|
The Forgotten Kings
''The Forgotten Kings'' (; also ''The Unknown Rulers'', ''The Forgotten Shahriars'' and ''The Anonymous Kings'') is a Chronicle account by Ahmad Kasravi. it is wrote since late 1928 to 1929, which includes documentary research on several At that time unknown and anonymous post-Islamic to pre-Seljuk Empire Iranian dynasties. Kasravi believes that the reason why these dynasties remain unknown until now is illiteracy and neglect of Iranian history reading and the destruction of documents by dynasties such as the Safavids. Kasravi has used handwritten sources such as Abu'l-Hasan Isfaraini, Ibn Khordadbeh, Hafiz-i Abru and Al-Tabari in writing this book. Although more than half a century has passed since the book was written, it is still recognized as one of the academic resources in the field of source. Kasravi believes that contrary to the opinion of most historians, the 3rd and 4th centuries in Iran are not clear at all and there are not enough resources to advance research in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Kasravi
Ahmad Hokmabadi Tabrizi ( fa, سید احمد حکمآبادی تبریزی, Ahmad-e Hokmabadi-ye Tabrizi; 29 September 1890 – 11 March 1946), later known as Ahmad Kasravi ( fa, احمد کسروی, Ahmad-e Kasravi), was a pre-eminent Iranian historian, jurist, linguist, theologian, a staunch secularist and intellectual. He was a professor of law at the University of Tehran, as well as an attorney and judge in Tehran, Iran. Born in Hokmavar (Hokmabad), Tabriz, Iran, Kasravi was an Iranian Azerbaijani. During his early years, Kasravi enrolled in a seminary. Later, he joined the Iranian Constitutional Revolution. He deserted his clerical training after this event and enrolled in the American Memorial School of Tabriz. Thenceforward he became, in Roy Mottahedeh's words, "a true anti-cleric." Kasravi was the founder of a political-social movement whose goal was to build an Iranian secular identity. The movement was formed during the Pahlavi dynasty. Kasravi authored more than 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylamites
The Daylamites or Dailamites (Middle Persian: ''Daylamīgān''; fa, دیلمیان ''Deylamiyān'') were an Iranian people inhabiting the Daylam—the mountainous regions of northern Iran on the southwest coast of the Caspian Sea, now comprising the southeastern half of Gilan Province. The Daylamites were warlike people skilled in close combat. They were employed as soldiers during the Sasanian Empire and in the subsequent Muslim empires. Daylam and Gilan were the only regions to successfully resist the Muslim conquest of Persia, albeit many Daylamite soldiers abroad accepted Islam. In the 9th century many Daylamites adopted Zaidi Islam. In the 10th century some adopted Isma'ilism, then in the 11th century Fatimid Isma'ilism and subsequently Nizari Isma'ilism. Both the Zaidis and the Nizaris maintained a strong presence in Iran up until the 16th century rise of the Safavids who espoused the Twelver sect of Shia Islam. In the 930s, the Daylamite Buyid dynasty emerged and manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaqut Al-Hamawi
Yāqūt Shihāb al-Dīn ibn-ʿAbdullāh al-Rūmī al-Ḥamawī (1179–1229) ( ar, ياقوت الحموي الرومي) was a Muslim scholar of Byzantine Greek ancestry active during the late Abbasid period (12th-13th centuries). He is known for his , an influential work on geography containing valuable information pertaining to biography, history and literature as well as geography. Life ''Yāqūt'' (''ruby'' or ''hyacinth'') was the '' kunya'' of Ibn Abdullāh ("son of Abdullāh"). He was born in Constantinople, and as his ''nisba'' "al-Rumi" ("from Rūm") indicates he had Byzantine Greek ancestry. Yāqūt was "mawali" to ‘Askar ibn Abī Naṣr al-Ḥamawī, a trader of Baghdad, Iraq, the seat of the Abbasid Caliphate, from whom he received the ''laqab'' "Al-Hamawī". As ‘Askar's apprentice, he learned about accounting and commerce, becoming his envoy on trade missions and travelling twice or three times to Kish in the Persian Gulf. In 1194 ‘Askar stopped his salary ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaidiyyah
Zaydism (''h'') is a unique branch of Shia Islam that emerged in the eighth century following Zayd ibn Ali‘s unsuccessful rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate. In contrast to other Shia Muslims of Twelver Shi'ism and Isma'ilism, Zaydis, also called Fivers, consider Zayd to be the fifth imam and successor to Ali ibn Husayn Zayn al-Abidin, instead of his half-brother Muhammad al-Baqir. Origin The Zaydi madhhab emerged in reverence of Zayd's failed uprising against the Umayyad Caliph, Hisham (ruling 724–743 AD), which set a precedent for revolution against corrupt rulers. According to Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, Zaydis find it difficult to "sit in their houses" and remain passive in an unjust world. Zaydis are the oldest branch of the Shia and are currently the second largest group after Twelvers. Zaydis do not believe in the infallibility of Imāms and do not ascribe them with any supernatural qualities, but promote their leadership. They also reject the notion of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zahir Al-Din Mar'ashi
Zahir al-Din Mar'ashi ( fa, ظهیرالدین مرعشی) was a Persian commander, diplomat and historian. He is the author of several books on the history of Tabarestan. He was born in 812 AH (1412 AD) and died after 894 AH (1489 AD). He was from Mar'ashi family, an originally seyyed family in Tabarestan who dominated the region from the later 8th/14th century until the province's incorporation into Safavid Empire by Abbas I of Persia Abbas I ( fa, ; 27 January 157119 January 1629), commonly known as Abbas the Great (), was the 5th Safavid Shah (king) of Iran, and is generally considered one of the greatest rulers of Iranian history and the Safavid dynasty. He was the third s ... in 1005/1596. He stemmed from the main branch of Mar'ashis, that of Kamal al-Din ibn Kiwan al-Din. He owned states at Bazargah at Gilan and was employed by Sultan Muhammad II of Kar Kia line in Gilan and then by his son an successor Mirza Ali. He was sent to resolve militarily a succession dispute in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylam
Daylam, also known in the plural form Daylaman (and variants such as Dailam, Deylam, and Deilam), was the name of a mountainous region of inland Gilan, Iran. It was so named for its inhabitants, known as the Daylamites. The Church of the East established a metropolitan diocese for Daylam and Gilan around 790 under Shubhalishoʿ., p. 166. See also *Buyid dynasty *Daylami language *Talysh people * al-Daylami *Zaydiyyah *Nizari Ismaili state The Nizari state (the Alamut state) was a Shia Nizari Ismaili state founded by Hassan-i Sabbah after he took control of the Alamut Castle in 1090 AD, which marked the beginning of an era of Ismailism known as the "Alamut period". Their people w ... References Bibliography * Historical regions of Iran History of Gilan {{Iran-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
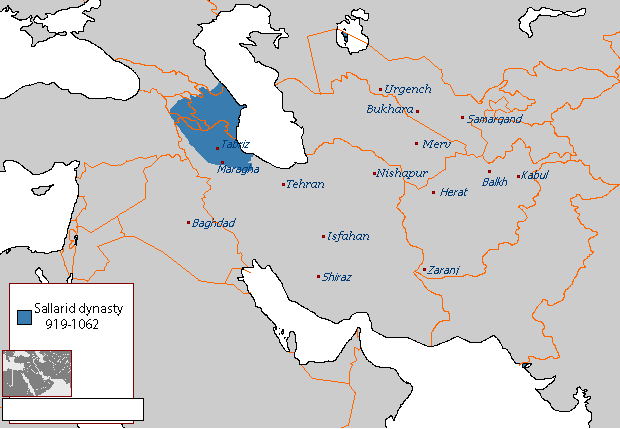
Sallarid Dynasty
The Sallarid dynasty ( fa, سالاریان), (also known as the Musafirids or Langarids) was a Muslim dynasty, of Daylami origin, which ruled in Tarom, Samiran, Daylam, Gilan and subsequently Azerbaijan, Arran, and some districts in Eastern Armenia in the 2nd half of the 10th century. They constitute part of the period in history that has been named the Iranian Intermezzo, a period that saw the rise of native Iranian dynasties during the 9th to the 11th centuries. Early years The Sallarids were Daylamites who, probably in the later 9th century, gained control of Shamiran, a mountain stronghold about twenty-five miles north of Zanjan. From Shamiran they established their rule over the surrounding region of Tarom. The Sallarids also established marriage ties with the neighboring Justanid dynasty of Rudbar. Muhammad bin Musafir In the early 10th century the Sallarid in control of Shamiran was Muhammad bin Musafir. He married a Justanid and subsequently involved himself in thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justanids
The Justanids or Jostanids ( fa, جستانیان) were an Iranian Zaydi Shia dynasty that ruled a part of Daylam (the mountainous district of Gilan) from 791 to the late 11th century. History The Justanids appear as kings of Daylam at the end of the 8th century. Their centre was in the Rudbar of Alamut, running into the valley of the Shahrood. Two centuries later, this had become the main centre of the historical Nizari Ismailis or Assassins (''Hashshashin''), as they are known in the west. They appear in Islamic history as part of what Vladimir Minorsky has called "the Iranian Intermezzo". This refers to a period in which indigenous Daylamite and Kurdish principalities took power in northwest Persia after two to three centuries of Arab rule. The Daylamite upsurge eventually culminated in the Buyid dynasty. After Marzuban ibn Justan converted to Islam in 805, the ancient family of Justans became connected to the Zaydi Alids of the Daylam region. The Justanids adopted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Prophets And Kings
The ''History of the Prophets and Kings'' ( ar, تاريخ الرسل والملوك ''Tārīkh al-Rusul wa al-Mulūk''), more commonly known as ''Tarikh al-Tabari'' () or ''Tarikh-i Tabari'' or ''The History of al-Tabari '' ( fa, تاریخ طبری) is an Arabic-language historical chronicle completed by the Muslim historian Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari (225–310 AH, 838–923 AD) in 915 AD. It begins with creation, and charts Muslim and Middle Eastern history from the myths and legends associated with the Old Testament through to the history of the Abbasid era, down to the year 915. An appendix or continuation, was written by Abu Abdullah b. Ahmad b. Ja'far al-Farghani, a student of al-Tabari. Editions Various editions of the Annals include: * An edition published under the editorship of M.J. de Goeje in three series comprising 13 volumes, with two extra volumes containing indices, introduction and glossary (Leiden, 1879–1901). * An edition published under the editorship o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_4.jpg)
