|
The Monolith (islands)
The Monolith is a pair of small islets located off the southern tip of Sabrina Island within the Ross Dependency of Antarctica Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine .... The smaller of the two islets rises at a steep incline to above sea level, and is uninhabited even by penguins which have colonized the other nearby islands. References {{reflist Islands of Antarctica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balleny Islands
The Balleny Islands () are a series of uninhabited islands in the Southern Ocean extending from 66°15' to 67°35'S and 162°30' to 165°00'E. The group extends for about in a northwest-southeast direction. The islands are heavily glaciated and of volcanic origin. Glaciers project from their slopes into the sea. The islands were formed by the so-called Balleny hotspot. The group includes three main islands: Young, Buckle and Sturge, which lie in a line from northwest to southeast, and several smaller islets and rocks: *northeast of Young Island: Seal Rocks, Pillar *southeast of Young Island: Row Island, Borradaile Island (with Swan Base shelter hut) *south of Buckle Island: Scott Cone, Chinstrap Islet, Sabrina Islet (with Sabrina Refuge shelter hut), and the Monolith The islands are claimed by New Zealand as part of the Ross Dependency (see Territorial claims in Antarctica). Islands and rocks from north to south The islands' area totals and the highest point has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanent or tidal (i.e. surfaced reef or seamount); and may exist in the sea, lakes, rivers or any other sizeable bodies of water. Definition As suggested by its origin ''islette'', an Old French diminutive of "isle", use of the term implies small size, but little attention is given to drawing an upper limit on its applicability. The World Landforms website says, "An islet landform is generally considered to be a rock or small island that has little vegetation and cannot sustain human habitation", and further that size may vary from a few square feet to several square miles, with no specific rule pertaining to size. Other terms * Ait (/eɪt/, like eight) or eyot (/aɪ(ə)t, eɪt/), a small island. It is especially used to refer to river i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabrina Island
Sabrina Island is the largest of three small islets lying south of Buckle Island in the Balleny Islands of Antarctica and are part of New Zealand's Ross Dependency. Sabrina Island was named after Thomas Freeman's cutter when John Balleny's squadron discovered the islands in 1839. A pair of islets called The Monolith are located off of the island's southern tip. Birds The island has outstanding environmental and scientific value as a representative sample of the Balleny Islands – the only oceanic archipelago located within the main Antarctic Coastal Current. It is a breeding site for chinstrap and Adélie penguins as well as Cape petrels. The site is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
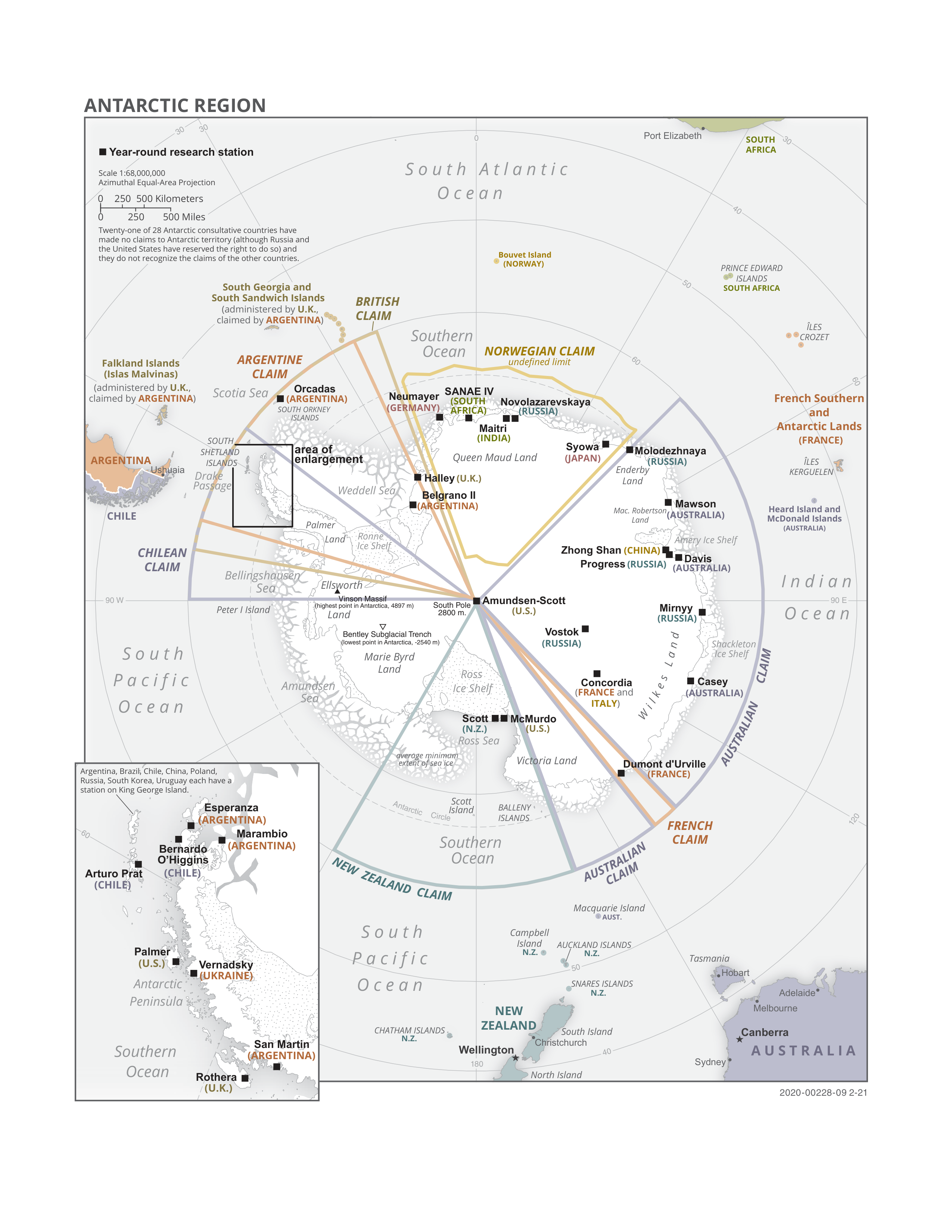
Ross Dependency
The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160° east to 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60° south. It is claimed by New Zealand, a claim accepted only by the other six countries with territorial claims in Antarctica. Under the 1961 Antarctic Treaty, of which all territorial claimants are signatories, including New Zealand, all claims are held in abeyance. Article IV states: "No acts or activities taking place while the present Treaty is in force shall constitute a basis for asserting, supporting or denying a claim to territorial sovereignty in Antarctica or create any rights of sovereignty in Antarctica". The Dependency takes its name from Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered the Ross Sea, and includes part of Victoria Land, and most of the Ross Ice Shelf. Ross, Balleny, Scott and Roosevelt Islands also form part of the Dependency. History of claim Following his discovery of Victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |