|
Thermophylae
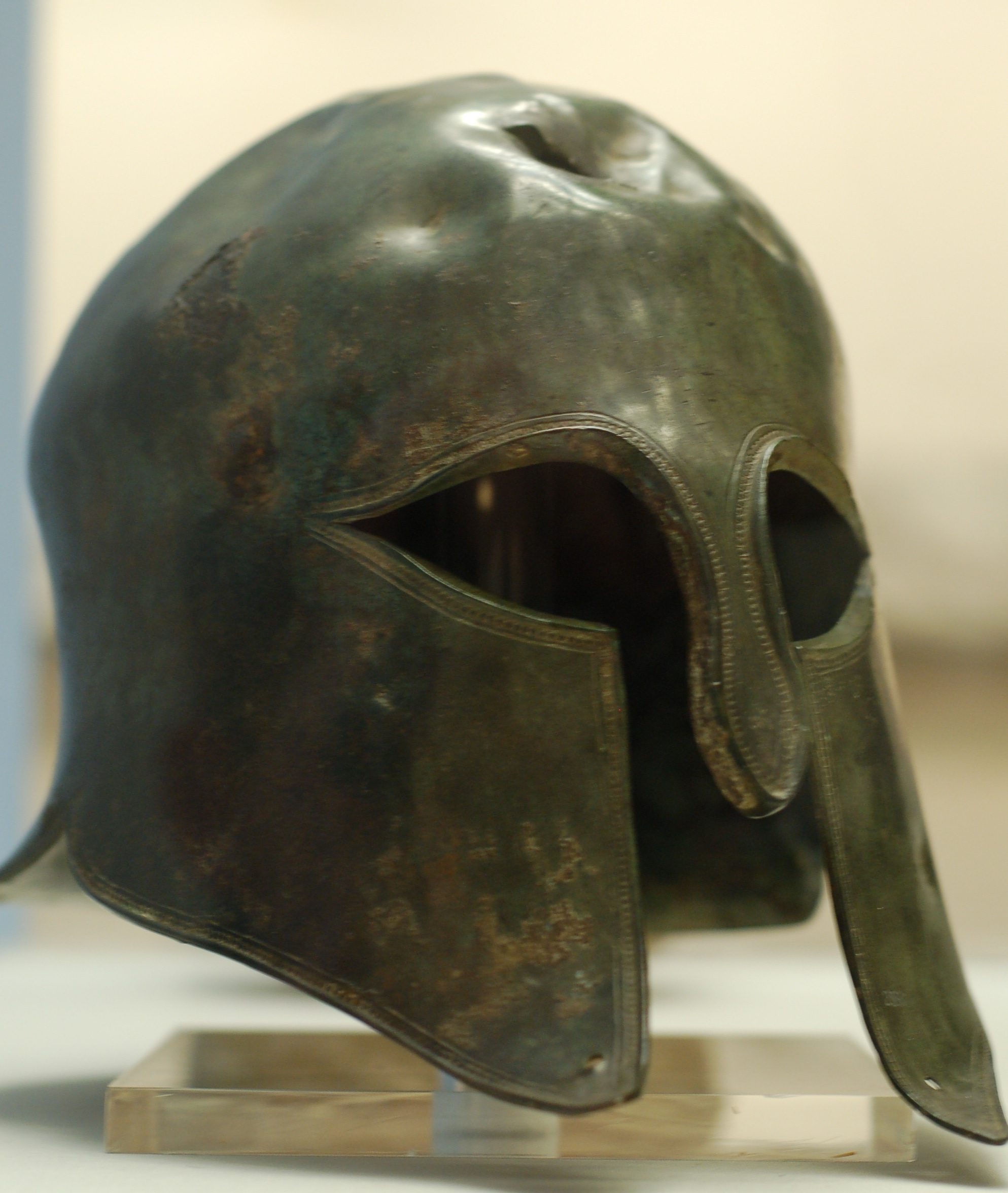
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label= Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Greco-Persian Wars. The engagement at Thermopylae occurred simultaneously with the Battle of Artemisium: between July and September 480 BC. The second Persian invasion under Xerxes I was a delayed response to the failure of the first Persian invasion, which had been initiated by Darius I and ended in 490 BC by an Athenian-led Greek victory at the Battle of Marathon. By 480 BC, a decade after the Persian defeat at Marathon, Xerxes had amassed a massive land and naval force, and subsequently set out to conquer all of Greece. In response, the Athenian politician and general Themistocles proposed that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great conquered the Greek-inhabited region of Ionia in 547 BC. Struggling to control the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed tyrants to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, embarked on an expedition to conquer the island of Naxos, with Persian support; however, the expedition was a debacle and, preempting his dismissal, Aristagoras incited all of Hellenic Asia Minor into rebellion against the Persians. This was the beginning of the Ionian Revolt, which would last until 493 BC, progressively drawing more regions of Asia Minor into the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
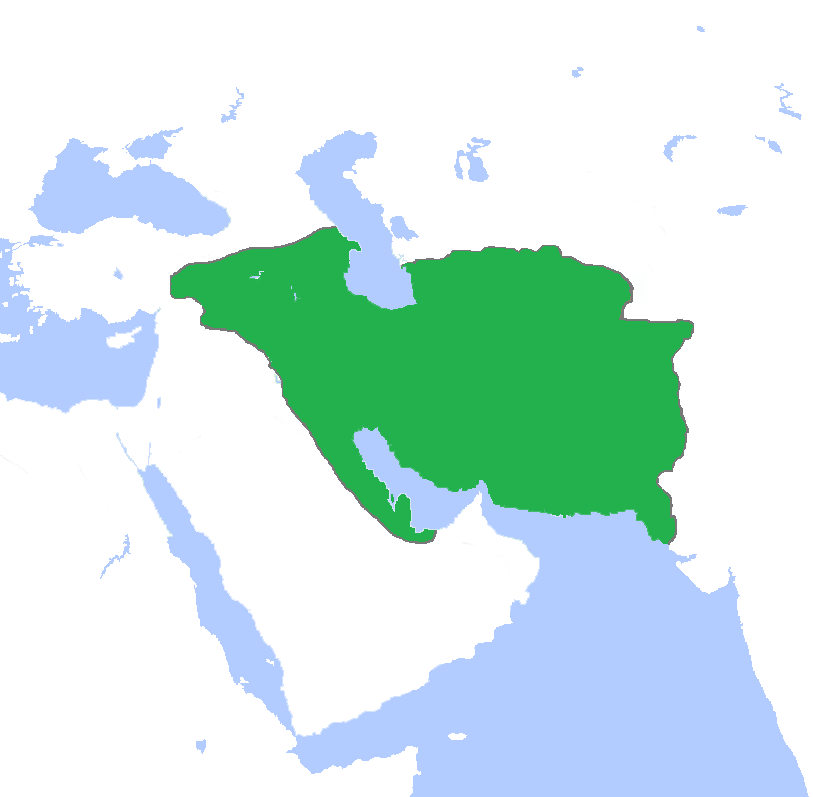
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Persian Invasion Of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece (492–490 BC) at the Battle of Marathon, which ended Darius I's attempts to subjugate Greece. After Darius's death, his son Xerxes spent several years planning for the second invasion, mustering an enormous army and navy. The History of Athens, Athenians and Spartans led the Greek resistance. About a tenth of the Greek city-states joined the 'Allied' effort; most remained neutral or submitted to Xerxes. The invasion began in spring 480 BC, when the Persian army crossed the Hellespont and marched through Thrace and Macedon to Thessaly. The Persian advance was blocked at the pass of Thermopylae by a small Allied force under King Leonidas I of Sparta; simultaneously, the Persian fleet was blocked by an Allied fleet at the straits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Iran
The military history of Iran has been relatively well-documented, with thousands of years' worth of recorded history. Largely credited to its historically unchanged geographical and geopolitical condition, the modern-day Islamic Republic of Iran (historically known as Persia) has had a long and checkered military culture and history; ranging from triumphant and unchallenged ancient military supremacy, affording effective superpower status for its time; to a series of near-catastrophic defeats (beginning with the destruction of Elam) at the hands of previously subdued and conquered peripheral nations, most notably including the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon as well as the Asiatic nomadic tribes at the northeastern boundary of the lands traditionally home to the Iranian peoples. Elam (3500–539 BCE) Medes (678–549 BCE) Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BCE) Oxus chariot model.jpg, A golden chariot made during Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BCE). Achaemenid true exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helots
The helots (; el, εἵλωτες, ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their exact characteristics, such as whether they constituted an Ancient Greek tribe, a social class, or both. For example, Critias described helots as " slaves to the utmost", whereas according to Pollux, they occupied a status "between free men and slaves". Tied to the land, they primarily worked in agriculture as a majority and economically supported the Spartan citizens. The number of helots in relation to Spartan citizens varied throughout the history of the Spartan state; according to Herodotus, there were seven helots for each Spartan at the time of the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC. Thus the need to keep the helot population in check and prevent rebellion was one of the main concerns of the Spartans. Helots were ritually mistreated and hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartan Army
The Spartan army stood at the center of the Spartan state, citizens trained in the disciplines and honor of a warrior society.Connolly (2006), p. 38 Subjected to military drills since early manhood, the Spartans became one of the most feared and formidable military forces in the Greek world, attaining legendary status in their wars against Persia. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – other Greeks commonly accepted that "one Spartan was worth several men of any other state." Tradition states that the semi-mythical Spartan legislator Lycurgus first founded the iconic army. Referring to Sparta as having a "wall of men, instead of bricks," he proposed reforming the Spartan society to develop a military-focused lifestyle following "proper virtues" such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. Spartan boys deemed strong enough entered the ''agoge'' regime at the age of seven, undergoing intense and rigorou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the '' Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artapanus (general)
Artapanus ( el, Αρτάπανος) was a Persian General under Xerxes I. He was the son of Artasyras, the chief of the Hyrcarnians. According to Ctesias' ''Persica'', Artapanus led the first wave of Persians against the Spartan force at the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. Although he led a force of 10,000 men, they were routed by the Spartan defenders. Artapanus is not mentioned by name in Herodotus' history of the battle. References See also * Artabanus of Persia Artabanus of Persia (or Artabanus the Hyrcanian; grc, Ἀρτάβανος) was a Persian political figure during the Achaemenid dynasty who was reportedly Regent of Persia for a few months (465 BC – 464 BC). This Artabanus is not to be confus ... Battle of Thermopylae Military leaders of the Achaemenid Empire 5th-century BC Iranian people Persian people of the Greco-Persian Wars {{MEast-mil-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydarnes The Younger
Hydarnes II ( peo, 𐎻𐎡𐎭𐎼𐎴, Vidṛna), also known as Hydarnes the Younger (by contrast with his father Hydarnes the Old) was a Persian commander of the Achaemenid Empire in the 5th century BC. He was the son of Hydarnes, satrap of the Persian empire and one of the seven conspirators against Gaumata. During the reign of Xerxes I, Hydarnes was one of the commanders for the Second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC. He was appointed as the leader of the 10,000-man contingent of "Immortals", while his brother Sisamnes commanded the levy of the Aryans. On the first day of the Battle of Thermopylae, Hydarnes led the Immortals against the phalanx of Spartans under Leonidas I, but an attempt to break through failed. On the second day, a local resident named Ephialtes betrayed the Greeks by telling the Persians about a hidden goat path around Thermopylae. This enabled Hydarnes and his Immortals to pass behind the Spartans, Thespians and Thebans and, as a result, defeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mardonius (nephew Of Darius I)
Mardonius ( peo, 𐎶𐎼𐎯𐎢𐎴𐎡𐎹 ; grc-gre, Μαρδόνιος ; died 479 BC) was a leading Persian military commander during the Persian Wars with Greece in the early 5th century BC who died at the Battle of Plataea. Early years Mardonius was the son of Gobryas, a Persian nobleman who had assisted the Achaemenid prince Darius when he claimed the throne. The alliance between the new king and his friend was cemented by diplomatic marriages: Darius married Gobryas' daughter, and Gobryas married Darius' sister. Furthermore, Mardonius married Darius' daughter Artozostra. Thus, Darius the Great was simultaneously Mardonius' uncle, father-in-law, and half-brother-in-law. Persian Wars with the Greeks First Persian invasion of Greece Darius appointed Mardonius as one of his generals and, after the Ionian Revolt, sent him in 492 BC to punish the Greek city-state of Athens for assisting the Ionians. On his way to Athens, he used his army in the Ionian cities to depose th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius the Great () and his mother was Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great (), the founder of the Achaemenid empire. Like his father, he ruled the empire at its territorial peak. He ruled from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC at the hands of Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard. Xerxes I is notable in Western history for his invasion of Greece in 480 BC. His forces temporarily overran mainland Greece north of the Isthmus of Corinth until losses at Salamis and Plataea a year later reversed these gains and ended the second invasion decisively. However, Xerxes successfully crushed revolts in Egypt and Babylon. Xerxes also oversaw the completion of various construction projects at Susa and Persepolis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |