|
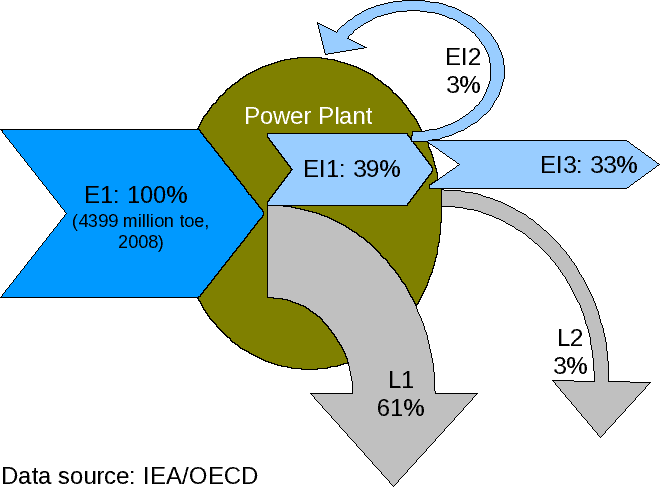
Thermodynamic Efficiency Limit
Thermodynamic efficiency limit is the absolute maximum theoretically possible conversion efficiency of sunlight to electricity. Its value is about 86%, which is the Chambadal-Novikov efficiency, an approximation related to the Carnot limit, based on the temperature of the photons emitted by the Sun's surface. Effect of band gap energy Solar cells operate as quantum energy conversion devices, and are therefore subject to the thermodynamic efficiency limit. Photons with an energy below the band gap of the absorber material cannot generate an electron-hole pair, and so their energy is not converted to useful output and only generates heat if absorbed. For photons with an energy above the band gap energy, only a fraction of the energy above the band gap can be converted to useful output. When a photon of greater energy is absorbed, the excess energy above the band gap is converted to kinetic energy of the carrier recombination. The excess kinetic energy is converted to heat thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conversion Efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency (''η'') is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The input, as well as the useful output may be chemical, electric power, mechanical work, light (radiation), or heat. The resulting value, ''η'' (eta), ranges between 0 and 1. Overview Energy conversion efficiency depends on the usefulness of the output. All or part of the heat produced from burning a fuel may become rejected waste heat if, for example, work is the desired output from a thermodynamic cycle. Energy converter is an example of an energy transformation. For example, a light bulb falls into the categories energy converter. \eta = \frac Even though the definition includes the notion of usefulness, efficiency is considered a technical or physical term. Goal or mission oriented terms include effectiveness and efficacy. Generally, energy conversion efficiency is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1.0, or 0% to 100%. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Mass (solar Energy)
The air mass coefficient defines the direct optical path length through the Earth's atmosphere, expressed as a ratio relative to the path length vertically upwards, i.e. at the zenith. The air mass coefficient can be used to help characterize the solar spectrum after solar radiation has traveled through the atmosphere. The air mass coefficient is commonly used to characterize the performance of solar cells under standardized conditions, and is often referred to using the syntax "AM" followed by a number. "AM1.5" is almost universal when characterizing terrestrial power-generating panels. Description Solar radiation closely matches a black body radiator at about 5,800 K.or more precisely 5,777 K as reported iNASA Solar System Exploration - Sun: Facts & Figures retrieved 27 April 2011 "Effective Temperature ... 5777 K" As it passes through the atmosphere, sunlight is attenuated by scattering and absorption; the more atmosphere through which it passes, the greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cell Efficiency
Solar-cell efficiency refers to the portion of energy in the form of sunlight that can be converted via photovoltaics into electricity by the solar cell. The efficiency of the solar cells used in a photovoltaic system, in combination with latitude and climate, determines the annual energy output of the system. For example, a solar panel with 20% efficiency and an area of 1 m2 will produce 200 kWh/yr at Standard Test Conditions if exposed to the Standard Test Condition solar irradiance value of 1000 W/m2 for 2.74 hours a day. Usually solar panels are exposed to sunlight for longer than this in a given day, but the solar irradiance is less than 1000 W/m2 for most of the day. A solar panel can produce more when the sun is high in the sky and will produce less in cloudy conditions or when the sun is low in the sky, usually the sun is lower in the sky in the winter. Two location dependant factors that affect solar PV efficiency are the dispersion and intensity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid state and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids. The effect has found use in electronic devices specialized for light detection and precisely timed electron emission. The experimental results disagree with classical electromagnetism, which predicts that continuous light waves transfer energy to electrons, which would then be emitted when they accumulate enough energy. An alteration in the intensity of light would theoretically change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, with sufficiently dim light resulting in a delayed emission. The experimental results instead show that electrons are dislodged only when the light exceeds a certain frequency—regardless of the light's intensity or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conversion Efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency (''η'') is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The input, as well as the useful output may be chemical, electric power, mechanical work, light (radiation), or heat. The resulting value, ''η'' (eta), ranges between 0 and 1. Overview Energy conversion efficiency depends on the usefulness of the output. All or part of the heat produced from burning a fuel may become rejected waste heat if, for example, work is the desired output from a thermodynamic cycle. Energy converter is an example of an energy transformation. For example, a light bulb falls into the categories energy converter. \eta = \frac Even though the definition includes the notion of usefulness, efficiency is considered a technical or physical term. Goal or mission oriented terms include effectiveness and efficacy. Generally, energy conversion efficiency is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1.0, or 0% to 100%. Ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Efficiency Of A Solar Cell
Solar-cell efficiency refers to the portion of energy in the form of sunlight that can be converted via photovoltaics into electricity by the solar cell. The efficiency of the solar cells used in a photovoltaic system, in combination with latitude and climate, determines the annual energy output of the system. For example, a solar panel with 20% efficiency and an area of 1 m2 will produce 200 kWh/yr at Standard Test Conditions if exposed to the Standard Test Condition solar irradiance value of 1000 W/m2 for 2.74 hours a day. Usually solar panels are exposed to sunlight for longer than this in a given day, but the solar irradiance is less than 1000 W/m2 for most of the day. A solar panel can produce more when the sun is high in the sky and will produce less in cloudy conditions or when the sun is low in the sky, usually the sun is lower in the sky in the winter. Two location dependant factors that affect solar PV efficiency are the dispersion and intensity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
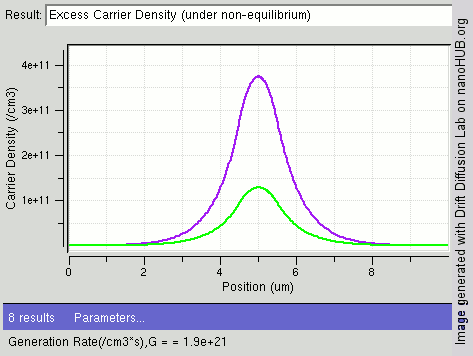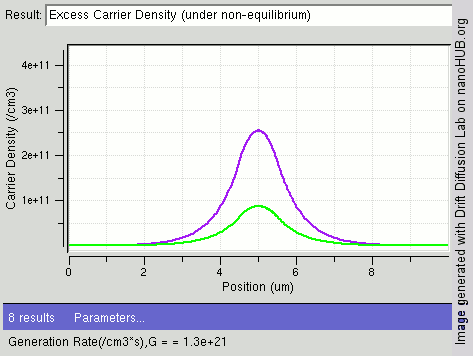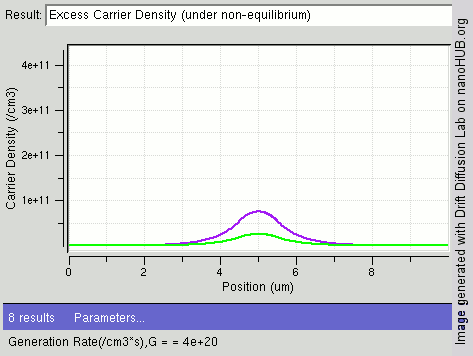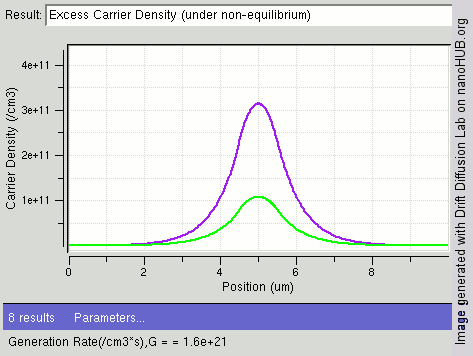
Radiative Recombination
In the solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes. The electron–hole pair is the fundamental unit of generation and recombination in inorganic semiconductors, corresponding to an electron transitioning between the valence band and the conduction band where generation of electron is a transition from the valence band to the conduction band and recombination leads to a reverse transition. Overview Like other solids, semiconductor materials have an electronic band structure determined by the crystal properties of the mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-body Radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous spectrum of wavelengths, inversely related to intensity, that depend only on the body's temperature, which is assumed, for the sake of calculations and theory, to be uniform and constant., Chapter 13. A perfectly insulated enclosure which is in thermal equilibrium internally contains black-body radiation, and will emit it through a hole made in its wall, provided the hole is small enough to have a negligible effect upon the equilibrium. The thermal radiation spontaneously emitted by many ordinary objects can be approximated as black-body radiation. Of particular importance, although planets and stars (including the Earth and Sun) are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Multiplication
In solar cell research, carrier multiplication is the phenomenon wherein the absorption of a single photon leads to the excitation of multiple electrons from the valence band to conduction band. In the theory of a conventional solar cell, each photon is only able to excite one electron across the band gap of the semiconductor, and any excess energy in that photon is dissipated as heat. In a material with carrier multiplication, high-energy photons excite on average more than one electron across the band gap, and so in principle the solar cell can produce more useful work. In quantum dot solar cells, the excited electron in the conduction band interacts with the hole it leaves behind in the valence band, and this composite uncharged object is known as an exciton. The carrier multiplication effect in a dot can be understood as creating multiple excitons, and is called multiple exciton generation (MEG). MEG may considerably increase the energy conversion efficiency of nanocrystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycrystalline Silicon Photovoltaics
Polycrystalline silicon, or multicrystalline silicon, also called polysilicon, poly-Si, or mc-Si, is a high purity, polycrystalline form of silicon, used as a raw material by the solar photovoltaic and electronics industry. Polysilicon is produced from metallurgical grade silicon by a chemical purification process, called the Siemens process. This process involves distillation of volatile silicon compounds, and their decomposition into silicon at high temperatures. An emerging, alternative process of refinement uses a fluidized bed reactor. The photovoltaic industry also produces upgraded metallurgical-grade silicon (UMG-Si), using metallurgical instead of chemical purification processes. When produced for the electronics industry, polysilicon contains impurity levels of less than one part per billion (ppb), while polycrystalline solar grade silicon (SoG-Si) is generally less pure. A few companies from China, Germany, Japan, Korea and the United States, such as GCL-Poly, Wacker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier Recombination
In the solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes. The electron–hole pair is the fundamental unit of generation and recombination in inorganic semiconductors, corresponding to an electron transitioning between the valence band and the conduction band where generation of electron is a transition from the valence band to the conduction band and recombination leads to a reverse transition. Overview Like other solids, semiconductor materials have an electronic band structure determined by the crystal properties of the material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |