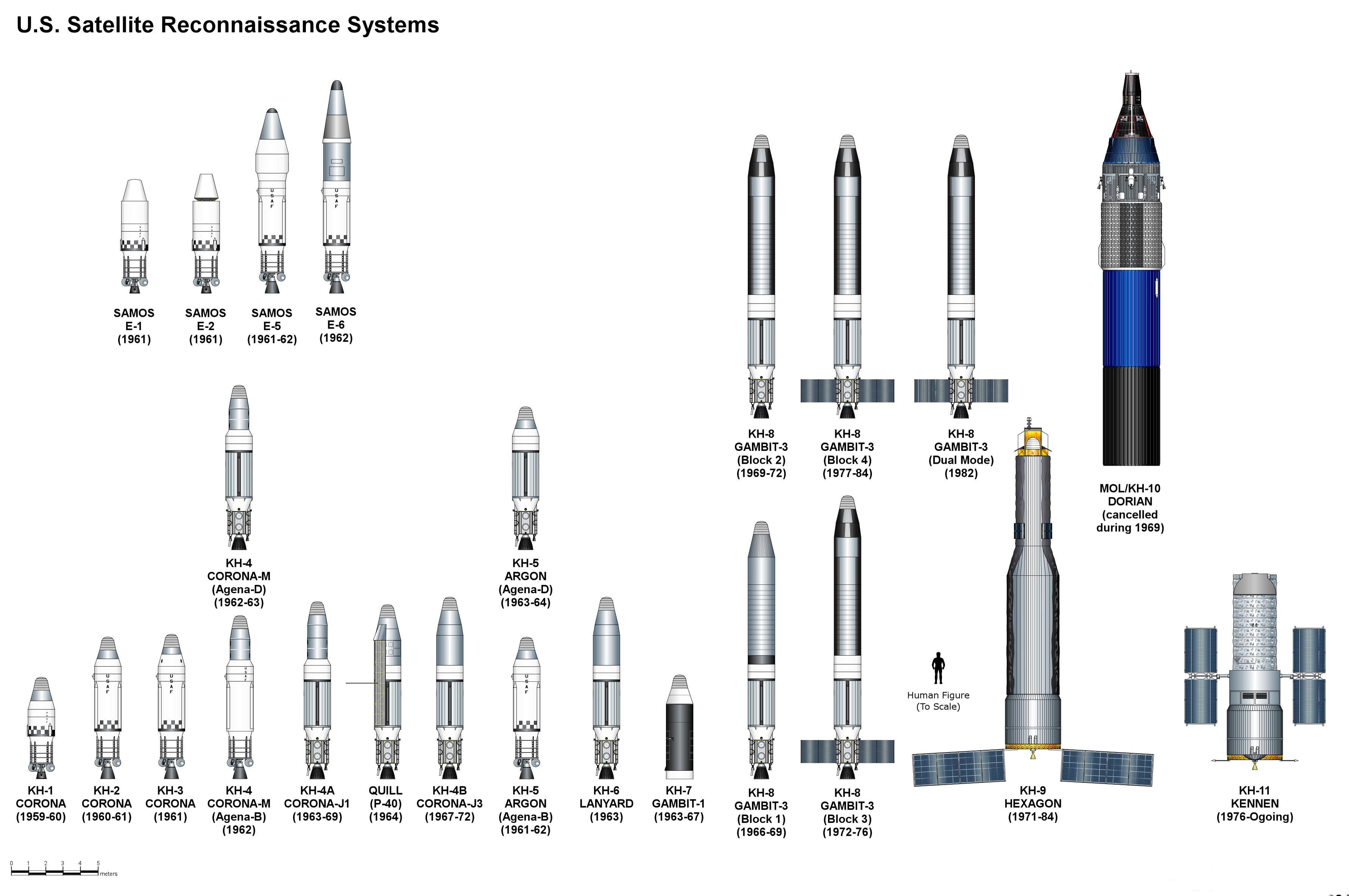
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassified o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)