|
Thiostrepton Building Block
Thiostrepton is a natural cyclic oligopeptide antibiotic of the thiopeptide class, derived from several strains of streptomycetes, such as ''Streptomyces azureus'' and ''Streptomyces laurentii''. Thiostrepton is a natural product of the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) class. History Thiostrepton was discovered by Donovick ''et al.'' who described its antibacterial properties in 1955. Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin solved the structure of thiostrepton in 1970. Early in 1978, Bycroft and Gowland proposed the biosynthesis of thiostrepton, which was still unclear until 2009. Several studies of thiopeptide biosynthesis have been contemporarily published in 2009 and two of them (Liao ''et al.'' and Kelly ''et al.'') included the similar biosynthesis of thiostrepton: it's ribosomally synthesized from thiostrepton biosynthetic genes (tsr genes) and posttranslational modification is needed. A total synthesis of thiostrepton was completed by K.C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck Index
''The Merck Index'' is an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs and biologicals with over 10,000 monograph on single substances or groups of related compounds published online by the Royal Society of Chemistry. History The first edition of the Merck's Index was published in 1889 by the German chemical company Emanuel Merck and was primarily used as a sales catalog for Merck's growing list of chemicals it sold. The American subsidiary was established two years later and continued to publish it. During World War I the US government seized Merck's US operations and made it a separate American "Merck" company that continued to publish the Merck Index. In 2012 the Merck Index was licensed to the Royal Society of Chemistry. An online version of The Merck Index, including historic records and new updates not in the print edition, is commonly available through research libraries. It also includes an appendix with monographs on organic named reactions. The 15th edition was published in A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiopeptides
Thiopeptides (thiazolyl peptides) are a class of peptide antibiotics produced by bacteria. They have antibiotic activity against Gram-positive bacteria, but little or no activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Many of the members of this class show activity against methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) and are therefore subjects of research interest. There are over 100 members of this class known. Chemical structure Thiopeptides are sulfur-rich macrocyclic peptides containing highly-modified amino acids. They are characterized by a nitrogen-containing six-membered ring (such as piperidine, dehydropiperidine, or pyridine) substituted with multiple thiazole rings and dehydroamino acids. A macrocylic ring serves as a scaffold for a tail that also incorporates modified amino acids often with azole rings, such as thiazoles, oxazoles, and thiazolines which are derived from serine, threonine, and cysteine residues. Examples Examples of thiopeptides include thiostre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Synthesis Of Thiostrepton
Total may refer to: Mathematics * Total, the summation of a set of numbers * Total order, a partial order without incomparable pairs * Total relation, which may also mean ** connected relation (a binary relation in which any two elements are comparable). * Total function, a partial function that is also a total relation Business * TotalEnergies, a French petroleum company * Total (cereal), a food brand by General Mills * Total, a brand of strained yogurt made by Fage * Total, a database management system marketed by Cincom Systems * Total Linhas Aéreas - a brazilian airline * Total, a line of dental products by Colgate Music and culture * Total (group), an American R&B girl group * '' Total: From Joy Division to New Order'', a compilation album * ''Total'' (Sebastian album) * ''Total'' (Total album) * ''Total'' (Teenage Bottlerocket album) * ''Total'' (Seigmen album) * ''Total'' (Wanessa album) * ''Total'' (Belinda Peregrín album) * ''Total 1'', an annual compilation alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiostrepton Building Block
Thiostrepton is a natural cyclic oligopeptide antibiotic of the thiopeptide class, derived from several strains of streptomycetes, such as ''Streptomyces azureus'' and ''Streptomyces laurentii''. Thiostrepton is a natural product of the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) class. History Thiostrepton was discovered by Donovick ''et al.'' who described its antibacterial properties in 1955. Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin solved the structure of thiostrepton in 1970. Early in 1978, Bycroft and Gowland proposed the biosynthesis of thiostrepton, which was still unclear until 2009. Several studies of thiopeptide biosynthesis have been contemporarily published in 2009 and two of them (Liao ''et al.'' and Kelly ''et al.'') included the similar biosynthesis of thiostrepton: it's ribosomally synthesized from thiostrepton biosynthetic genes (tsr genes) and posttranslational modification is needed. A total synthesis of thiostrepton was completed by K.C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Mechanism For The Dehydropiperidine Thiopeptides Biosynthesis
Alternative or alternate may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Alternative (''Kamen Rider''), a character in the Japanese TV series ''Kamen Rider Ryuki'' * ''The Alternative'' (film), a 1978 Australian television film * ''The Alternative'', a radio show hosted by Tony Evans * ''120 Minutes'' (2004 TV program), an alternative rock music video program formerly known as ''The Alternative'' *''The American Spectator'', an American magazine formerly known as ''The Alternative: An American Spectator'' * Alternative comedy, a range of styles used by comedians and writers in the 1980s * Alternative comics, a genre of comic strips and books * Alternative media, media practices falling outside the mainstreams of corporate communication * Alternative reality, in fiction * Alternative title, the use of a secondary title for a work when it is distributed or sold in other countries Music * ''Alternative'' (album), a B-sides album by Pet Shop Boys * ''The Alternative'' (album), an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
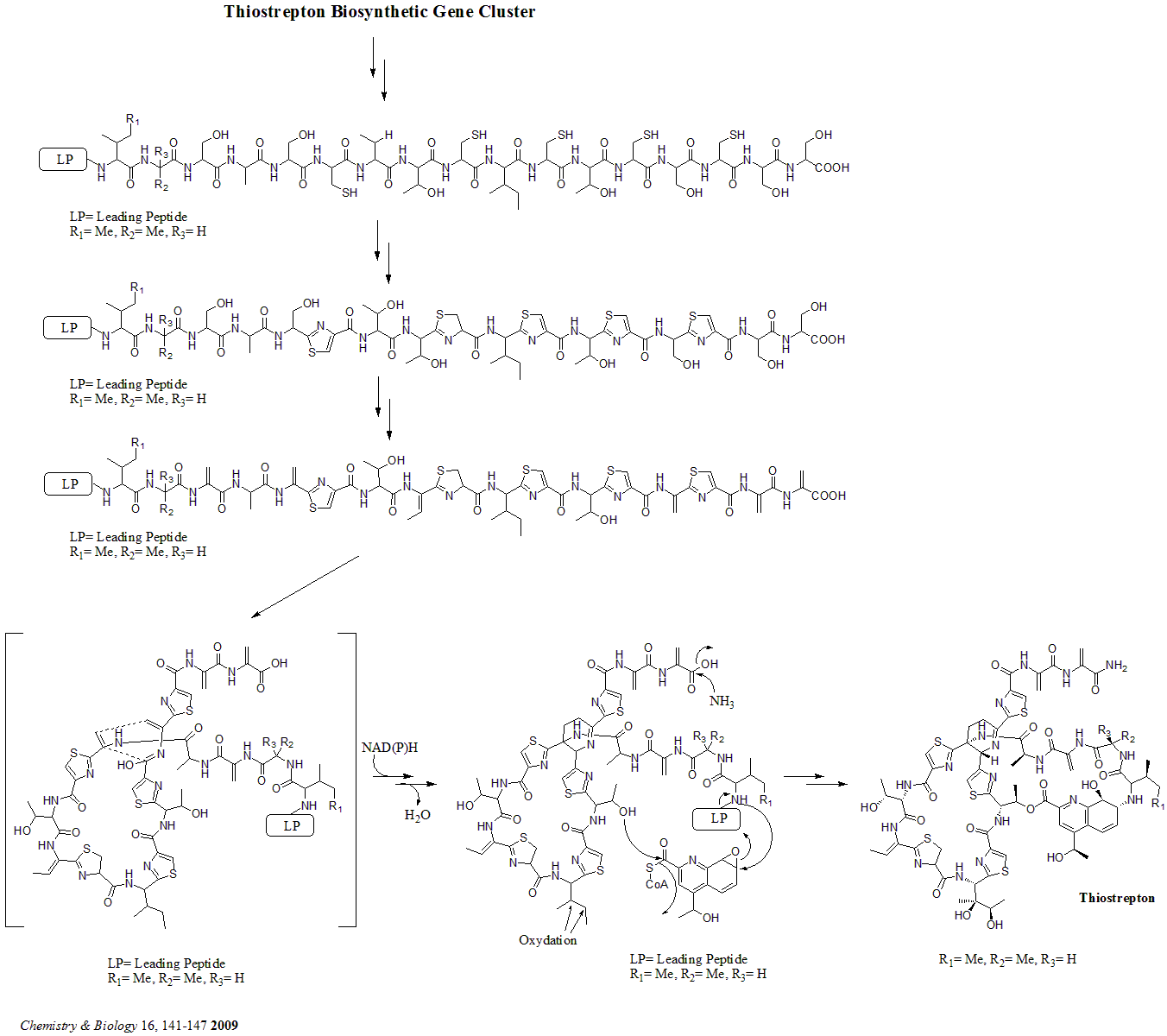
Biosynthesis Of Thiostrepton
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Cancer Research
''Molecular Cancer Research'' is a monthly peer reviewed academic journal published by the American Association for Cancer Research The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) is the world's oldest and largest professional association related to cancer research. Based in Philadelphia, the AACR focuses on all aspects of cancer research, including basic, clinical, and tr .... Prior to September 2002 it was known as ''Cell Growth & Differentiation''. External links * Cell Growth & Differentiation Oncology journals Monthly journals American Association for Cancer Research academic journals {{oncology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FOXM1
Forkhead box protein M1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FOXM1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the FOX family of transcription factors. Its potential as a target for future cancer treatments led to it being designated the 2010 Molecule of the Year. Function FOXM1 is known to play a key role in cell cycle progression where endogenous FOXM1 expression peaks at S and G2/M phases. FOXM1-null mouse embryos were neonatal lethal as a result of the development of polyploid cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes, highlighting the role of FOXM1 in mitotic division. More recently a study using transgenic/knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts and human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) has shown that FOXM1 regulates expression of a large array of G2/M-specific genes, such as Plk1, cyclin B2, Nek2 and CENPF, and plays an important role in maintenance of chromosomal segregation and genomic stability. Cancer link FOXM1 gene is now known as a human proto-oncogene. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol ( opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nystatin
Nystatin, sold under the brandname Mycostatin among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat '' Candida'' infections of the skin including diaper rash, thrush, esophageal candidiasis, and vaginal yeast infections. It may also be used to prevent candidiasis in those who are at high risk. Nystatin may be used by mouth, in the vagina, or applied to the skin. Common side effects when applied to the skin include burning, itching, and a rash. Common side effects when taken by mouth include vomiting and diarrhea. During pregnancy use in the vagina is safe while other formulations have not been studied in this group. It works by disrupting the cell membrane of the fungal cells. Nystatin was discovered in 1950 by Rachel Fuller Brown and Elizabeth Lee Hazen. It was the first polyene macrolide antifungal. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. It is made from the bacterium '' Streptomyces noursei' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neomycin
Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against gram-positive bacilli and anaerobic gram-negative bacilli. Neomycin comes in oral and topical formulations, including creams, ointments, and eyedrops. Neomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds. Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. Neomycin received approval for medical use in 1952. Rutgers University was granted the patent for neomycin in 1957. Discovery Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by the microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. It is produced naturally by the bacterium ''Streptomyces fradiae''. Synthesis requires specific nutrient conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |