|
The Pas, Manitoba
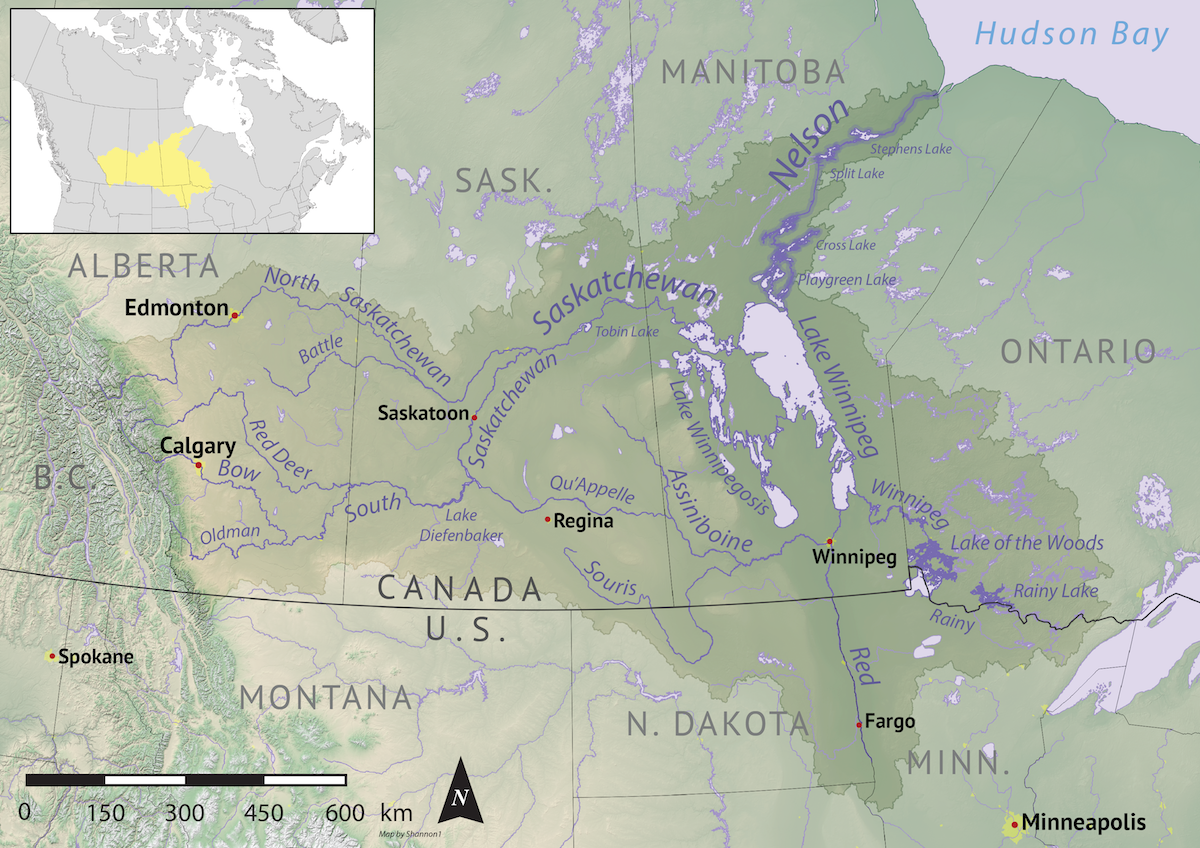
The Pas ( , ) is a town in Manitoba, Canada, at the confluence of the Pasquia River and the Saskatchewan River and surrounded by the unorganized Northern Region of the province. It is approximately northwest of the provincial capital, Winnipeg, and from the border of Saskatchewan. It is sometimes still called ''Paskoyac'' by locals after the first trading post, called Fort Paskoya, constructed in the 1740s by French and Canadian traders. The Pasquia River begins in the Pasquia Hills in east central Saskatchewan. The French in 1795 knew the river as Basquiau. Known as "The Gateway to the North", The Pas is a multi-industry northern Manitoba town serving the surrounding region. The main components of the region's economy are agriculture, forestry, commercial fishing, tourism, transportation, and services (especially health and education). The main employer is a paper mill operated by Canadian Kraft Paper Industries Ltd. The Pas contains one of the two main campuses of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces And Territories Of Canada
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully Independence, independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the List of countries and dependencies by area, world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the ''British North America Acts, British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territories are federal territories whose governments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Paskoya
Fort Paskoya (or Paskoyac or Pasquia) was a French fort and trading post on the lower Saskatchewan River above Cedar Lake. It was named after a Cree word for 'narrows', or after the Opaskwayak Cree Nation, whom the explorers encountered. "Paskoyac" was also an old name for the Saskatchewan River. There is also a Pasquia River at The Pas. History Around 1740, Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye built four forts to control the chain of lakes west of Lake Winnipeg. These were Fort Pascoya, Fort Bourbon, Fort Dauphin, and Fort La Reine. Their purpose was to trade in furs and to divert to Montreal furs that had previously gone to the English on Hudson Bay. Pascoya had a good location because most of the furs from the west and northwest came down the Saskatchewan. The forts were also part of a quest for a river that led to the western sea, which Verendrye now thought was the Saskatchewan. ''First Paskoya:'' In 1740 Louis-Joseph Gaultier de La Vérendrye mapped t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Most are members of national or regional Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, one of the largest Christian bodies in the world, and the world's third-largest Christian communion. When united and uniting churches, united churches in the Anglican Communion and the breakaway Continuing Anglican movement were not counted, there were an estimated 97.4 million Anglicans worldwide in 2020. Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The provinces within the Anglican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes (dimensional lumber). The Portable sawmill, "portable" sawmill is simple to operate. The log lies flat on a steel bed, and the motorized saw cuts the log horizontally along the length of the bed, by the operator manually pushing the saw. The most basic kind of sawmill consists of a chainsaw and a customized jig ("Alaskan sawmill"), with similar horizontal operation. Before the invention of the sawmill, boards were made in various manual labour, manual ways, either wood splitting, rived (split) and plane (tool), planed, hewing, hewn, or more often hand sawn by two men with a whipsaw, one above and another in a saw pit below. The earliest known mechanical mill is the Hierapolis sawmill, a Roman water-powered stone mill at Hierapolis, Asia M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
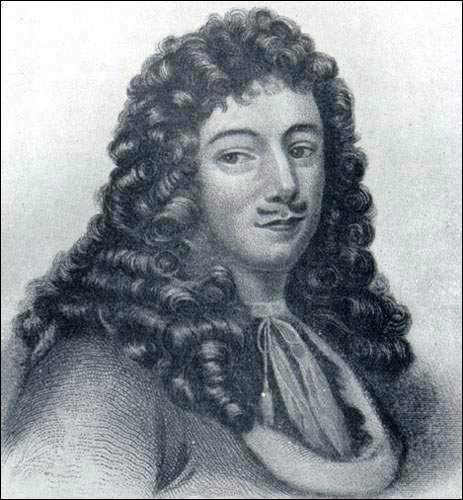
Pierre Gaultier De Varennes, Sieur De La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (17 November 1685 – 5 December 1749) was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader, and explorer. In the 1730s, he and his four sons explored the area west of Lake Superior and established trading posts there. They were part of a process that added Western Canada to the original New France territory that was centred along the Saint Lawrence basin. He was the first known European to reach present-day North Dakota and the upper Missouri River in the United States. In the 1740s, two of his sons crossed the prairie as far as present-day Wyoming, United States, and were the first Europeans to see the Rocky Mountains north of New Mexico. Early life Born in Trois-Rivières, New France, Pierre was the eldest son of René Gaultier de Varennes, who came to Canada as a soldier in 1665, and Marie, the daughter of Pierre Boucher, the first Governor of Trois-Rivières. The Gaultier family were minor nobility or landowners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and History of Spain (1700–1808), Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris (1763), Treaty of Paris. A vast viceroyalty, New France consisted of five colonies at its peak in 1712, each with its own administration: Canada (New France), Canada, the most developed colony, which was divided into the districts of Quebec (around what is now called Quebec City), Trois-Rivières, and Montreal; Hudson Bay; Acadia in the northeast; Terre-Neuve (New France), Terre-Neuve on the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland; and Louisiana (New France), Louisiana. It extended from Newfoundland to the Canadian Prairies and from Hudson Bay to the Gulf of Mexico, including all the Great Lakes of North America. The continent-traversing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provinces are partially covered by grasslands, plains, and Upland and lowland#Lowland, lowlands, mostly in the southern regions. The northernmost reaches of the Canadian Prairies are less dense in population, marked by forests and more variable topography. If the region is defined to include areas only covered by prairie land, the corresponding region is known as the Interior Plains. Physical or ecological aspects of the Canadian Prairies extend to northeastern British Columbia, but that area is not included in political use of the term. The prairies in Canada are a biome of Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands, temperate grassland and shrubland within the prairie ecoregion of Canada that consists of Canadian Aspen Forests and Parkland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the namesake Hudson's Bay (department store), Hudson's Bay department stores (colloquially The Bay), and also owns or manages approximately of gross leasable real estate through its HBC Properties and Investments business unit. HBC previously owned the full-line Saks Fifth Avenue and off-price Saks Off 5th in the United States, which were spun-off into the Saks Global holding company in 2024. After incorporation by royal charter issued in 1670 by Charles II of England, King Charles II, the company was granted a right of "sole trade and commerce" over an expansive area of land known as Rupert's Land, comprising much of the Hudson Bay drainage basin. This right gave the company a monopoly, commercial monopoly over that area. The HBC functioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Kelsey
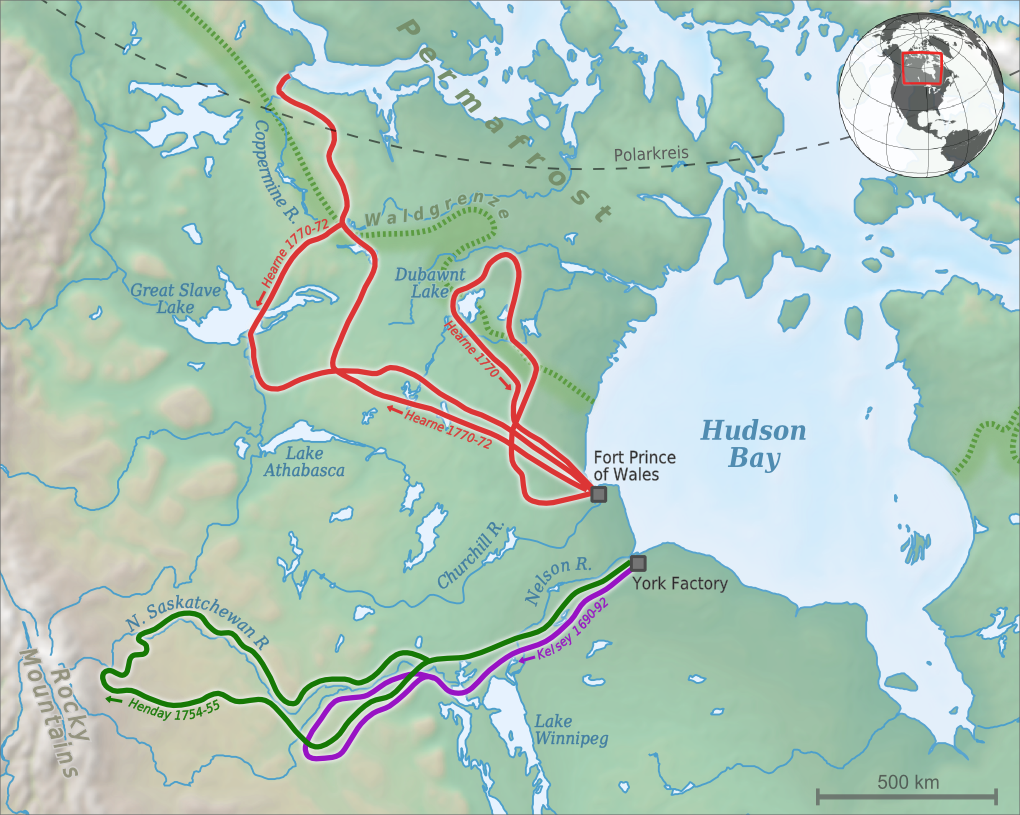
Henry Kelsey ( – 1 November 1724) was an English fur trader, explorer, and sailor who played an important role in establishing the Hudson's Bay Company in Canada. He is the first recorded European to have visited the present-day provinces of Saskatchewan and, possibly, Alberta, as well as the first to have explored the Great Plains from the north. In his travels to the plains he encountered several Plains First Nations, as well as vast herds of the American bison, their primary source of food. Early life and career Kelsey was born and married in East Greenwich, south-east of central London. Kelsey was apprenticed in London at age 17 to the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and departed England for Canada on 6 May 1684. He was posted at a fort on Hudson's Bay near present-day York Factory, Manitoba, near the mouth of the Nelson River on Hudson Bay. Kelsey started exploring in the winter of 1688–1689 when he and a First Nations boy carried mail overland 200 miles southeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swampy Cree
The Swampy Cree people, also known by their Exonym and endonym, autonyms ''Néhinaw'', ''Maskiki Wi Iniwak'', ''Mushkekowuk,'' ''Maškékowak, Maskegon'' or ''Maskekon'' (and therefore also ''Muskegon'' and ''Muskegoes'') or by exonyms including ''West Main Cree,'' ''Lowland Cree'', and ''Homeguard Cree'', are a division of the Cree Nation occupying lands located in northern Manitoba, along the Saskatchewan River in northeastern Saskatchewan, along the shores of Hudson Bay and adjoining interior lands south and west as well as territories along the shores of Hudson and James Bay in Ontario. They are geographically and to some extent culturally split into two main groupings, and therefore speak two dialects of the Swampy Cree language, which is an "n-dialect": * Western Swampy Cree called themselves: ''Mushkego'', ''Mushkegowuk'' (or ''Maškēkowak''), also called ''Lowland (Half-Homeguard) Cree'', speak the western dialect of the Swampy Cree language, while the ''s''/''š'' dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opaskwayak Cree Nation
The Opaskwayak Cree Nation (; OCN, Cree: ) is a First Nations band government located in Manitoba, Canada. The main OCN reserve is regarded as one of three distinct communities that comprise "The Pas area" in northern Manitoba, with the two others being the Town of The Pas and the Rural Municipality of Kelsey. Most of the OCN's on- reserve population lives near the Town of The Pas on the OCN 21E reserve, but the band also has many other reserves stretching from Goose Lake in the north to Mountain Cabin, Saskatchewan, in the south. OCN is accessible by rail, road, water, and air travel. Peoples of the OCN are Swampy Cree, and their dominant language is from the Swampy Cree ''n''-dialect.Klemp, Travis. 2022 March 8.Opaskwayak Cree Nation" ''The Canadian Encyclopedia''. Historica Canada. Retrieved 2023-01-15. The Opaskwayak people first negotiated and entered into Treaty 5 in 1876. The First Nation hosts the Opaskwayak Indigenous Days annually each August. History When the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |