|
The Pre-Socratics
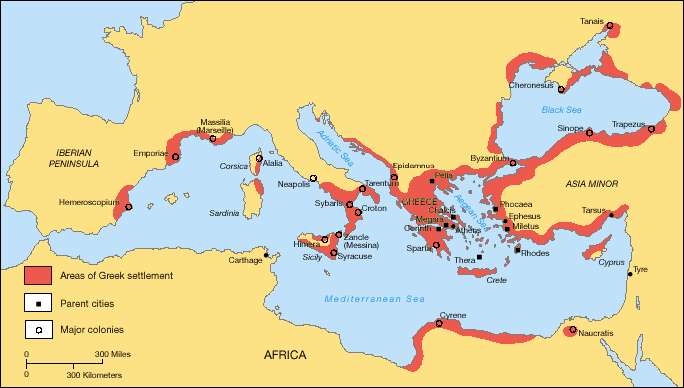
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of these early philosophers spanned the workings of the natural world as well as human society, ethics, and religion. They sought explanations based on natural law rather than the actions of gods. Their work and writing has been almost entirely lost. Knowledge of their views comes from ''testimonia'', i.e. later authors' discussions of the work of pre-Socratics. Philosophy found fertile ground in the ancient Greek world because of the close ties with neighboring civilizations and the rise of autonomous civil entities, ''poleis''. Pre-Socratic philosophy began in the 6th century BCE with the three Milesians: Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes. They all attributed the ''arche'' (a word that could take the meaning of "origin," "substance" or " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samos, Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionians, Ionian Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of Plato, Aristotle, and, through them, the Western philosophy, West in general. Knowledge of his life is clouded by legend, but he appears to have been the son of Mnesarchus, a gem-engraver on the island of Samos. Modern scholars disagree regarding Pythagoras's education and influences, but they do agree that, around 530 BC, he travelled to Crotone, Croton in southern Italy, where he founded a school in which initiates were sworn to secrecy and lived a communal, asceticism, ascetic lifestyle. This lifestyle entailed a number of dietary prohibitions, traditionally said to have included vegetarianism, although m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arche
''Arche'' (; grc, ἀρχή; sometimes also transcribed as ''arkhé'') is a Greek word with primary senses "beginning", "origin" or "source of action" (: from the beginning, οr : the original argument), and later "first principle" or "element". By extension, it may mean "first place", "method of government", "empire, realm", "authorities" (in plural: ), "command". The first principle or element corresponds to the "ultimate underlying substance" and "ultimate indemonstrable principle". In the philosophical language of the archaic period (8th to 6th century BC), ''arche'' (or ''archai'') designates the source, origin or root of things that exist. In ancient Greek philosophy, Aristotle foregrounded the meaning of ''arche'' as the element or principle of a thing, which although undemonstrable and intangible in itself, provides the conditions of the possibility of that thing. Mythical cosmogonies In the mythical Greek cosmogony of Hesiod (8th to 7th century BC), the origin of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empedocles
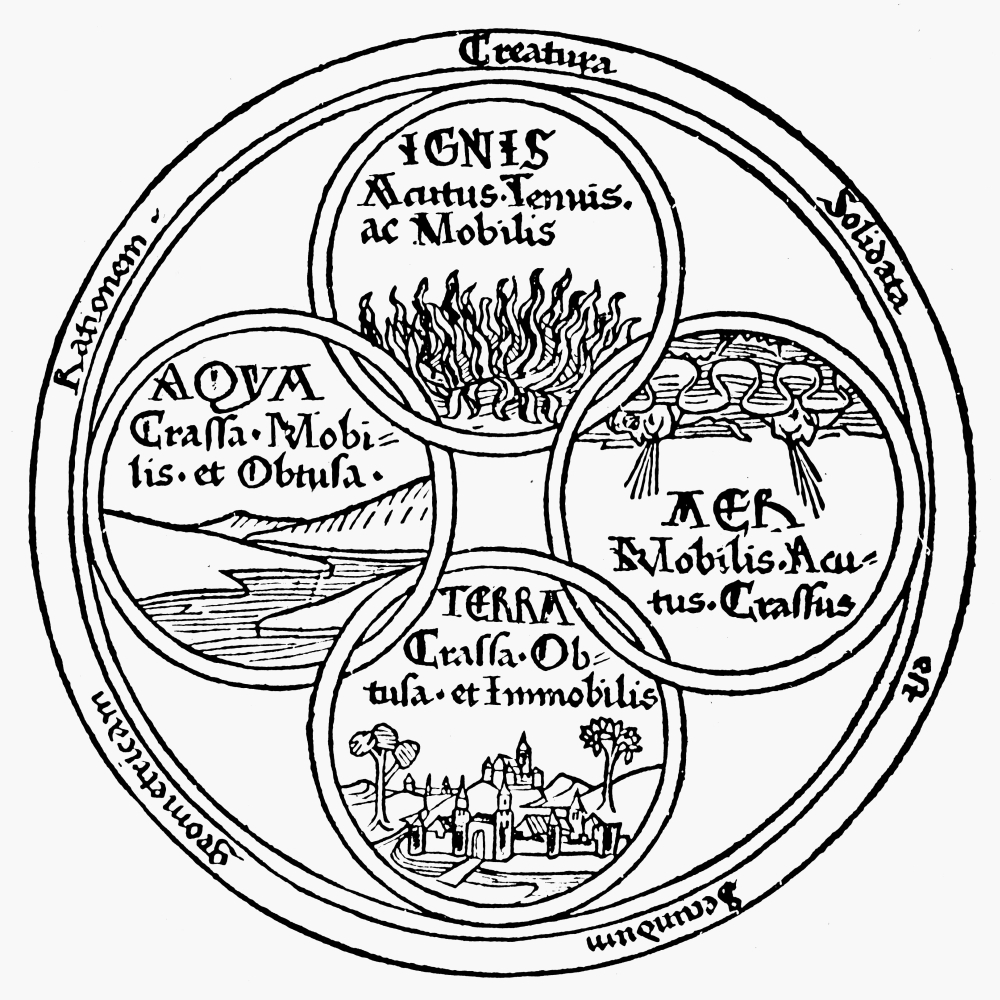
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the four classical elements. He also proposed forces he called Love and Strife which would mix and separate the elements, respectively. Empedocles challenged the practice of animal sacrifice and killing animals for food. He developed a distinctive doctrine of reincarnation. He is generally considered the last Greek philosopher to have recorded his ideas in verse. Some of his work survives, more than is the case for any other pre-Socratic philosopher. Empedocles' death was mythologized by ancient writers, and has been the subject of a number of literary treatments. Life Although the exact dates of Empedocles birth and death are unknown and ancient accounts of his life conflict on the exact details, they agree that he was born in the early 5th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaxagoras
Anaxagoras (; grc-gre, Ἀναξαγόρας, ''Anaxagóras'', "lord of the assembly"; 500 – 428 BC) was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, Anaxagoras came to Athens. According to Diogenes Laërtius and Plutarch, in later life he was charged with impiety and went into exile in Lampsacus; the charges may have been political, owing to his association with Pericles, if they were not fabricated by later ancient biographers. Responding to the claims of Parmenides on the impossibility of change, Anaxagoras introduced the concept of '' Nous'' ( Cosmic Mind) as an ordering force. He also gave a number of novel scientific accounts of natural phenomena, including the notion of panspermia, that life exists throughout the universe and could be distributed everywhere. He deduced a correct explanation for eclipses and described the Sun as a fiery mass larger than the Peloponnese, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melissus Of Samos
Melissus of Samos (; grc, Μέλισσος ὁ Σάμιος; ) was the third and last member of the ancient school of Eleatic philosophy, whose other members included Zeno and Parmenides. Little is known about his life, except that he was the commander of the Samian fleet in the Samian War. Melissus’ contribution to philosophy was a treatise of systematic arguments supporting Eleatic philosophy. Like Parmenides, he argued that reality is ungenerated, indestructible, indivisible, changeless, and motionless. In addition, he sought to show that reality is wholly unlimited, and infinitely extended in all directions; and since existence is unlimited, it must also be one. Life Not much information remains regarding the life of Melissus. He may have been born around 500 BC; the date of his death is unknown. The little which is known about him is mostly gleaned from a small passage in Plutarch’s ''Life of Pericles''. He was the commander of the Samian fleet in the Samian War, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeno Of Elea
Zeno of Elea (; grc, Ζήνων ὁ Ἐλεᾱ́της; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher of Magna Graecia and a member of the Eleatic School founded by Parmenides. Aristotle called him the inventor of the dialectic. He is best known for his paradoxes, which Bertrand Russell described as "immeasurably subtle and profound". Life Little is known for certain about Zeno's life. Although written nearly a century after Zeno's death, the primary source of biographical information about Zeno is Plato's ''Parmenides'' and he is also mentioned in Aristotle's ''Physics''. In the dialogue of ''Parmenides'', Plato describes a visit to Athens by Zeno and Parmenides, at a time when Parmenides is "about 65", Zeno is "nearly 40", and Socrates is "a very young man".Plato, ''Parmenides'127b–e (at footnote n. 2) Assuming an age for Socrates of around 20 and taking the date of Socrates' birth as 469 BC gives an approximate date of birth for Zeno of 490 BC. Plato says that Zeno was "tall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleatic School
The Eleatics were a group of pre-Socratic philosophers in the 5th century BC centered around the ancient Italian Greek colony of Elea ( grc, Ἐλέα), located in present-day Campania in southern Italy. The primary philosophers who are associated with the Eleatic doctrines are Parmenides, Zeno of Elea, and Melissus of Samos, although Xenophanes of Colophon and Empedocles have also sometimes been classified as members of this movement. The Eleatics have traditionally been seen as advocating a strict metaphysical view of monism in response to the materialist monism advocated by their predecessors, the Ionian school. History Patricia Curd states that the chronology of pre-Socratic philosophers is one of the most contentious issues of pre-Socratic philosophy. Many of the historical details mentioned by Plato, Diogenes Laertius, or Apollodorus are generally considered by modern scholarship to be of little value, and there are generally few exact dates that can be verified, so most e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called ''numerals''; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any number using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). In common usage, a ''numeral'' is not clearly distinguished from the ''number'' that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products. At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames are produced. The ''flame'' is the visible portion of the fire. Flames consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce Plasma (physics), plasma. Depending on the substances alight, and any impurities outside, the color of the flame and the fire's Intensity (heat transfer), intensity will be different. Fire in its most common form can result in conflagration, which has the potential to cause physical damage through burning. Fire is an important process that affects ecological systems around the globe. The positive effects of fire include stimulating growth and maintaining various ecological systems. Its negative effects include hazard to life and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impermanence
Impermanence, also known as the philosophical problem of change, is a philosophical concept addressed in a variety of religions and philosophies. In Eastern philosophy it is notable for its role in the Buddhist three marks of existence. It is also an element of Hinduism. In Western philosophy it is most famously known through its first appearance in Greek philosophy in the writings of Heraclitus and in his doctrine of ''panta rhei'' (everything flows). In Western philosophy the concept is also referred to as '' ''becoming''. Indian religions The Pali word for impermanence, ''anicca'', is a compound word consisting of ''"a"'' meaning non-, and ''"nicca"'' meaning "constant, continuous, permanent". While 'nicca' is the concept of continuity and permanence, 'anicca' refers to its exact opposite; the absence of permanence and continuity. The term is synonymous with the Sanskrit term ''anitya'' (a + nitya). The concept of impermanence is prominent in Buddhism, and it is also foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to abstract concepts such as nations, emotions, and natural forces, such as seasons and weather. Both have ancient roots as storytelling and artistic devices, and most cultures have traditional fables with anthropomorphized animals as characters. People have also routinely attributed human emotions and behavioral traits to wild as well as domesticated animals. Etymology Anthropomorphism and anthropomorphization derive from the verb form ''anthropomorphize'', itself derived from the Greek ''ánthrōpos'' (, "human") and ''morphē'' (, "form"). It is first attested in 1753, originally in reference to the heresy of applying a human form to the Christian God.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "anthropomorphism, ''n.''" Oxford University P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophanes
Xenophanes of Colophon (; grc, Ξενοφάνης ὁ Κολοφώνιος ; c. 570 – c. 478 BC) was a Greek philosopher A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ..., theologian, poet, and critic of Homer from Ionia who travelled throughout the Greek-speaking world in early Classical Antiquity. As a poet, Xenophanes was known for his critical style, writing poems that are considered among the first satires. He also composed elegiac couplets that criticised his society's traditional values of wealth, excesses, and athletic victories. He also criticised Homer and the other poets in his works for representing the gods as foolish or morally weak. His poems have not survived intact; only fragments of some of his work survives in quotations by later philosophers and literary c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

