|
Thomas King (botanist)
Thomas King (14 April 1834 – 14 September 1896) was a British botanist and author. He discovered twenty-nine species of plant while in Chile during the 1860s and 1870s. In 1885, he contributed a section on Scotland's botany to Francis Hindes Groome's book '' Ordnance Gazetteer of Scotland: A Graphic and Accurate Description of Every Place in Scotland''. Early life and career King was born in 1834 at Yardfoot, a farm in Lochwinnoch, Renfrewshire. While attending school in Glenhead, he developed a love of nature, having grown up amongst it. In 1855, the family sold the farm and relocated to Glasgow. There, King trained as a teacher at the Normal Training College of the Free Church of Scotland, after which he taught in schools in Paisley and Chryston. In 1862, he was installed in the English and botany department of Glasgow's Garnet Bank Academy. Failing health forced him to seek a warmer climate, and in July 1864 he set sail on a three-month journey to Chile, where one of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochwinnoch
Lochwinnoch (; sco, Lochineuch, gd, Loch Uinneach) is a village in the council area and historic county of Renfrewshire in the west central Lowlands of Scotland. Lying on the banks of Castle Semple Loch and the River Calder, Lochwinnoch is chiefly a residential dormitory village serving nearby urban centres such as Glasgow and Paisley. Its population in 2001 was 2628. The Town also lends its name to a civil parish of some of the surrounding countryside, including the nearby village of Howwood. The parish borders seven others: Beith, Kilbarchan, Kilbirnie, Kilmacolm, Largs, Neilston and Paisley. History Lochwinnoch is first recorded in the 12th Century as a parish under the higher control of Paisley and Renfrew, but the area has been inhabited since the neolithic period. The 1729 St John's Kirk, also known as ''Auld Simon'' (Old Simon) (whose front gable still stands at the eastern end of the High Street), was probably built on the site of a pre-Reformation church dati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federico Errázuriz Zañartu
Federico Marcos del Rosario Errázuriz Zañartu (; April 25, 1825 – July 20, 1877) was a Chilean political figure. He served as the president of Chile between 1871 and 1876. Biography He was born in Santiago in 1825, of Basque descent. He studied law in the University of Chile. He was made a deputy in parliament at an early age, and took some part in the parliamentary debates. In 1860 he was made chief of the province of Santiago, and introduced many reforms. In 1862, during Pérez's administration, he became secretary of justice and of public instruction; and in 1865, during the Chincha Islands War with Spain, he was secretary of war and the navy. In 1871 Errázuriz became president of the republic of Chile, and introduced liberal reforms of great importance to the country, tending toward the secularization of public instruction and freedom of worship. He amended the constitution of 1833 by means of a law which was very much discussed in congress, abolished ecclesiastical priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Stirton
James Stirton (1833, Coupar Angus, Perthshire – 14 January 1917, Glasgow) was a Scottish physician and one of Scotland's leading experts on cryptogamic botany. His investigations in bryology and lichenology earned him a world-wide reputation. Biography Stirton taught mathematics from 1856 to 1858 at the Merchiston Castle School in Edinburgh. At the University of Edinburgh he graduated in 1857 L.R.C.P.Edin and in 1858 M.D.Edin. Soon after acquiring his M.D. he moved to Glasgow and established an extensive practice in obstetrics and gynaecology. In 1876 Stirton was appointed a lecturer in gynaecology at the Glasgow Royal Infirmary, where for many years he had charge of the gynaecological wards. In 1889 he became a professor of midwifery at Anderson’s College Medical School and held the professorship for about fifteen years. Stirton made many visits to the Scottish mountains to investigate lichens and mosses and there discovered numerous species that were previously undescribed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Glasgow Herald
''The Herald'' is a Scottish broadsheet newspaper founded in 1783. ''The Herald'' is the longest running national newspaper in the world and is the eighth oldest daily paper in the world. The title was simplified from ''The Glasgow Herald'' in 1992. Following the closure of the ''Sunday Herald'', the ''Herald on Sunday'' was launched as a Sunday edition on 9 September 2018. History Founding The newspaper was founded by an Edinburgh-born printer called John Mennons in January 1783 as a weekly publication called the ''Glasgow Advertiser''. Mennons' first edition had a global scoop: news of the treaties of Versailles reached Mennons via the Lord Provost of Glasgow just as he was putting the paper together. War had ended with the American colonies, he revealed. ''The Herald'', therefore, is as old as the United States of America, give or take an hour or two. The story was, however, only carried on the back page. Mennons, using the larger of two fonts available to him, put it in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
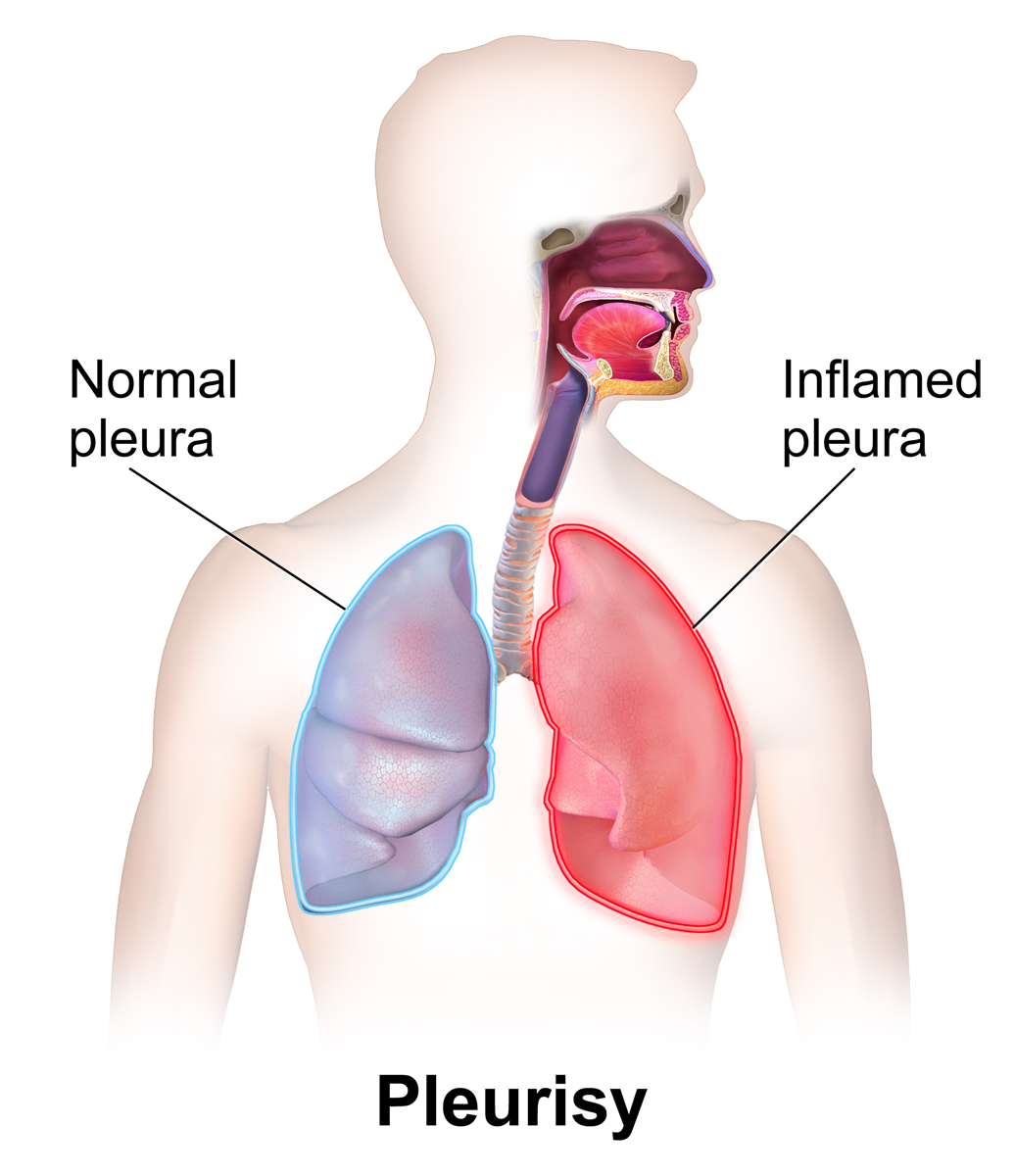
Pleurisy
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever, or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause. The most common cause is a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infection, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, autoimmune disorders, lung cancer, following heart surgery, pancreatitis and asbestosis. Occasionally the cause remains unknown. The underlying mechanism involves the rubbing together of the pleurae instead of smooth gliding. Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include pericarditis, heart attack, cholecystitis, pulmonary embolism, and pneumothorax. Diagnostic testing may include a chest X-ray, electrocardiogram (ECG), and blood tests. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Paracetamol (acetaminop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Society Of Scotland
The Botanical Society of Scotland (BSS) is the national learned society for botanists of Scotland. The Society's aims are to advance knowledge and appreciation of flowering and cryptogamic plants, algae and fungi. The Society's activities include lectures (mainly held in Edinburgh, but also in other Scottish cities), symposia, field excursions, field projects and an annual Scottish Botanist's Conference, held jointly with the Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland for exchange of information between botanists working in different areas. Its publications include a twice-yearly newsletter, BSS News, and a scientific journal, ''Plant Ecology & Diversity''. The society is closely linked to the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh and the Scottish universities. History It was founded on 8 February 1836 as the Botanical Society of Edinburgh. Its founding members included Prof Edward Forbes, Prof John Hutton Balfour and Dr Richard Parnell. In 1935 the Botanical Society of Edinburgh incorpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Society Of Glasgow
The Geological Society of Glasgow is a scientific society devoted to the study of geology in Scotland. The society contributed to the understanding of Scotland's glacial history, and the relationship between the Earth's rotation and climate change. The Geological Society of Glasgow is registered as a charity in Scotland. History The society was founded on 17 May 1858, by a group of amateur geology enthusiasts. The society organized its first field trip, to Campsie Glen, in June of that year. Some fossils from these early excursions are on display in the Kelvingrove Museum in Glasgow. The society continues to attract lecturers at the forefront of the field, and publishes field guides of the Glasgow region. Programs Each summer, the society runs day-long and residential field trips, open to members. Each winter, the society hosts a lecture series, open to all, in the Gregory Building at Glasgow University. Publications The ''Transactions of the Geological Society of Glasgow' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Glasgow School Of Veterinary Medicine
The School of Veterinary Medicine at the University of Glasgow is one of nine veterinary schools in the United Kingdom, and offers undergraduate and postgraduate qualifications in Veterinary Medicine. It was established in 1862 as the independent Glasgow Veterinary College, being subsumed into the university in 1949 and gaining independent faculty status in 1969. In 2010 it became a constituent school of the new College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences. It ranked second in the UK by the Complete University Guide 2016 and in 2015, QS World University Rankings ranked the veterinary school seventh in the world for veterinary medicine. Early days In 1859, James McCall, Professor of Anatomy and Physiology at the Dick Veterinary College in Edinburgh, moved to Glasgow and started a practice in Hope Street, from which he gave informal lectures in veterinary medicine. In 1862, formal classes were instituted and the practice moved to a larger accommodation, a set of stables at 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Strathclyde
The University of Strathclyde ( gd, Oilthigh Shrath Chluaidh) is a public research university located in Glasgow, Scotland. Founded in 1796 as the Andersonian Institute, it is Glasgow's second-oldest university, having received its royal charter in 1964 as the first technological university in the United Kingdom. Taking its name from the historic Kingdom of Strathclyde, it is Scotland's third-largest university by number of students, with students and staff from over 100 countries. The institution was named University of the Year 2012 by Times Higher Education and again in 2019, becoming the first university to receive this award twice. The annual income of the institution for 2019–20 was £334.8 million of which £81.2 million was from research grants and contracts, with an expenditure of £298.8 million.. History The university was founded in 1796 through the will of John Anderson, professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow, who left i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnethill
Garnethill is a predominantly residential area of the city of Glasgow, Scotland with a number of important public buildings. Geography Located in the city centre, the area borders Cowcaddens to its north, Sauchiehall Street to its south, Cambridge Street to its east and now the M8 motorway to its west. The hill forms part of the historic Lands of Blythswood which the Douglas-Campbell families sold in stages from the late 18th century onwards, the largest purchaser/developer being William Harley of Blythswood Hill, cotton merchant and builder. Harley laid out Renfrew Street and encouraged the building of villas, which extended round into St George's Road. One major site was developed as Garnethill Observatory in 1810. Later developments included spacious tenements as families moved upward from the overcrowded Cowcaddens. Harley also laid out Blythswood Square. The area was named Garnet Hill by William Harley, in honour of Professor Thomas Garnett, one of the first professors of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Glasgow
, image = UofG Coat of Arms.png , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of arms Flag , latin_name = Universitas Glasguensis , motto = la, Via, Veritas, Vita , mottoeng = The Way, The Truth, The Life , established = , type = Public research universityAncient university , endowment = £225.2 million , budget = £809.4 million , rector = Rita Rae, Lady Rae , chancellor = Dame Katherine Grainger , principal = Sir Anton Muscatelli , academic_staff = 4,680 (2020) , administrative_staff = 4,003 , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Glasgow , country = Scotland, UK , colours = , website = , logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |