|
The Herodotus Machine
The Herodotus Machine was a machine described by Herodotus, a Greek historian born in Halicarnassus, Caria (modern-day Bodrum, Turkey). Herodotus claims this invention enabled the ancient Egyptians to construct the pyramids. The contraption supposedly allowed workers to lift heavy building materials. Herodotus is believed to have encountered the device while traveling through Egypt. With limited reference and no true schematics, this machine has stimulated many historians' theories of how the ancient Egyptians were able to create pyramids. Herodotus in Egypt Herodotus is suspected of having embellished – or made up entirely – some of his historical accounts, but scholars generally accept this particular account as Herodotus provides otherwise reasonable accounts of Egypt and it would have been quite possible for someone living in Halicarnassus to safely and easily travel to Egypt during Herodotus' lifetime. Trade existed between the Greek City States and the kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the '' Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histories (Herodotus)
The ''Histories'' ( el, Ἱστορίαι, ; also known as ''The History'') of Herodotus is considered the founding work of history in Western literature. Written around 430 BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, ''The Histories'' serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that were known in Greece, Western Asia and Northern Africa at that time. Although not a fully impartial record, it remains one of the West's most important sources regarding these affairs. Moreover, it established the genre and study of history in the Western world (despite the existence of historical records and chronicles beforehand). ''The'' ''Histories'' also stands as one of the earliest accounts of the rise of the Persian Empire, as well as the events and causes of the Greco-Persian Wars between the Persian Empire and the Greek city-states in the 5th century BC. Herodotus portrays the conflict as one between the forces of slavery (the Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
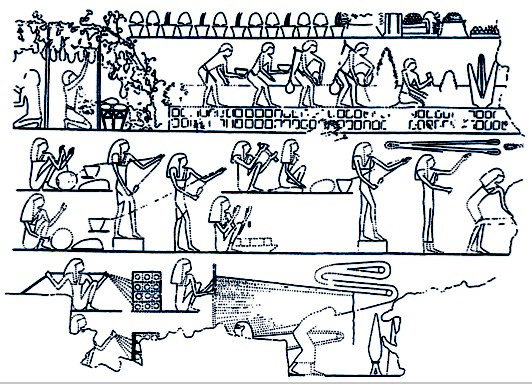
Ancient Egyptian Technology
Ancient Egyptian technology describes devices and technologies invented or used in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope trusses to stiffen the beam of ships. Egyptian paper, made from papyrus, and pottery were mass-produced and exported throughout the Mediterranean Basin. The wheel was used for a number of purposes, but chariots only came into use after the Second Intermediate Period. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime technology including ships and lighthouses. Technology in Dynastic Egypt Significant advances in ancient Egypt during the dynastic period include astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. Their geometry was a necessary outgrowth of surveying to preserve the layout and ownership of fertile farmland, which was flooded annually by the Nile River. The 3,4,5 right triangle and other rules of thumb served to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Science
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia around 3000 to 1200 BCE. These civilizations' contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine influenced later Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, wherein formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Latin-speaking Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but continued to thrive in the Greek-speaking Eastern Roman (or Byzantine) Empire. Aided by translations of Greek texts, the Hellenistic worldview was preserved and absorbed into the Arabic-speaking Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. The recovery and as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Architecture
Spanning over three thousand years, ancient Egypt was not one stable civilization but in constant change and upheaval, commonly split into periods by historians. Likewise, ancient Egyptian architecture is not one style, but a set of styles differing over time but with some commonalities. The best known example of ancient Egyptian architecture are the Egyptian pyramids, while excavated temples, palaces, tombs, and fortresses have also been studied. Most buildings were built of locally available mud brick and limestone by levied workers. Monumental buildings were built using the post and lintel method of construction. Many buildings were aligned astronomically. Columns were typically adorned with capitals decorated to resemble plants important to Egyptian civilization, such as the papyrus plant. Ancient Egyptian architectural motifs have influenced architecture elsewhere, reaching the wider world first during the Orientalizing period and again during the nineteenth-century E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Pyramid Construction Techniques
Egyptian pyramid construction techniques are the controversial subject of many hypotheses. These techniques seem to have developed over time; later pyramids were not constructed in the same way as earlier ones. Most of the construction hypotheses are based on the belief that huge stones were carved from quarries with copper chisels, and these blocks were then dragged and lifted into position. Disagreements chiefly concern the methods used to move and place the stones. In addition to the many unresolved arguments about the construction techniques, there have been disagreements as to the kind of workforce used. The Greeks, many years after the event, believed that the pyramids must have been built by slave labor. Archaeologists now believe that the Great Pyramid of Giza (at least) was built by tens of thousands of skilled workers who camped near the pyramids and worked for a salary or as a form of tax payment (levy) until the construction was completed, pointing to workers' cemeteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Madrid (Leonardo)
The Madrid Codices I–II (I – Ms. 8937 i II – Ms. 8936), are two manuscripts by Leonardo da Vinci which were discovered in the Biblioteca Nacional de España in Madrid in 1965 by Dr. Jules Piccus, Language Professor at the University of Massachusetts. The Madrid Codices I was finished during 1490 and 1499, and II from 1503 to 1505.Codexes The two codices were brought to Spain by , a sculptor in the court of . After various changes of ownership, they were transferred to the monastic library of |
Leonardo Da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on his achievements as a painter, he also became known for #Journals and notes, his notebooks, in which he made drawings and notes on a variety of subjects, including anatomy, astronomy, botany, cartography, painting, and paleontology. Leonardo is widely regarded to have been a genius who epitomized the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist ideal, and his List of works by Leonardo da Vinci, collective works comprise a contribution to later generations of artists matched only by that of his younger contemporary, Michelangelo. Born Legitimacy (family law), out of wedlock to a successful Civil law notary, notary and a lower-class woman in, or near, Vinci, Tuscany, Vinci, he was educated in Florence by the Italian painter and sculptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Sources cite at least 118 identified "Egyptian" pyramids. Approximately 80 pyramids were built within the Kingdom of Kush, now located in the modern country of Sudan. Of those located in modern Egypt, most were built as tombs for the country's pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. The earliest known Egyptian pyramids are found at Saqqara, northwest of Memphis, although at least one step-pyramid-like structure has been found at Saqqara, dating to the First Dynasty: Mastaba 3808, which has been attributed to the reign of Pharaoh Anedjib, with inscriptions, and other archaeological remains of the period, suggesting there may have been others. The otherwise earliest among these is the Pyramid of Djoser built during the Third Dynasty. This pyramid and its surrounding complex are generally considered to be the world's oldest monumental structures constructed of dresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

.jpg)