Thiostrepton Building Block on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thiostrepton is a natural cyclic oligopeptide



antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of ...
of the thiopeptide class, derived from several strains of streptomycetes, such as ''Streptomyces azureus
''Streptomyces azureus'' is a bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has isolated from soil.Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen]/ref> ''Streptomyces azureus'' produces the antibiotic thiostrepton.
See also ...
'' and ''Streptomyces laurentii
''Streptomyces laurentii'' is a bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from soil.Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturenbr>/ref> ''Streptomyces laurentii'' produces thiostrepton
Thiostrepto ...
''. Thiostrepton is a natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical syn ...
of the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) class.
History
Thiostrepton was discovered by Donovick ''et al.'' who described its antibacterial properties in 1955. Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin solved the structure of thiostrepton in 1970. Early in 1978, Bycroft and Gowland proposed the biosynthesis of thiostrepton, which was still unclear until 2009. Several studies of thiopeptide biosynthesis have been contemporarily published in 2009 and two of them (Liao ''et al.'' and Kelly ''et al.'') included the similar biosynthesis of thiostrepton: it's ribosomally synthesized from thiostrepton biosynthetic genes (tsr genes) and posttranslational modification is needed. A total synthesis of thiostrepton was completed byK.C. Nicolaou
Kyriacos Costa Nicolaou ( el, Κυριάκος Κ. Νικολάου; born July 5, 1946) is a Cypriot-American chemist known for his research in the area of natural products total synthesis. He is currently Harry C. and Olga K. Wiess Professor o ...
, ''et al.'' in 2004.
Applications
Thiostrepton has been used in veterinary medicine in mastitis caused by gram-negative organisms and in dermatologic disorders. It is mostly used in complex ointments containing neomycin, nystatin, Thiostrepton and topicalsteroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s. It is also active against gram-positive bacteria. It is notable that ointments for human usage contain neomycin, nystatin, and topical steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
s, but no thiostrepton.
Thiostrepton was reported (in 2008) to exhibit activity against breast cancer cells through targeting the transcription factor forkhead box M1 ( FOXM1), also in 2011.
It has also been shown to circumvent acquired cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells under in invitro conditions.
Thiostrepton is used in molecular biology as a reagent for both positive and negative selection of genes involved in nucleotide metabolism.
Biosynthesis
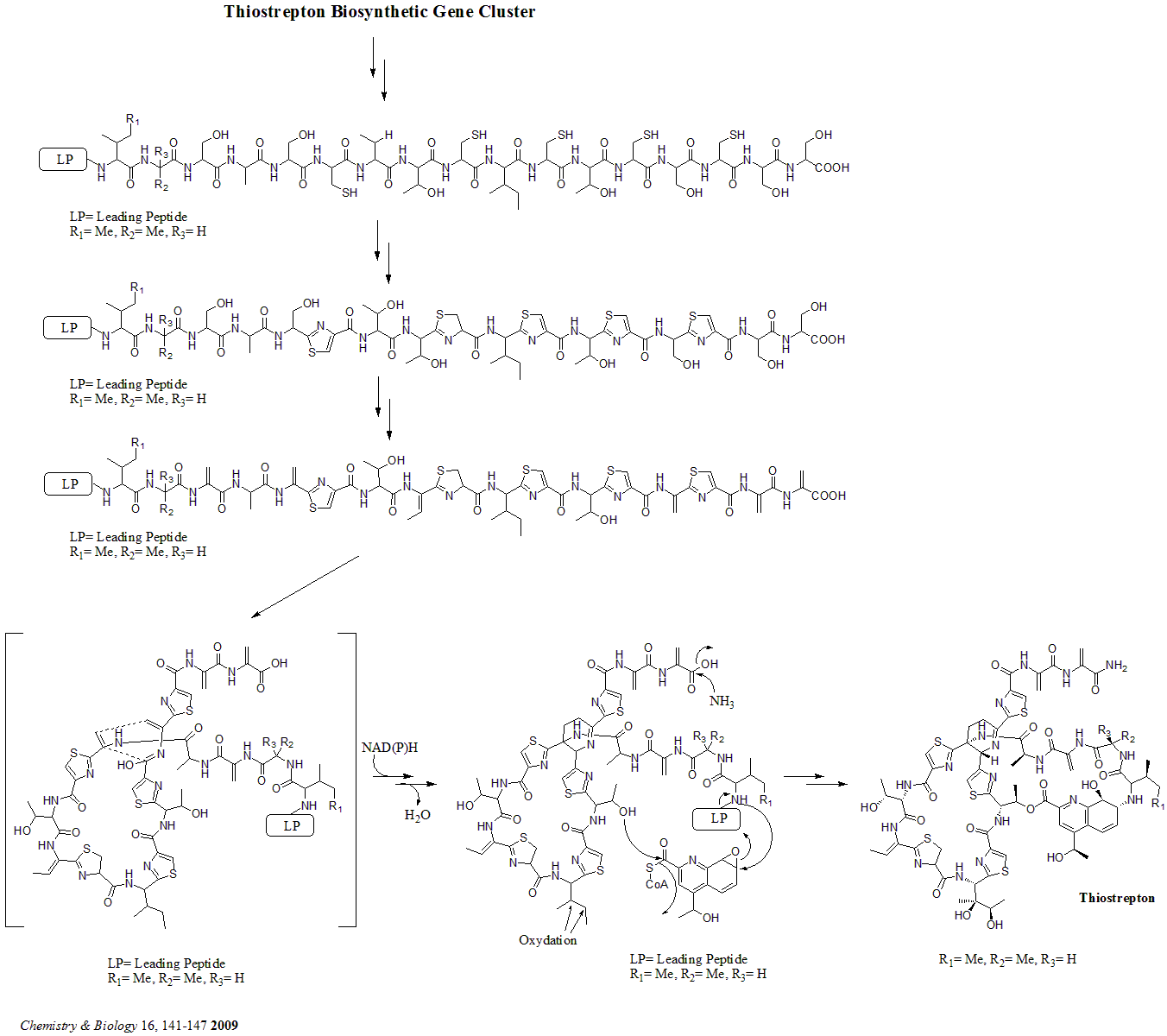
There are total 21 genes (tsrA~tsrU) in the biosynthetic gene cluster. The precursor of thiostrepton contains 58 amino acids in the peptide chain, which includes 41-aa leader peptide (LP) and 17-aa structural peptide (IASASCTTCICTCSCSS). Once the precursor is synthesized, cyclodehydratase tsrO and dehydrogenase tsrM catalyze the formation of thiazole or thiazoline from every cysteine residues in the peptide chain. After thiazole/thiazoline formation, dehydratases tsrJ, K and S then convert all the serine residues into dehydroalanines. A hetero Diels-Alder cyclization of the central dehydropiperidine (at S5, C13, and S14) has been suggested by Bycroft back to 1978 and been employed in the chemical synthesis of this core structure by Nicolaou ''et al.'' in 2005. An alternative mechanism of the dehydropiperidine formation has also been suggested by Kelly ''et al''. in 2009. Nevertheless, based on experimental evidence, tsrN and L are suggested to be responsible for the hetero Diels-Alder cyclization. The quinaldic acid moiety is suggested to be synthesized by the nine genes tsrFAEBDUPQI from tryptophan and then results in the closure of quinaldic acid macrocycle. At last, tsrR serves as a candidate for the oxidation of the Ile residue to afford thiostrepton.
Alternative mechanism for the formation of the dehydropiperidine core

Total synthesis
In 2005, Nicolaou ''et al.'' published the total synthesis of thiostrepton. At first, they constructed the key building blocks of thiostrepton (1): dehydropiperidine core (2), thiazoline macrocycle (3), bis-dehydroalanine tail (4), and quinaldic acid macrocycle (5). Then they assembled the building blocks sequentially as shown in the synthetic scheme (compound numbers are from the reference).Building blocks

Synthetic scheme

References
{{reflist, 33em Thiopeptides Heterocyclic compounds with 7 or more rings Antibiotics