|
Theodora Kantakouzene, Wife Of Alexios IV Of Trebizond
Theodora Kantakouzene Megale Komnene (died 12 November 1426) was the Empress consort of Alexios IV of Trebizond. Said to be very beautiful, according to the chronicle of Laonikos Chalkokondyles, she was accused by her son, John Megas Komnenos, of having an affair with the ''protovestiarios'' of the court of Trebizond; however, other accounts describe her as a faithful and loving wife, who kept the peace between Alexios and his sons. In either case, during her lifetime their son John fled to Georgia and did not return until after Theodora's death. Family Theodora's parentage is described by the Byzantinist Donald Nicol as "obscure". The '' Ecthesis Chronica'' implies she was the daughter of a holder of the military rank of ''protostrator'', and Nicol notes there are chronological grounds against identifying her father with one Manuel Kantakouzenos who was sent on a diplomatic mission to Sultan Mehmet I in the winter of 1420–1421.Donald M. Nicol, ''The Byzantine family of Kantak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
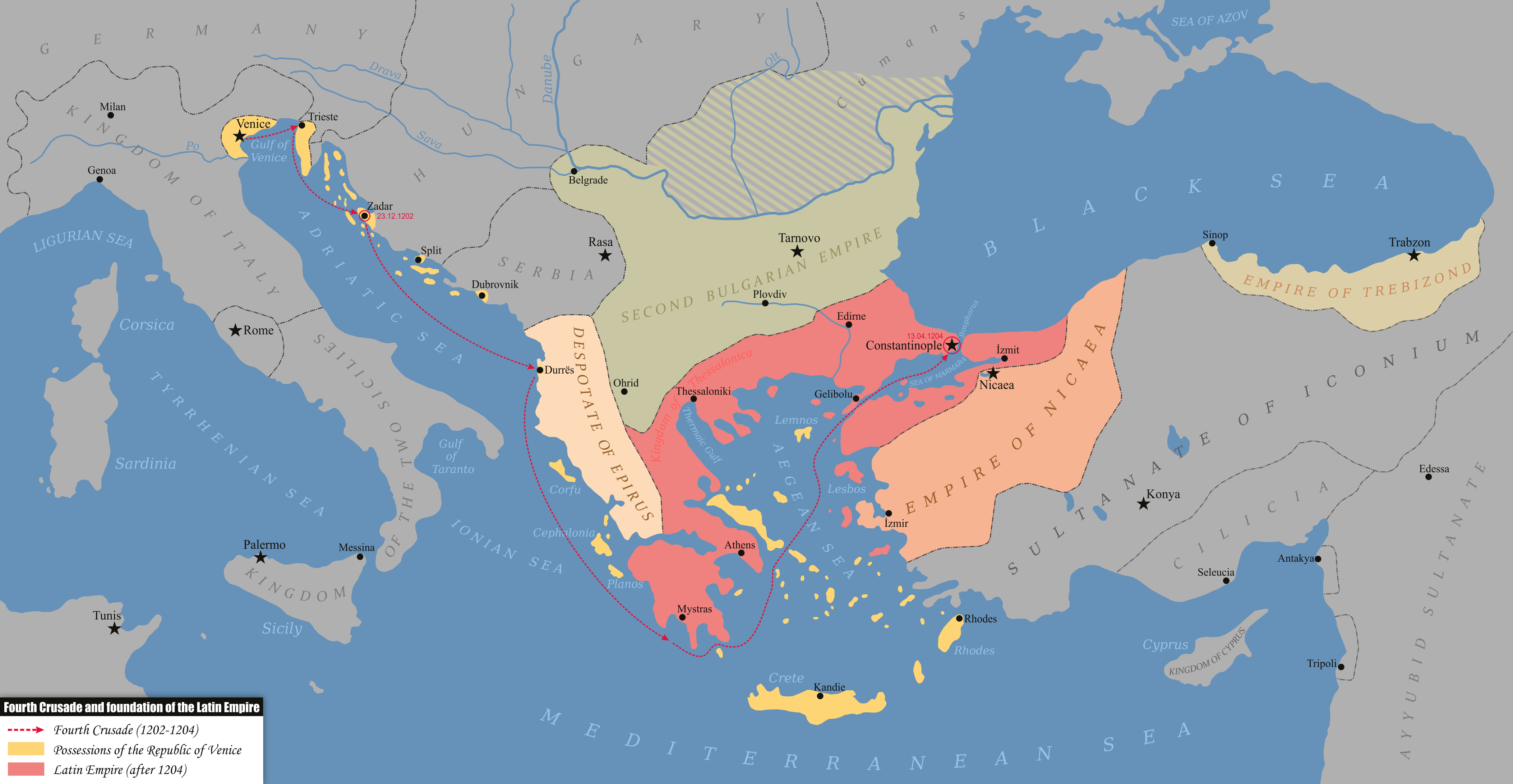
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of Anatolia, and portions of southern Crimea. The Trapezuntine Empire was formed in 1204 with the help of Queen Tamar of Georgia after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, which was commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the Sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself emperor and established himself in Trebizond (now Trabzon in Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of the deposed emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as Roman emperors against Alexios V Doukas. While the rulers of Trebizond bore the title of emperor until the end of their state in 1461, their rivals, the Laskarids in Nikaia and the Palaiologoi in Constantinople contested their claim to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecthesis Chronica
The Ecthesis () is a letter published in 638 CE by the Byzantine emperor Heraclius which defined monotheletism as the official imperial form of Christianity. Background The ''Ecthesis'' was another attempt by the Byzantine emperors to heal the divisions in the Christian Church over the disputes over the nature of Jesus Christ. In 451 the Council of Chalcedon had ruled that Christ did not possess one divine nature, but instead possessed two distinct natures, one fully divine and one fully human, with both acting in harmony together. This ruling was consistently rejected by the Non-Chalcedonians, who were against the idea of the two natures, maintaining that the humanity and divinity of Christ were united in one nature.Bury 2005, p. 249 Throughout the 6th century, the Byzantine Emperors either covertly encouraged this group ( Anastasius I), or actively persecuted them (Justin II). By the beginning of the 7th century, the court and the religious hierarchy at Constantinople were by and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Miller (historian)
William Miller, FBA (8 December 1864 – 23 October 1945) was a British-born medievalist and journalist. Biography The son of a Cumberland mine owner, Miller was educated at Rugby School and Hertford College, Oxford, where he gained a double first, and was called to the bar in 1889, but never practised law. He married Ada Mary Wright in 1895, and in 1896 published ''The Balkans'', followed in 1898 by ''Travels and Politics in the Near East''. In 1903 he and his wife left England for Italy, and despite an effort by Ronald Burrows to recruit Miller as the first incumbent of the Chair of Modern Greek and Byzantine History, Language, and Literature at London University, he and his wife spent the rest of their lives abroad. They lived in Rome (at ''Via Palestro'' 36) until 1923, when Miller found Benito Mussolini's rise to power distasteful, and they moved to Athens. There he was associated with the British School at Athens until the German invasion of Greece in 1941. During his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia (), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a Middle Ages, medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in Anno Domini, AD. It reached Georgian Golden Age, its Golden Age of political and economic strength during the reign of King David IV of Georgia, David IV and Queen Tamar of Georgia, Tamar the Great from the 11th to 13th centuries. Georgia became one of the pre-eminent nations of the Eastern_Orthodoxy#Distribution, Christian East, and its pan-Caucasus, Caucasian empire and network of tributaries stretched from Eastern Europe to Anatolia and northern frontiers of History_of_Iran#Medieval_period, Iran, while Georgia also maintained religious possessions abroad, such as the Monastery of the Cross in Jerusalem and the Iviron, Monastery of Iviron in Greece. It is the principal historical precursor of present-day Georgia (country), Georgia. Lasting for several centuries, the kingdom fell to the Mongol invasions of Georgia, Mongol invasions in the 13th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archon
''Archon'' (, plural: , ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem , meaning "to be first, to rule", derived from the same root as words such as monarch and hierarchy. Ancient Greece In the early literary period of ancient Greece, the chief magistrates of various Greek city states were called ''archontes''. The term was also used throughout Greek history in a more general sense, ranging from "club leader" to "master of the tables" at '' syssitia'' to "Roman governor". In Athens, a system of three concurrent archons evolved, the three office holders being known as ''archon eponymos'' (), the '' polemarch'' (), and the '' archon basileus'' (). According to Aristotle's '' Constitution of the Athenians'', the power of the king first devolved to the archons, and these offices were filled from the aristocracy by elections every ten years. During this period, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel III Of Trebizond
Manuel III Megas Komnenos (; 16 December 13645 March 1417) was Emperor of Empire of Trebizond, Trebizond from 20 March, 1390 to his death in 1417. The major event of Manuel's reign was the arrival of the Central Asian conqueror Timur, Tamerlane to Anatolia. This led to the virtual destruction of the Ottoman Empire, which had threatened the existence of Manuel's domain, in the Battle of Ankara. Although the Ottomans reconstituted their state after 10 years of civil war, this defeat extended the life and security of the Empire of Trebizond for several more decades. Life Manuel was the son of Emperor Alexios III of Trebizond by Theodora Kantakouzene. He was made heir apparent in 1377, after the death of his elder brother Basil. Manuel's domain had come under the growing threat of the ruler of the Ottoman Empire, Sultan Bayezid I, who in 1398 had led his army along the Black Sea coast as far as the border of the Empire of Trebizond. Tamerlane, who had campaigned in eastern Anatolia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revue Des études Byzantines
The ''Revue des études byzantines'' is an annual peer-reviewed academic journal covering the study of Greek Christianity and especially Byzantine civilization. It was established in 1897 as ''Échos d'Orient'', renamed ''Études byzantines'' in (with volume numbering restarting at 1), and obtaining its current title in 1946. The journal is published by Peeters on behalf of the Institut français d'études byzantines (Paris) and the editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ... is Olivier Delouis. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: References External links * Academic journals established in 1897 History journals Multilingual journals Peeters Publishers academic journals Annual journals {{history-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Spandounes
Theodore Spandounes (, ) was an early 16th-century Greek historian of noble Byzantine extraction; the son of exiles fleeing the Ottoman conquest of Byzantium who had settled in Venice, Italy. As a youth he stayed with relatives in Ottoman-ruled Macedonia and visited the Ottoman capital at Constantinople, acquiring a knowledge of their history and culture. In later life he served successive Popes as a counsellor and repeatedly advocated the dispatch of a new Crusade against the Ottomans. His chief legacy is his Italian-language history on the origins of the Ottoman state and its history up to that time, whose first version was published in 1509 in Italian and was soon translated into French. Spandounes continued working on it, with the final version appearing in 1538. The work is disorganized and contains errors, but is extremely valuable as a historical source for its wealth of information. Family and origin Theodore Spandounes was most probably born in Venice, the son of Matthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Kantakouzenos
Thomas Kantakouzenos ({{langx, el, Θωμάς Καντακουζηνός, ''Thomás Kantakouzenós'', modern pronunciation ''Thomás Kantakouzinós'', {{langx, sr, Тома Кантакузин/''Toma Kantakuzin''; died 25 July 1463) was a Byzantine aristocrat, a member of the Kantakouzenos family, who became a Serbian magnate and general that served Despot Đurađ Branković. He was the brother of Irene Kantakouzene, Đurađ's wife. Origin The Byzantinist Donald Nicol, who researched the family's history, categorically identifies him as the brother of George Palaiologos Kantakouzenos; Giovanni Musachi makes him the brother of Irene Kantakouzene, wife of Serbian Despot Đurađ Branković, but incorrectly states Thomas was the son of the Emperor John VI Kantakouzenos, an error DuCange repeats. Instead, he is more probably the son of Theodore Kantakouzenos.{{harvnb, Nicol, 1968, p=182. Nicol had backed away from his initial identification of Thomas' and George's father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos Palaiologos Kantakouzenos
Andronikos Palaiologos Kantakouzenos (died 4 June 1453) was the last Grand Domestic of the Byzantine Empire. Present in the city at the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, he was one of the group of high Imperial officials executed by Ottoman Sultan Mehmet II five days after the city was taken. Andronikos was amongst those who advised Emperor Constantine XI Palaiologos to take for his third wife Anna, the daughter of Emperor David of Trebizond, instead of Mara Mara or MARA may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Mara (''Doctor Who''), an evil being in two ''Doctor Who'' serials * Mara (She-Ra), fictional characters from the ''She-Ra and the Princesses of Power'' and ''The New Advent ..., the daughter of Đurađ Branković, despot of Serbia. His name appears on the treaty between Byzantium and Venice concluded in April 1448, in place of Demetrios Palaiologos Kantakouzenos, who was indisposed at the time.Nicol, ''Byzantine Family'', p. 180 He is likely the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megas Domestikos
The title of Grand domestic () was given in the 11th–15th centuries to the commander-in-chief of the Byzantine army, directly below the Byzantine Emperor. It evolved from the earlier office of the domestic of the Schools, and came to rank as one of the senior dignities in the Byzantine state during the last centuries of its existence. From Byzantium, it was also adopted by the breakaway Empire of Trebizond, as well as by the 14th-century Serbian Empire. History and evolution The title of the grand domestic is first mentioned in the 9th century, and most likely derives from the older office of ''domestikos tōn scholōn'' ("Domestic of the Schools"), with the epithet ''megas'' added to connote the supreme authority of its holder, following contemporary practice evident in other offices as well. Both titles appear to have co-existed for a time, with the grand domestic being a more exalted variant of the plain titles of the domestics of the East and of the West, until the late 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Palaiologos Kantakouzenos
George Palaiologos Kantakouzenos (; ca. 1390 – 1456/59.) was a Byzantine aristocrat, a member of the Kantakouzenos family, and adventurer. He is also known by the Turkish nickname Sachatai, which he earned in the service of the Despot Constantine early in his military career. Life George Palaiologos Kantakouzenos was likely the son of Theodore Palaiologos Kantakouzenos.Donald M. Nicol, ''The Byzantine Family of Kantakouzenos: Some Addenda and Corrigenda, Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 27'' (1973), p. 312-3 Among his siblings were the Despotess of Serbia Irene Kantakouzene, the Empress of Trebizond Helena, and the unnamed wife of King George VIII of Georgia. He was also a cousin of the last two Byzantine emperors, John VIII Palaiologos and Constantine XI Palaiologos. He spent his youth in the Byzantine capital, Constantinople, where he studied under John Chortasmenos. In later life he moved to the Despotate of the Morea, where he is attested in documents from Dubrovnik written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |