Proserpina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Proserpina ( , ) or Proserpine ( ) is an ancient Roman
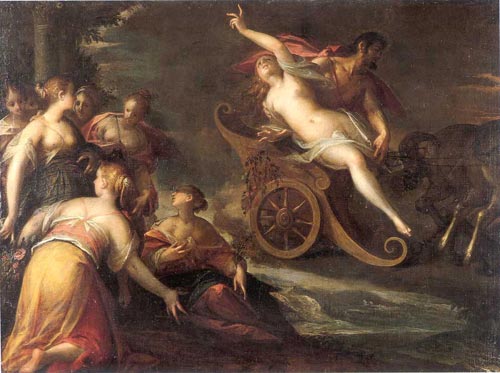 The best-known myth surrounding Proserpina is of her abduction by the god of the Underworld, her mother Ceres' frantic search for her, and her eventual but temporary restitution to the world above. In Latin literature, several versions are known, all similar in most respects to the myths of Greek Persephone's abduction by the King of the underworld, named variously in Latin sources as
The best-known myth surrounding Proserpina is of her abduction by the god of the Underworld, her mother Ceres' frantic search for her, and her eventual but temporary restitution to the world above. In Latin literature, several versions are known, all similar in most respects to the myths of Greek Persephone's abduction by the King of the underworld, named variously in Latin sources as 
 In Claudian's version, the unprepossessing Dis yearns for the joys of married love and fatherhood, and threatens to make war on the other gods if he remains alone in Erebus. The Fates ( Parcae), who determine the destinies of all, arrange a future marriage for Dis, to prevent the outbreak of war. Jupiter orders
In Claudian's version, the unprepossessing Dis yearns for the joys of married love and fatherhood, and threatens to make war on the other gods if he remains alone in Erebus. The Fates ( Parcae), who determine the destinies of all, arrange a future marriage for Dis, to prevent the outbreak of war. Jupiter orders
Google books
Latin
an
Bill Thayer's edition of the
"Proserpina" on the Mythology Guide
*
Proserpina
', Proserpina.net. Accessed 27 January 2012 *
Il Ratto di Proserpina
' {{Authority control Death goddesses Life-death-rebirth goddesses Roman goddesses Roman underworld Spring (season) Underworld goddesses Harvest goddesses Agricultural goddesses Fertility goddesses
goddess
A goddess is a female deity. In many known cultures, goddesses are often linked with literal or metaphorical pregnancy or imagined feminine roles associated with how women and girls are perceived or expected to behave. This includes themes of s ...
whose iconography, functions and myths are virtually identical to those of Greek Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld afte ...
. Proserpina replaced or was combined with the ancient Roman fertility goddess Libera, whose principal cult was housed in the Aventine temple of the grain-goddess Ceres, along with the wine god Liber.
Each of these three deities occupied their own ''cella'' at the temple. Their cults were served or supervised by a male public priesthood. Ceres was by far the senior of the three, one of the dii consentes
The ''Dii Consentes'', also known as ''Di'' or ''Dei Consentes'' (once ''Dii Complices''), is an ancient list of twelve major deities, six gods and six goddesses, in the pantheon of Ancient Rome. Their gilt statues stood in the Roman Forum, a ...
, Rome's approximate equivalent to the Greek Twelve Olympians
upright=1.8, Fragment of a relief (1st century BC1st century AD) depicting the twelve Olympians carrying their attributes in procession; from left to right: Hestia (scepter), Hermes (winged cap and staff), Aphrodite (veiled), Ares (helmet and ...
. She was identified with Greek Demeter and Liber was identified with Bacchus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; grc, wikt:Διόνυσος, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstas ...
and Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
. Libera is sometimes described as a female version of Liber Pater, concerned with female fertility. Otherwise she is given no clear identity or mythology by Roman sources, and no Greek equivalent. Nothing is known of her native iconography: her name translates as a feminine form of Liber, "the free one". Proserpina's name is a Latinisation of "Persephone", perhaps influenced by the Latin ''proserpere'' ("to emerge, to creep forth"), with reference to the growing of grain. Her iconography is "entirely based" on that of her Greek original, Persephone.
Proserpina was imported from southern Italy as part of an official religious strategy, towards the end of the second Punic war
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
, when
antagonism between Rome's lower and upper social classes, crop failures and intermittent famine were thought to be signs of divine wrath, provoked by Roman impiety. The new cult was installed around 205 BC at Ceres' Aventine temple. Ethnically Greek priestesses were recruited to serve Ceres and Proserpina as "Mother and Maiden". This innovation might represent an attempt by Rome's ruling class to please the gods and the plebs; the latter shared strong cultural ties with Italian '' magna Graeca''. The reformed cult was based on the Greek, women-only Thesmophoria, and was promoted as morally desirable for respectable Roman women, both as followers and priestesses. It was almost certainly supervised by Rome's '' Flamen Cerealis'', a male priesthood usually reserved to plebeians. The new cult might have partly subsumed the Aventine temple's older, native cults to Ceres, Liber and Libera, but it also functioned alongside them. Liber played no part in the reformed cult. Ceres, Proserpina/Libera and Liber are known to have received cult in their own right, at their Aventine temple and elsewhere, though details are lacking.
The Roman cult of Mother and Maiden named Proserpina as queen of the underworld, spouse to Rome's king of the underworld, Dis pater, and daughter to Ceres. The cult's functions, framework of myths and roles involved the agricultural cycle, seasonal death and rebirth, dutiful daughterhood and motherly care. They included secret initiations and nocturnal torchlit processions, and cult objects concealed from non-initiates. Proserpina's forcible abduction by the god of the underworld, her mother's search for her, and her eventual but temporary restoration to the world above are the subject of works in Roman and later art and literature. In particular, her seizure by the god of the Underworld – usually described as the Rape of Proserpina, or of Persephone – has offered dramatic subject matter for Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
and later sculptors and painters.
Cult and myths
Origin of Libera
In early Roman religion, Libera was the female equivalent of Liber Pater, protector of plebeian rights, god of wine, male fertility and liberty, equivalent to GreekBacchus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; grc, wikt:Διόνυσος, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstas ...
or Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
. Libera was originally an Italic goddess, paired with Liber as an "etymological duality" at some time during Rome's Regal or very early Republican eras. She enters Roman history as part of a so-called Triadic cult alongside Ceres and Liber, in a temple established around 493 BC on the Aventine Hill
The Aventine Hill (; la, Collis Aventinus; it, Aventino ) is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth '' rione'', or ward, of Rome.
Location and boundaries
The Aventine Hill is the ...
at state expense, promised by Rome's governing class to the plebs (Rome's citizen-commoners), who had threatened secession. Collectively, these three deities were divine patrons and protectors of Rome's commoner-citizens, and guardians of Rome's senatorial records and written laws, housed at the temple soon after its foundation. Libera might have been offered cult on March 17 during Liber's festival, Liberalia
In ancient Roman religion, the Liberalia (March 17) was the festival of Liber Pater and his consort Libera. T.P. Wiseman, ''Remus: a Roman myth'', Cambridge University Press, 1995, p.133. The Romans celebrated Liberalia with sacrifices, proc ...
, or at some time during the seven days of Cerealia, held in mid-to-late April; in the latter festival, she would have been subordinate to Ceres; the names of both Liber and Libera were a later addition to Ceres's festival. Otherwise, Libera's functional relationship to her Aventine cult partners is uncertain. She has no known native iconography or mythology.
Libera and Proserpina
Libera was officially identified as Proserpina from 205 BC, when she and Ceres acquired a Romanised form of Greek mystery rite, the '' ritus graecia cereris''. This was part of Rome's religious recrecruitment of deities to serve as divine allies against Carthage, towards the end of theSecond Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
. In the late Republican era, Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the est ...
described Liber and Libera as Ceres' children. At around the same time, possibly in the context of popular or religious drama, Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Gramma ...
equated Libera with Greek Ariadne, as bride to Liber's Greek equivalent, Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
. The older and newer forms of her names, cult, and rites, and their diverse associations, persisted well into the late Imperial era. St. Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afri ...
(354–430 AD) wrote that Libera was a goddess of female fertility, just as Liber was a god of male fertility.
Proserpina
Proserpina was officially introduced to Rome as the daughter of Ceres in the newly Romanised cult of "Mother and Daughter". The cult's origins lay in southern Italy, which was politically allied to Rome but culturally a part of Magna Graecia. The cult was based on the women-only Greek Thesmophoria, which was a part public and part mystery cult to Demeter and Persephone as "Mother and Maiden". It arrived in Rome along with its Greek priestesses, who were grantedRoman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome (Latin: ''civitas'') was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in Ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, t ...
so that they could pray to the gods "with a foreign and external knowledge, but with a domestic and civil intention".
The exclusively female initiates and priestesses of the new " Greek-style" mysteries of Ceres and Proserpina were expected to uphold Rome's traditional, patrician-dominated social hierarchy and traditional morality. Unmarried girls were expected to emulate the chastity of Proserpina, the maiden; married women were expected to seek to emulate Ceres, the devoted and fruitful Mother. Their rites were intended to secure a good harvest, and increase the fertility of those who partook in the mysteries. Each of the Aventine triad's deities continued to receive cult in their own right. Liber's open, gender-mixed cult and festivals continued, though likely caught up in the suppression of the Bacchanalia some twenty years on. Proserpina's individual cult, and her joint cult with Ceres became widespread throughout the Republic and Empire. A Temple of Proserpina was located in a suburb of Melite, in modern Mtarfa, Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
. The temple's ruins were quarried away between the 17th and 18th centuries; only a few fragments survive.
Myths
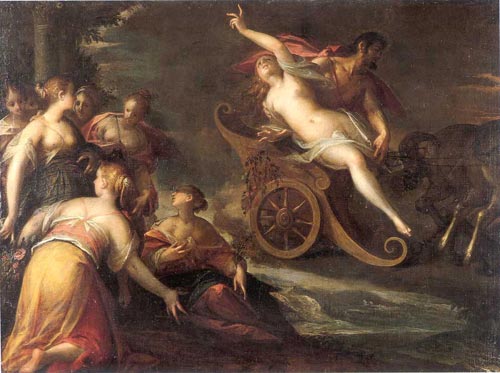 The best-known myth surrounding Proserpina is of her abduction by the god of the Underworld, her mother Ceres' frantic search for her, and her eventual but temporary restitution to the world above. In Latin literature, several versions are known, all similar in most respects to the myths of Greek Persephone's abduction by the King of the underworld, named variously in Latin sources as
The best-known myth surrounding Proserpina is of her abduction by the god of the Underworld, her mother Ceres' frantic search for her, and her eventual but temporary restitution to the world above. In Latin literature, several versions are known, all similar in most respects to the myths of Greek Persephone's abduction by the King of the underworld, named variously in Latin sources as Dis
Dis, DIS or variants may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Dis'' (album), by Jan Garbarek, 1976
* ''Dís'', a soundtrack album by Jóhann Jóhannsson, 2004
* "Dis", a song by The Gazette from the 2003 album ''Hankou Seimeibun''
* "dis� ...
or Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Sun. It is the largest k ...
, and in Greek sources as Hades or Pluto. "Hades" can mean both the hidden Underworld and its king ('the hidden one'), who in early Greek versions of the myth is a dark, unsympathetic figure; Persephone is "Kore" ('the maiden'), taken against her will; in the Greek Eleusinian Mysteries
The Eleusinian Mysteries ( el, Ἐλευσίνια Μυστήρια, Eleusínia Mystḗria) were initiations held every year for the cult of Demeter and Persephone based at the Panhellenic Sanctuary of Elefsina in ancient Greece. They are th ...
, her captor is known as Hades; they form a divine couple who rule the underworld together, and receive Eleusinian initiates into some form of better afterlife. Renamed Pluto, the king of the underworld is distanced from his violent abduction of his consort. In 27 BC Vergil presented his own version of the myth, in his ''Georgics''. In the early 1st century AD, Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the ...
gives two poetic versions: one in Book 5 of his ''Metamorphoses
The ''Metamorphoses'' ( la, Metamorphōsēs, from grc, μεταμορφώσεις: "Transformations") is a Latin narrative poem from 8 CE by the Roman poet Ovid. It is considered his '' magnum opus''. The poem chronicles the history of the ...
'' and another in Book 4 of his ''Fasti
In ancient Rome, the ''fasti'' (Latin plural) were chronological or calendar-based lists, or other diachronic records or plans of official and religiously sanctioned events. After Rome's decline, the word ''fasti'' continued to be used for si ...
'' An early 5th century AD Latin version of the same myth is Claudian
Claudius Claudianus, known in English as Claudian (; c. 370 – c. 404 AD), was a Latin poet associated with the court of the Roman emperor Honorius at Mediolanum (Milan), and particularly with the general Stilicho. His work, written almost en ...
's ''De raptu Proserpinae''; in most cases, these Latin works identify Proserpina's underworld abductor and later consort as Dis
Dis, DIS or variants may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Dis'' (album), by Jan Garbarek, 1976
* ''Dís'', a soundtrack album by Jóhann Jóhannsson, 2004
* "Dis", a song by The Gazette from the 2003 album ''Hankou Seimeibun''
* "dis� ...
.

 In Claudian's version, the unprepossessing Dis yearns for the joys of married love and fatherhood, and threatens to make war on the other gods if he remains alone in Erebus. The Fates ( Parcae), who determine the destinies of all, arrange a future marriage for Dis, to prevent the outbreak of war. Jupiter orders
In Claudian's version, the unprepossessing Dis yearns for the joys of married love and fatherhood, and threatens to make war on the other gods if he remains alone in Erebus. The Fates ( Parcae), who determine the destinies of all, arrange a future marriage for Dis, to prevent the outbreak of war. Jupiter orders Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
to bring love to Dis, in fulfillment of the prophesy. Ceres has already sought to conceal the innocent Proserpina by sending her to safety in Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Ceres' earthly home and sanctuary; but Dis comes out from the volcano at Mount Etna in his chariot, seizes Proserpina at the Pergusa Lake near Enna, and takes her down into the underworld. The poem ends at this point.
Proserpina's mother, Ceres, seeks her daughter across the world, but in vain. The sun sinks and darkness falls as Ceres walks the earth, stopping the growth of crops and creating a desert with each step.
Jupiter sends Mercury to order Dis to free Proserpina; but Proserpina has melted Dis' hard heart, and eats "several" of the pomegranate seeds he offers her; those who have eaten the food of the dead cannot return to the world of the living. Pluto insists that she had willingly eaten his pomegranate seeds and in return she must stay with him for half the year. Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
asserts that Proserpina agrees to this, and is reluctant to ascend from the underworld and re-unite with her mother. When Ceres greets her daughter's return to the world of the living, the crops grow, flowers blossom, and in summer all growing crops flourish, to be harvested in Autumn. During the time that Proserpina resides with Pluto, the world goes through winter, when the earth gives no crops.
The earth can only be fertile when she is above.
Orpheus and Eurydice
The most extensive myth of Proserpina in Latin isClaudian
Claudius Claudianus, known in English as Claudian (; c. 370 – c. 404 AD), was a Latin poet associated with the court of the Roman emperor Honorius at Mediolanum (Milan), and particularly with the general Stilicho. His work, written almost en ...
's (4th century AD). It is closely connected with that of Orpheus
Orpheus (; Ancient Greek: Ὀρφεύς, classical pronunciation: ; french: Orphée) is a Thracians, Thracian bard, legendary musician and prophet in ancient Greek religion. He was also a renowned Ancient Greek poetry, poet and, according to ...
and Eurydice
Eurydice (; Ancient Greek: Εὐρυδίκη 'wide justice') was a character in Greek mythology and the Auloniad wife of Orpheus, who tried to bring her back from the dead with his enchanting music.
Etymology
Several meanings for the name ...
. In Virgil's Georgics, Orpheus' beloved wife, Eurydice, died from a snake-bite; Proserpina allowed Orpheus into Hades without losing his life; charmed by his music, she allowed him to lead his wife back to the land of the living, as long as he did not look back during the journey. But Orpheus could not resist a backward glance, so Eurydice was forever lost to him.
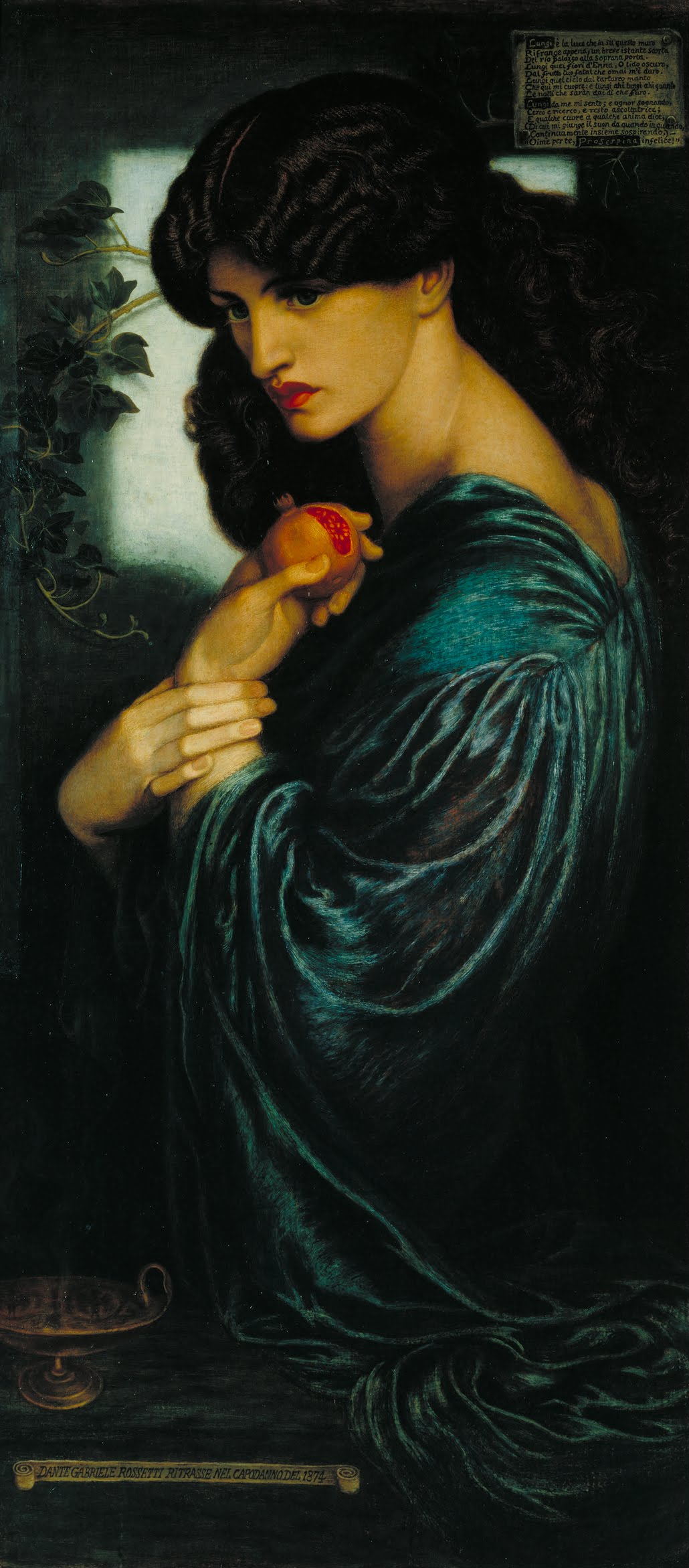
In artwork
Proserpina's figure inspired many artistic compositions, eminently insculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
( Bernini, see '' The Rape of Proserpina (Bernini)'' ) in painting (D.G.Rossetti, a fresco by Pomarancio, J. Heintz, Rubens, A. Dürer, Dell'Abbate, Parrish Parrish may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Parrish, Alabama
* Parrish, Florida
* Parrish, Illinois, a town destroyed in 1925 by the infamous Tri-State Tornado
* Parrish, Wisconsin, a town
* Parrish (community), Wisconsin, an unincorp ...
) and in literature ( Goethe's ''Proserpina'' and Swinburne's '' Hymn to Proserpine'' and '' The Garden of Proserpine'') The statue of the Rape of Prosepina by Pluto that stands in the Great Garden of Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth ...
, Germany is also referred to as "Time Ravages Beauty". Kate McGarrigle's song about the legend was one of the last things she wrote prior to her death, and received its only performance at her last concert at Royal Albert Hall in December 2009.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * Miles, Gary B. (1980), ''Virgil's Georgics: A New Interpretation'',University of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by facult ...
, Google books
External links
*Claudian
Claudius Claudianus, known in English as Claudian (; c. 370 – c. 404 AD), was a Latin poet associated with the court of the Roman emperor Honorius at Mediolanum (Milan), and particularly with the general Stilicho. His work, written almost en ...
, ''De raptu Proserpinae'' ("The Rape of Proserpine"), three books iLatin
an
Bill Thayer's edition of the
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann_(publisher), Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works ...
text at LacusCurtius"Proserpina" on the Mythology Guide
*
Proserpina
', Proserpina.net. Accessed 27 January 2012 *
Il Ratto di Proserpina
' {{Authority control Death goddesses Life-death-rebirth goddesses Roman goddesses Roman underworld Spring (season) Underworld goddesses Harvest goddesses Agricultural goddesses Fertility goddesses