|
Thessalian League
The Thessalian League (Thessalian Aeolic: , ''KoinÃĠn toÃṠn PetthaloÃṠn''; Attic: , ''KoinÃĠn tÃṀn ThettalÃṀn''; Ionic and Koine Greek: , ''KoinÃĠn tÃṀn ThessalÃṀn'') was a ''koinon'' or loose confederacy of feudal-like ''poleis'' and tribes in ancient Thessaly, located in the Thessalian plain in Greece. The seat of the Thessalian League was Larissa. Organization and Civil War The history of the Thessalian League can be traced back to the rule of king Aleuas, a member of the Aleuadae clan. One source states that it was under Aleuas that Thessaly was divided into four regions. Some time after the death of Aleuas, it is believed that the Aleuadae split into two families, the Aleuadae and the Scopadae. The former were based in the city of Larissa, which later became the capital of the League. The two families formed two powerful aristocratic parties and bore considerable influence over Thessaly. Jason and Macedon A lack of records makes it difficult to have any details of Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolic Greek
In linguistics, Aeolic Greek (), also known as Aeolian (), Lesbian or Lesbic dialect, is the set of dialects of Ancient Greek spoken mainly in Boeotia; in Thessaly; in the Aegean island of Lesbos; and in the Greek colonies of Aeolis in Anatolia and adjoining islands. The Aeolic dialect shows many archaisms in comparison to the other Ancient Greek dialects ( Arcadocypriot, Attic, Ionic, and Doric varieties), as well as many innovations. Aeolic Greek is widely known as the language of Sappho and of Alcaeus of Mytilene. Aeolic poetry, which is exemplified in the works of Sappho, mostly uses four classical meters known as the Aeolics: Glyconic (the most basic form of Aeolic line), hendecasyllabic verse, Sapphic stanza, and Alcaic stanza (the latter two are respectively named for Sappho and Alcaeus). In Plato's ''Protagoras'', Prodicus labelled the Aeolic dialect of Pittacus of Mytilene as "barbarian" (''barbaros''), because of its difference from the Attic literary style: "He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: ΣÏÎỲÏÏÎḟ, ''SpÃḂrtÄ''; Attic Greek: ΣÏÎỲÏÏÎṖ, ''SpÃḂrtÄ'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431â404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
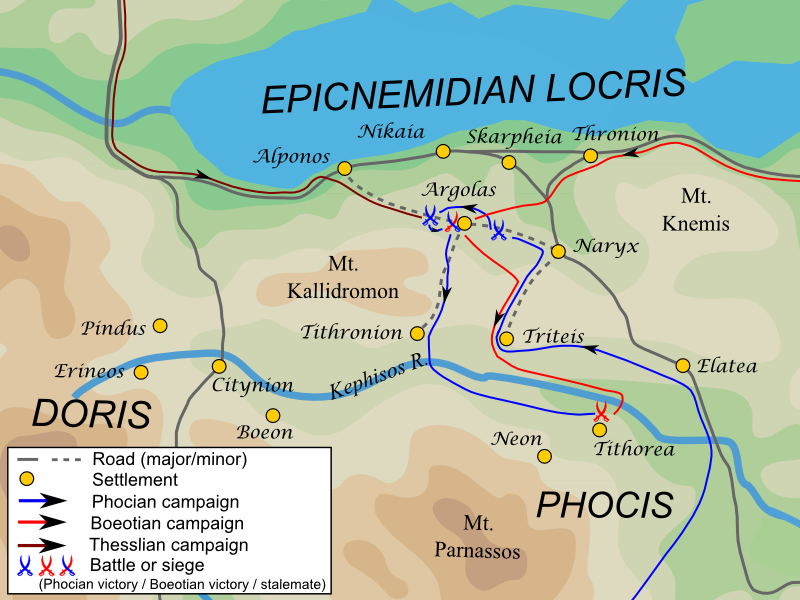
Third Sacred War
The Third Sacred War (356–346 BC) was fought between the forces of the Delphic Amphictyonic League, principally represented by Thebes, and latterly by Philip II of Macedon, and the Phocians. The war was caused by a large fine imposed in 357 BC on the Phocians by the Amphictyonic League (dominated at that moment by Thebes), for the offense of cultivating sacred land; refusing to pay, the Phocians instead seized the Temple of Apollo in Delphi, and used the accumulated treasures to fund large mercenary armies. Thus, although the Phocians suffered several major defeats, they were able to continue the war for many years, until eventually all parties were nearing exhaustion. Philip II used the distraction of the other states to increase his power in northern Greece, in the process becoming ruler of Thessaly. In the end, Philip's growing power, and the exhaustion of the other states, allowed him to impose a peaceful settlement of the war, marking a major step in the rise of Maced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phocis (ancient Region)
Phocis was an ancient region in the central part of Ancient Greece, which included Delphi. A modern administrative unit, also called Phocis, is named after the ancient region, although the modern region is substantially larger than the ancient one. Geopolitically, Phocis was the country of the Phocians, who spoke their own version of Doric Greek, one of the three main dialects of ancient Greek. They were one of several small mountain states of Central Greece, whose dialects are classified as Northwest Doric. It was from their region that the Dorians crossed the Gulf of Corinth at the beginning of the Greek Iron Age to burn Pylos and other southern Greek strongholds and seize control of the Peloponnesus. The dialects of the two groups of Dorians north and south of the Gulf then began to diverge. One of the states around Phocis was still called Doris in classical times. As there is considerable evidence that the invasion began about 1000 BC, the ancestors of the classical Phocia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphictyonic League
In Archaic Greece, an amphictyony ( grc-gre, áỳÎỳÏÎṗÎẃÏÏ ÎṡÎẄΟÎḟ, a "league of neighbors"), or amphictyonic league, was an ancient religious association of tribes formed before the rise of the Greek ''poleis''. The six Dorian cities of coastal southwest Anatolia and the twelve Ionian cities to the north that formed the Ionian League after a Meliac war in the mid-7th century BC, were already of considerable antiquity when the first written records emerge. An amphictyony consisting of polities under the aegis of Apollo's shrine at Delos was apparently well-established in the seventh century, as the Homeric Hymn to Delian Apollo of that approximate date lists them, those cities and islands that trembled and refused to offer themselves for the birthplace of Apollo when pregnant Leto went to each in turn; the Homeric hymn presents an origin myth for the cult of Apollo on Delos. The joint Ionian festival celebrated there was the Delia. The Delian Amphictyony arose in the 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Regions North And West Greece
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cineas Of Larissa
Cineas ( el, ÎÎṗÎẄÎÎḟÏ) was a man from Thessaly and an important adviser of King Pyrrhus. He had a reputation for great wisdom and was a pupil of Demosthenes the orator and was the only man who could be compared in skill with Demosthenes. Pyrrhus held him in high regard. Cineas was an Epicurean according to Cicero and Plutarch. Plutarch wrote that Pyrrhus sent Cineas to many cities in Greece as an ambassador and "used to say that more cities had been won for him by the eloquence of Cineas than by his own arms; and he continued to hold Cineas in especial honour and to demand his services." Plutarch wrote that prior to Pyrrhus undertaking the Pyrrhic War, Cineas tried to dissuade him from waging war against Rome in Italy and urged him to be satisfied with the possessions he already had. He asked Pyrrhus a series of questions: how he would use a victory against the Romans, what he would do after taking Italy, whether his expedition would stop with the taking of Sicily (according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archon
''Archon'' ( gr, áỳÏÏÏÎẄ, ÃḂrchÅn, plural: áỳÏÏÎṡÎẄÏÎṁÏ, ''ÃḂrchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem ÎḟÏÏ-, meaning "to be first, to rule", derived from the same root as words such as monarch and hierarchy. Ancient Greece In the early literary period of ancient Greece the chief magistrates of various Greek city states were called ''archontes''. The term was also used throughout Greek history in a more general sense, ranging from "club leader" to "master of the tables" at '' syssitia'' to "Roman governor". In Athens, a system of three concurrent archons evolved, the three office holders being known as ''archon eponymos'' (), the ''polemarch'' (), and the ''archon basileus'' (). According to Aristotle's '' Constitution of the Athenians'', the power of the king first devolved to the archons, and these offices were filled from the aristocracy by el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagus (title)
Tagus ( grc, ÏáẅḟÎġÏÏ, ÏÎỲÎġÎṖÏ) was a Thessalian title for a leader or general, especially the military leader of the Thessalian League. When occasion required, a chief magistrate was elected under the name of Tagus, whose commands were obeyed by all the four districts of Thessaly (Phthiotis, Thessaliotis, Histiaeotis, Pelasgiotis). He is sometimes called king ("''basileus''", Herodotus, V.63), and sometimes "''archon''" (Dionysius. V.74). Accordingly, Pollux (I.128), in his list of military designations, classes together the Boeotarchs of the Thebans, the Kings of Sparta, the Polemarchs of the Athenians, (in reference to their original duties), and the Tagoi of the Thessalians. When Jason of Pherae was Tagus, he had an army of more than 8,000 cavalry and not less than 20,000 hoplites. When Thessaly was not united under a Tagus, the subject towns possessed more independence. Philip II of Macedon and his son Alexander the Great Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:á ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy Aloros
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Î ÏÎṡÎṠÎṁÎỳÎḟáṡÎṡÏ, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''MathÄmatikÄ Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' TetrÃḂbiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadriparti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelopidas
Pelopidas (; grc-gre, Î ÎṁÎṠÎṡÏΟÎṀÎḟÏ; died 364 BC) was an important Theban statesman and general in Greece, instrumental in establishing the mid-fourth century Theban hegemony. Biography Athlete and warrior Pelopidas was a member of a distinguished family and possessed great wealth, which he expended on his friends and on public service while he himself was content to lead the rough life of an athlete.T Duff ed., ''Plutarch: The Age Of Alexander'' (Penguin 2011) p. 48-9 In 384 BC, he served in a Theban contingent sent to the support of the Spartans during the Siege of Mantinea, where he was saved, when dangerously wounded by the Arcadians, by Epaminondas and Agesipolis. ::Pelopidas, after receiving seven wounds in front, sank down upon a great heap of friends and enemies who lay dead together; but Epaminondas, although he thought him lifeless, stood forth to defend his body and his arms, and fought desperately, single-handed against many, determined to die rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip II Of Macedonia
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, ÎḊΟÎṠÎṗÏÏÎṡÏ ; 382 â 21 October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ancient kingdom, and the father of Alexander the Great. The rise of Macedonâits conquest and political consolidation of most of Classical Greece during his reignâwas achieved by his reformation of the army (the establishment of the Macedonian phalanx that proved critical in securing victories on the battlefield), his extensive use of siege engines, and his utilization of effective diplomacy and marriage alliances. After defeating the Greek city-states of Athens and Thebes at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, Philip II led the effort to establish a federation of Greek states known as the League of Corinth, with him as the elected hegemon and commander-in-chief of Greece for a planned invasion of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |