|
The Goddess Of Spring
''The Goddess of Spring'' is a 9-minute ''Silly Symphonies'' animated Disney short film. The Symphony is imbued with operatic themes and is often cited as melodramatic. It was released in 1934, and its production was important to the future development of Disney's ''Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs'' animation. Each Silly Symphony was a technological marvel at the time and proceeded to further advancements in the animation industry. While the plot of ''The Goddess of Spring'' follows the Greek myth of Persephone (known as “Proserpina” in Roman Mythology) and Hades (Pluto), the imagery is more evocative of Hell and Satan (or, more specifically, a traditional stage Mephistopheles). Plot There once was a time in the long, long, ago, when there was joy and laughter everywhere, when the flowers that grew, blossomed all the year through, and the world was eternally fair. For there lived a maiden, so gentle was she, that all the world loved her tenderly, and life was then so pleasant, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfred Jackson
Wilfred Jackson (January 24, 1906 – August 7, 1988) was an American animator, arranger, composer and director best known for his work on the ''Mickey Mouse'' and ''Silly Symphonies'' series of cartoons and the ''Night on Bald Mountain''/''Ave Maria'' segment of ''Fantasia'' from Walt Disney Productions. He was also instrumental in developing the system with which Disney added music and sound to ''Steamboat Willie'', the first ''Mickey Mouse'' cartoon. Several of the ''Silly Symphony'' shorts he directed, including ''The Old Mill'' (1937), won Academy Awards during the 1930s. Starting with ''Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs'' in 1937, he directed sequences in many of the major Disney animated features up to ''Lady and the Tramp'' in 1955, including all of the animated sequences in ''Song of the South'' (1946). He later moved into television, producing and directing for Disney's ''Disneyland'' series. After continuing health issues, he retired in 1961. Jackson died at age 82 in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animated Film
Animation is a method by which image, still figures are manipulated to appear as Motion picture, moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent cel, celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most animations are made with computer-generated imagery (CGI). Computer animation can be very detailed Computer animation#Animation methods, 3D animation, while Traditional animation#Computers and traditional animation, 2D computer animation (which may have the look of traditional animation) can be used for stylistic reasons, low bandwidth, or faster real-time renderings. Other common animation methods apply a stop motion technique to two- and three-dimensional objects like cutout animation, paper cutouts, puppets, or Clay animation, clay figures. A cartoon is an animated film, usually a short film, featuring an cartoon, exaggerated visual style. The style takes inspiration from comic strips, often featuring anthropomorphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld. The concept of an underworld is found in almost every civilization and "may be as old as humanity itself". Common features of underworld myths are accounts of living people making journeys to the underworld, often for some heroic purpose. Other myths reinforce traditions that entrance of souls to the underworld requires a proper observation of ceremony, such as the ancient Greek story of the recently dead Patroclus haunting Achilles until his body could be properly buried for this purpose. Persons having social status were dressed and equipped in order to better navigate the underworld. A number of mythologies incorporate the concept of the soul of the deceased making its own journey to the underworld, with the dead needing to be taken a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Angiospermae). The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing (fusion of sperm and eggs from different individuals in a population) resulting from cross-pollination or allow selfing (fusion of sperm and egg from the same flower) when self-pollination occurs. There are two types of pollination: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower, or another flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination is when pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. Self-pollination happens in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time, and are positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mephistopheles
Mephistopheles (, ), also known as Mephisto, is a demon featured in German folklore. He originally appeared in literature as the demon in the Faust legend, and he has since appeared in other works as a stock character (see: Mephistopheles in the arts and popular culture). Etymology and name meaning The name ''Mephistopheles'' is a corrupted Greek compound. The Greek particle of negation (μη, ''mē'') and the Greek word for love or loving (φίλος, ''philos'') are the first and last terms of the compound but the middle term is more doubtful. For the middle term, three meanings have been noticed and three different complete etymologies have been established: *not loving light (φως το, ''phōs to''; the old form of the word being ''Mephostopheles'') *not loving Faust *allied to '' mephitic,'' a term which designates the poisonous vapors arising from the earth in certain places—pools, caverns, springs—destructive of human life. It is likely that the name was invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satan
Satan,, ; grc, ὁ σατανᾶς or , ; ar, شيطانالخَنَّاس , also known as Devil in Christianity, the Devil, and sometimes also called Lucifer in Christianity, is an non-physical entity, entity in the Abrahamic religions that seduces humans into sin or falsehood. In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God in Judaism, God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the ''yetzer hara'', or "evil inclination." In Christianity and Islam, he is usually seen as a fallen angel or jinn who has rebelled against God in Abrahamic religions, God, who nevertheless allows him temporary power over the fallen world and a host of demons. In the Quran, Shaitan, also known as Iblis, is an entity made of fire who was cast out of Heaven because he refused to bow before the newly created Adam in Islam, Adam and incites humans to sin by infecting their minds with ''waswās'' ("evil suggestions"). A figure known as ''ha-satan'' ("the satan") first appears in the Hebrew B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hells as eternal destinations, the biggest examples of which are Christianity and Islam, whereas religions with reincarnation usually depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations, as is the case in the dharmic religions. Religions typically locate hell in another dimension or under Earth's surface. Other afterlife destinations include heaven, paradise, purgatory, limbo, and the underworld. Other religions, which do not conceive of the afterlife as a place of punishment or reward, merely describe an abode of the dead, the grave, a neutral place that is located under the surface of Earth (for example, see Kur, Hades, and Sheol). Such places are sometimes equated with the English word ''hell'', though a more correct translatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluto (mythology)
In Religion in ancient Greece, ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Pluto ( gr, Πλούτων, ') was the ruler of the Greek underworld. The earlier name for the god was Hades, which became more common as the name of the underworld itself. Pluto represents a more positive concept of the god who presides over the afterlife. ''Ploutōn'' was frequently conflation, conflated with Plutus, Ploûtos, the Greek god of wealth, because mineral wealth was found underground, and because as a chthonic god Pluto ruled the deep earth that contained the seeds necessary for a bountiful harvest. The name ''Ploutōn'' came into widespread usage with the Eleusinian Mysteries, in which Pluto was venerated as both a stern ruler and a loving husband to Persephone. The couple received souls in the afterlife and are invoked together in religious inscriptions, being referred to as ''Plouton'' and as ''Kore'' respectively. Hades, by contrast, had few temples and religious practices assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also made him the last son to be regurgitated by his father. He and his brothers, Zeus and Poseidon, defeated their father's generation of gods, the Titans, and claimed rulership over the cosmos. Hades received the underworld, Zeus the sky, and Poseidon the sea, with the solid earth, long the province of Gaia, available to all three concurrently. In artistic depictions, Hades is typically portrayed holding a bident and wearing his helm with Cerberus, the three-headed guard dog of the underworld, standing to his side. The Etruscan god Aita and the Roman gods Dis Pater and Orcus were eventually taken as equivalent to Hades and merged into Pluto, a Latinisation of Plouton ( grc-gre, , Ploútōn), itself a euphemistic title often given to Had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proserpina
Proserpina ( , ) or Proserpine ( ) is an ancient Roman goddess whose iconography, functions and myths are virtually identical to those of Greek Persephone. Proserpina replaced or was combined with the ancient Roman fertility goddess Libera, whose principal cult was housed in the Aventine temple of the grain-goddess Ceres, along with the wine god Liber. Each of these three deities occupied their own ''cella'' at the temple. Their cults were served or supervised by a male public priesthood. Ceres was by far the senior of the three, one of the dii consentes, Rome's approximate equivalent to the Greek Twelve Olympians. She was identified with Greek Demeter and Liber was identified with Bacchus and Dionysus. Libera is sometimes described as a female version of Liber Pater, concerned with female fertility. Otherwise she is given no clear identity or mythology by Roman sources, and no Greek equivalent. Nothing is known of her native iconography: her name translates as a feminine form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after her abduction by and marriage to her uncle Hades, the king of the underworld.Martin Nilsson (1967). ''Die Geschichte der Griechische Religion'' Vol I pp 462–463, 479–480 The myth of her abduction, her sojourn in the underworld, and her temporary return to the surface represents her functions as the embodiment of spring and the personification of vegetation, especially grain crops, which disappear into the earth when sown, sprout from the earth in spring, and are harvested when fully grown. In Classical Greek art, Persephone is invariably portrayed robed, often carrying a sheaf of grain. She may appear as a mystical divinity with a sceptre and a little box, but she was mostly represented in the process of being carried off by Hades. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow White And The Seven Dwarfs (1937 Film)
''Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs'' is a 1937 American animated musical fantasy film produced by Walt Disney Productions and released by RKO Radio Pictures. Based on the 1812 German fairy tale by the Brothers Grimm, it is the first full-length traditionally animated feature film and the first Disney animated feature film. The story was adapted by storyboard artists Dorothy Ann Blank, Richard Creedon, Merrill De Maris, Otto Englander, Earl Hurd, Dick Rickard, Ted Sears and Webb Smith. David Hand was the supervising director, while William Cottrell, Wilfred Jackson, Larry Morey, Perce Pearce, and Ben Sharpsteen directed the film's individual sequences. ''Snow White'' premiered at the Carthay Circle Theatre in Los Angeles, California on December 21, 1937. It was a critical and commercial success and, with international earnings of more than $8 million during its initial release (compared to its $1.5 million budget), it briefly held the record of highest-grossing sound film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







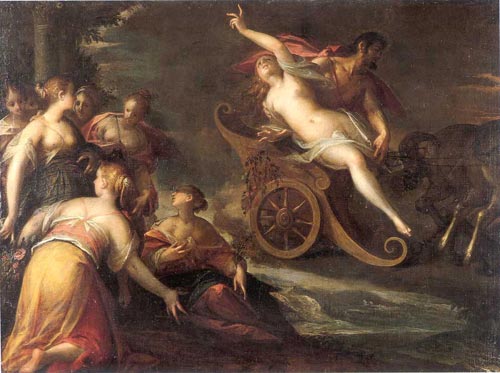
.jpg)