|
Theodor Scherer
Theodor Scherer (17 September 1889 – 17 May 1951) was a German lieutenant general and divisional commander in the Wehrmacht during World War II. Biography Early life and career Scherer was born at Höchstädt an der Donau on 17 September 1889. In July 1908, he enlisted as cadet officer in the Bavarian Army which served as part of the Imperial German Army. He was commissioned as lieutenant in the 12th Bavarian Infantry Regiment in 1910. He fought in World War I, and was captured by the British in July 1916 during the Battle of the Somme. Upon returning to his home country after the war, he was not retained in Germany's post-war military, the ''Reichswehr''. In 1920, Scherer became a police officer in Bavaria. In 1935, he rejoined the German Army, and was appointed Lieutnant-Colonel. By the start of World War II, Scherer had risen to Colonel and operated as a regimental commander at the Western Front. He led an infantry assault during the Wehrmacht's crossing of the Marne in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Höchstädt An Der Donau
Höchstädt an der Donau is a town in the district of Dillingen, Bavaria, Germany. It is situated near the banks of the Danube. It consists of the following suburbs: Höchstädt an der Donau, Deisenhofen, Oberglauheim, Schwennenbach and Sonderheim. The town is the seat of the municipal association Höchstädt an der Donau, which includes the towns Blindheim, Finningen, Lutzingen and Schwenningen. In the fifteenth and sixteenth century, the wealthy mercantile family Höchstetter, which came from the town, was part of the mercantile patriciate of Augsburg. In the early 18th century, the town was the site of two battles. The First Battle of Höchstädt (german: Erste Schlacht von Höchstädt) on 20 September 1703 cost over 5,000 lives. A year later in 1704, the Battle of Blenheim or Second Battle of Höchstädt (german: Zweite Schlacht von Höchstädt) occurred between the British and Austrian forces (led by John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War II)
The Western Front was a European theatre of World War II, military theatre of World War II encompassing Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, Netherlands, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, France, and Germany. The Italian campaign (World War II), Italian front is considered a separate but related theater. The Western Front's 1944-1945 phase was officially deemed the European Theater of Operations, United States Army, European Theater by the United States, whereas Italy fell under the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army, Mediterranean Theater along with North Africa. The Western Front was marked by two phases of large-scale combat operations. The first phase saw the capitulation of Luxembourg, Netherlands, Belgium, and France during May and June 1940 after their defeat in the Low Countries and the northern half of France, and continued into an air war between Germany and Britain that climaxed with the Battle of Britain. The second phase consisted of large- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
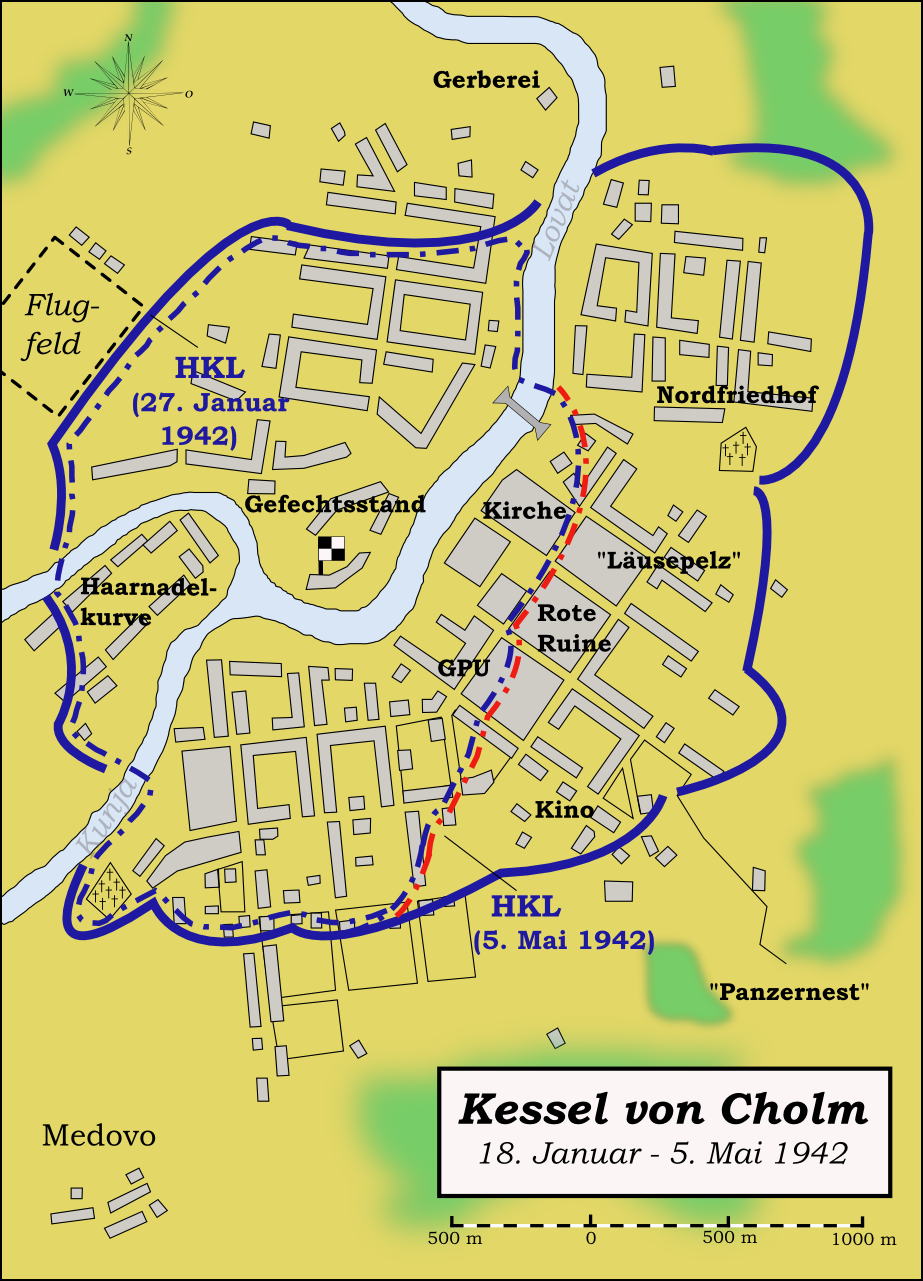
Cholm Shield
The Cholm Shield () was a World War II German military decoration awarded to those who fought in the Cholm Pocket on the Eastern Front between 21 January and 5 May 1942. It was instituted on 1 July 1942 and is the rarest of the German combat shields, with approximately 5,500 recipients. Awards ceased to be bestowed on 1 April 1943. Background and design In January 1942, the Soviet Red Army began a series of counteroffensives against the German Army. In the course of these operations, the German occupied town of Cholm (or Kholm) was attacked on 18 January 1942. By the 21 January the town was surrounded and cut off, creating the Cholm Pocket. Led by Generalmajor Theodor Scherer, a mixed group of Wehrmacht Heer, Luftwaffe fallschirmjager, Waffen-SS panzergrenadiers and Ordnungspolizei personnel were supplied by air until relieved on 5 May 1942. After the relief of Cholm, a commemorative shield was suggested by General Scherer to Adolf Hitler, who agreed to the award. A design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight's Cross Of The Iron Cross
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes), or simply the Knight's Cross (), and its variants, were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. The Knight's Cross was awarded for a wide range of reasons and across all ranks, from a senior commander for skilled leadership of his troops in battle to a low-ranking soldier for a single act of military valour. Presentations were made to members of the three military branches of the : the (army), the (navy) and the (air force), as well as the , the Reich Labour Service and the (German People storm militia), along with personnel from other Axis powers. The award was instituted on 1 September 1939, at the onset of the German invasion of Poland. The award was created to replace the many older merit and bravery neck awards of the German Empire. A higher grade, the Oak Leaves to the Knight's Cross, was instituted in 1940. In 1941, two higher grades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampfgruppe
In military history, the German term (pl. ; abbrev. KG, or KGr in usage during World War II, literally "fighting group" or "battle group") can refer to a combat formation of any kind, but most usually to that employed by the of Nazi Germany and its allies during World War II and, to a lesser extent, of the German Empire in World War I. It also referred to bomber groups in ''Luftwaffe'' usage, which themselves consisted of three or four (squadrons), and usually (but not exclusively) existed within bomber wings of three or four per wing. Nature The ''Kampfgruppe'' was an ''ad hoc'' combined arms formation, usually employing a combination of tanks, infantry, and artillery (including anti-tank) elements, generally organised for a particular task or operation.While the word ''Kampfgruppe'' in German literally refers to any battle group, the modern usage in the English-speaking world is restricted to World War II. ''Kampfgruppen'' in World War I lacked the panzer componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
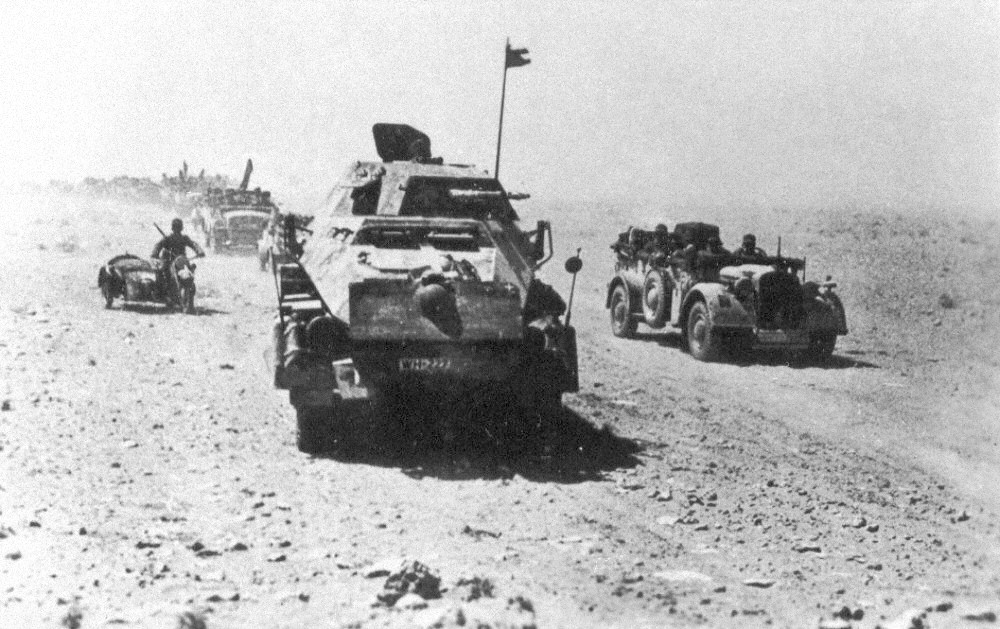
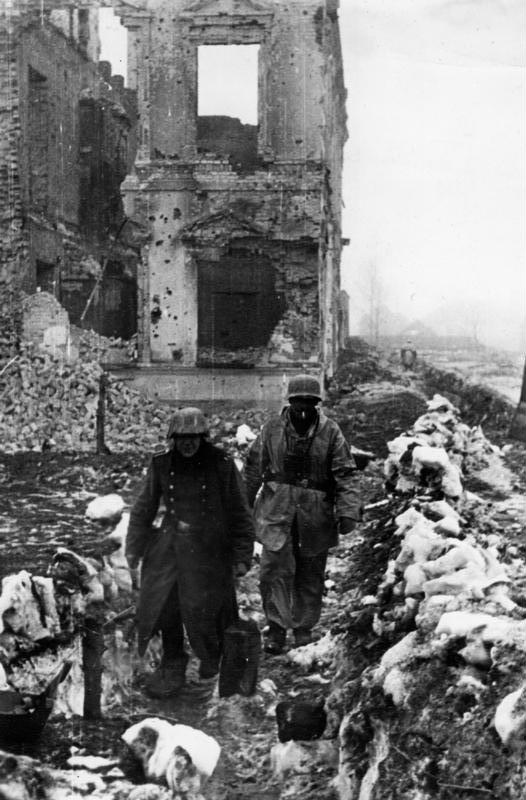
Kholm Pocket
The Kholm Pocket (german: Kessel von Cholm; russian: Холмский котёл) was the name given for the encirclement of German troops by the Red Army around Kholm, south of Leningrad, in World War II's the Eastern Front, from 23 January 1942 to 5 May 1942. A much larger pocket was meanwhile surrounded in Demyansk, about to the northeast. Both were the results of the German retreat following the defeat during the Battle of Moscow.Zabecki, p. 695–696 The air supply of Kholm and Demyansk was successful but led to an overconfidence in the German High Command on the Luftwaffe's ability to supply encircled forces by air, which would lead to disastrous consequences at the Battle of Stalingrad in late 1942 and early 1943. Overview At the Kholm pocket, 5,500 German soldiers held out for 105 days. The pocket was supplied by air but since it was too small for planes to land, supplies had to be dropped in and recovered by the German defenders. Among the airdropped supplies were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of Annihilation
A war of annihilation (german: Vernichtungskrieg) or war of extermination is a type of war in which the goal is the complete annihilation of a state, a people or an ethnic minority through genocide or through the destruction of their livelihood. The goal can be outward-directed or inward, against elements of one's own population. The goal is not like other types of warfare, the recognition of limited political goals, such as recognition of a legal status (such as in a war of independence), control of disputed territory (as in war of aggression or defensive war), or the total military defeat of an enemy state. Features War of annihilation is defined as a radicalized form of warfare in which "all psycho-physical limits" are abolished. The Hamburg Institute for Social Research social scientist Jan Philipp Reemtsma sees a war, "which is led, in the worst case, to destroy or even decimate a population", as the heart of the war of annihilation. The state organization of the enemy w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The army was established in January 1918. The Bolsheviks raised an army to oppose the military confederations (especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army) of their adversaries during the Russian Civil War. Starting in February 1946, the Red Army, along with the Soviet Navy, embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces; taking the official name of "Soviet Army", until its dissolution in 1991. The Red Army provided the largest land force in the Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its invasion of Manchuria assisted the unconditional surrender of Imperial Japan. During operations on the Eastern Front, it accounted for 75–80% of casual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kholm, Kholmsky District, Novgorod Oblast
Kholm (russian: Холм) is a town and the administrative center of Kholmsky District in Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Lovat and Kunya Rivers, north of Toropets, southwest of Staraya Russa, and south of Veliky Novgorod, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: History The Lovat River was a part of the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, one of the oldest trading routes passing through Rus'. The settlement was first mentioned in 1144 as Kholmsky pogost (). During the Middle Ages, the town, then a seat of the Princes of Kholm, withstood innumerable sieges by Lithuanians, Poles, and Swedes. In 1777, it was elevated in status to that of an uyezd town of Pskov Viceroyalty and given its present name. In 1796, it was transferred to Pskov Governorate. In August 1927, the uyezds were abolished and, effective October 1, 1927, Kholmsky District was established, with the administrative center in Kholm.Snytko et al., p. 85 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
281st Security Division (Wehrmacht)
281st Security Division (''281. Sicherungs-Division'') was a rear-security division in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany. Established in 1941, the unit was deployed in German-occupied areas of the Soviet Union, in the Army Group North Rear Area. The unit was converted to an infantry division in 1945, while stationed in Courland. Operational history Formed in March 1941, the 281st Security Division served in Army Group North Rear Area, in Northern Russia. In early 1942, commanded by General Theodor Scherer, elements of the division were encircled by the Soviet forces at Kholm in what became known as the Kholm Pocket. The pocket was relieved after four months.Mitcham, pp. 332–333 For the next two years, it was stationed in the northern sector and engaged in rear-area security and anti-partisan operations, although elements of the division saw action at the front line. One of the major anti-partisan operations it engaged in was Operation Frühjahrsbestellung in April 1943.Hill It w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a Theater (warfare), theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland and other Allies of World War II, Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, expos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |