|
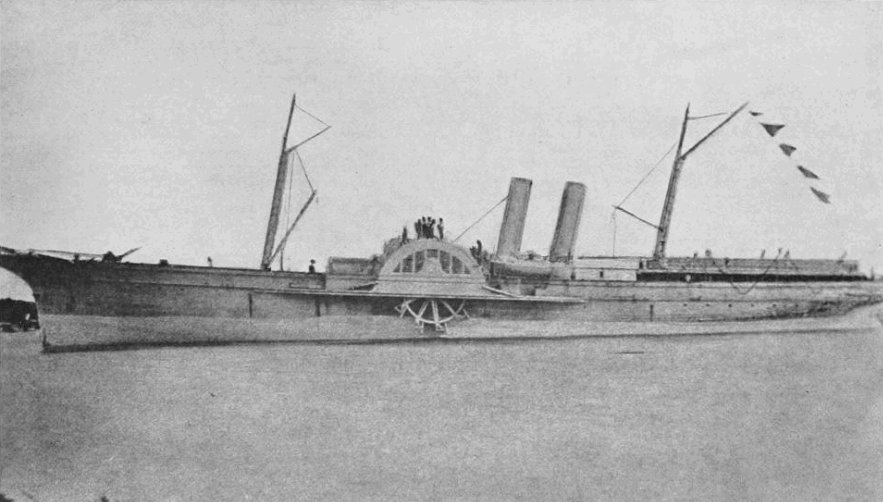
Thomas H. Stevens, Jr.
Thomas Holdup Stevens Jr. (27 May 1819 – 15 May 1896) was an admiral of the United States Navy who fought in the American Civil War. Early life and commission Stevens, the son of Captain Thomas Holdup Stevens (1795–1841) was born in Middletown, Connecticut, on 27 May 1819. He was appointed acting midshipman on 14 December 1836 and, after two years at sea in , was warranted midshipman. After three months leave, from April to June 1840, he served at the Depot of Charts and Instruments. Following a tour at the Washington Navy Yard and coast survey duty at New York, he attended the Naval School at Philadelphia, stood his examination on 2 June 1842, and was warranted a passed midshipman on 2 July. Between 1842 and 1855, Stevens served at various posts ashore, among which were two tours on coast survey duty, one tour as acting master of during her construction and 30 months as storekeeper in Honolulu, Hawaii. In September 1855, Lt. Stevens was dropped from the Navy under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington National Cemetery
Arlington National Cemetery is one of two national cemeteries run by the United States Army. Nearly 400,000 people are buried in its 639 acres (259 ha) in Arlington, Virginia. There are about 30 funerals conducted on weekdays and 7 held on Saturday. The other Army cemetery is in Washington, D.C. and is called the U.S. Soldiers' and Airmen's Home National Cemetery. All other national cemeteries are run by the National Cemetery System of the Department of Veterans Affairs. Arlington National Cemetery was established during the U.S. Civil War after the land the cemetery was built upon, Arlington Estate, was confiscated from private ownership following a tax dispute. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places in April 2014, the Arlington National Cemetery Historic District includes the Cemetery, Arlington House, Memorial Drive, the Hemicycle, and Arlington Memorial Bridge. History George Washington Parke Custis was the grandson of Martha Dandridge Custis Washington th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Beauregard
Fort Beauregard, located half a mile north of the village of Harrisonburg, Catahoula Parish, Louisiana, was one of four Confederate forts guarding the Ouachita River during the American Civil War. In 1863, four Union gunboats attacked it, unsuccessfully. Significance Fort Beauregard is located on a hill overlooking the Ouachita River, several miles north of where it joins with the Tensas River and Little River to form the Black. The fort is situated on almost the only point where the upland hills of Louisiana come within artillery range of the Ouachita; thus the batteries of the fort controlled the water approach to Monroe, the only city of military importance in Northeast Louisiana. Because the Confederates concentrated here, the fort took on a greater significance: it was the key to the entire Ouachita River Valley. Naval attacks Four Federal gunboats commanded by Commodore Selim E. Woodworth arrived on May 10, 1863. They anchored at the mouth of the Bushley, and immediat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John A
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (January 10 or 11, 1815 – June 6, 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 to 1891. The dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, he had a political career that spanned almost half a century. Macdonald was born in Scotland; when he was a boy his family immigrated to Kingston in the Province of Upper Canada (today in eastern Ontario). As a lawyer, he was involved in several high-profile cases and quickly became prominent in Kingston, which elected him in 1844 to the legislature of the Province of Canada. By 1857, he had become premier under the colony's unstable political system. In 1864, when no party proved capable of governing for long, Macdonald agreed to a proposal from his political rival, George Brown, that the parties unite in a Great Coalition to seek federation and political reform. Macdonald was the leading figure in the subsequent discussions and conferences, which resulted in the Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Atlantic Blockading Squadron
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading. The blockade was proclaimed by President Abraham Lincoln in April 1861, and required the monitoring of of Atlantic and Gulf coastline, including 12 major ports, notably New Orleans and Mobile. Those blockade runners fast enough to evade the Union Navy could carry only a small fraction of the supplies needed. They were operated largely by foreign citizens, making use of neutral ports such as Havana, Nassau and Bermuda. The Union commissioned around 500 ships, which destroyed or captured about 1,500 blockade runners over the course of the war. Proclamation of blockade and legal implications On April 19, 1861, President Lincoln issued a ''Proclamation of Blockade Against Southern Ports'': Whereas an insurrection against the Government of the United States has broken out in the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander (United States)
In the United States, commander is a military rank that is also sometimes used as a military billet title—the designation of someone who manages living quarters or a base—depending on the branch of service. It is also used as a rank or title in non-military organizations; particularly in law enforcement. As rank History The commander rank started out as "Master and Commander" in 1674 within the Royal Navy for the officer responsible for sailing a ship under the Captain and sometimes second-in-command. Sub-captain, under-captain, rector and master-commanding were also used for the same position. With the Master and Commander also serving as captain of smaller ships the Royal Navy subsumed as the third and lowest of three grades of captain given the various sizes of ships. The Continental Navy had the tri-graded captain ranks. Captain 2nd Grade, or Master Commandant, became Commander in 1838. Naval In the Navy, the Coast Guard, the NOAA Corps, and the Public Health Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as a letter of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes, and taking prize crews as prisoners for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Privateering allowed sovereigns to raise revenue for war by mobilizing privately owned armed ships and sailors to supplement state power. For participants, privateerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky and Missouri also declared secession and had full representation in the Confederate Congress, though their territory was largely controlled by Union forces. The Confederacy was formed on February 8, 1861, by seven slave states: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. All seven were in the Deep South region of the United States, whose economy was heavily dependent upon agriculture—particularly cotton—and a plantation system that relied upon enslaved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George B
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Atlantic Blockading Squadron
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading. The blockade was proclaimed by President Abraham Lincoln in April 1861, and required the monitoring of of Atlantic and Gulf coastline, including 12 major ports, notably New Orleans and Mobile. Those blockade runners fast enough to evade the Union Navy could carry only a small fraction of the supplies needed. They were operated largely by foreign citizens, making use of neutral ports such as Havana, Nassau and Bermuda. The Union commissioned around 500 ships, which destroyed or captured about 1,500 blockade runners over the course of the war. Proclamation of blockade and legal implications On April 19, 1861, President Lincoln issued a ''Proclamation of Blockade Against Southern Ports'': Whereas an insurrection against the Government of the United States has broken out in the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernandina, Florida
Fernandina Beach is a city in northeastern Florida and the county seat of Nassau County, Florida, United States. It is the northernmost city on Florida's Atlantic coast, situated on Amelia Island, and is one of the principal municipalities comprising Greater Jacksonville. The area was first inhabited by the Timucuan Indian people. Known as the "Isle of 8 Flags", Amelia Island has had the flags of the following nations flown over it: France, Spain, Great Britain, Spain (again), the Republic of East Florida (1812), the Republic of the Floridas (1817), Mexico, the Confederate States of America, and the United States. The French, English, and Spanish all maintained a presence on Amelia Island at various times during the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, but the Spanish established Fernandina. The town of Fernandina, which was about a mile from the present city, was named in honor of King Ferdinand VII of Spain by the governor of the Spanish province of East Florida, Enrique White. Fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Clinch
Fort Clinch is a 19th-century masonry Coastal defence and fortification, coastal fortification, built as part of the Seacoast Defense (US)#Third system, Third System of seacoast defense conceived by the United States. It is located on a peninsula near the northernmost point of Amelia Island in Nassau County, FL, Nassau County, Florida. The fort lies to the northeast of Fernandina Beach, Florida, Fernandina Beach at the entrance to the Cumberland Sound (Florida), Cumberland Sound, in the northeast part of the state. Today it is included within the boundaries of Fort Clinch State Park. History This site was first fortified in 1736 by the Spanish, when they held colonies in Florida. From 1736, various nations to control the territory have garrisoned and fortified this site to protect the entrance to the St. Marys River (Florida–Georgia), St. Marys River and Cumberland Sound. After the end of the Second Seminole War, the United States started construction of a fort, later named Fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |