|
Tezosentan
Tezosentan is a non-selective ETA and ETB receptor antagonist. It acts as a vasodilator and was designed by Actelion as a therapy for patients with acute heart failure. However, studies showed that tezosentan did not improve dyspnea Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ... or reduce the risk of fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular events. References Vasodilators Tetrazoles Pyridines Pyrimidines Phenol ethers Sulfonamides Alcohols Endothelin receptor antagonists Isopropyl compounds Diaryl ethers {{cardiovascular-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin Receptor Type A
Endothelin receptor type A, also known as ETA, is a human G protein-coupled receptor. Interactions Endothelin receptor type A has been shown to interact with HDAC7A and HTATIP. See also * Endothelin receptor There are at least four known endothelin receptors, ETA, ETB1, ETB2 and ETC, all of which are G protein-coupled receptors whose activation result in elevation of intracellular-free calcium, which constricts the smooth muscles of the blood vessels ... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin Receptor Type B
Endothelin receptor type B, also known as ETB is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EDNRB'' gene. Function Endothelin receptor type B is a G protein-coupled receptor which activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its ligand, endothelin, consists of a family of three potent vasoactive peptides: ET1, ET2, and ET3. A splice variant, named SVR, has been described; the sequence of the ETB-SVR receptor is identical to ETRB except for the intracellular C-terminal domain. While both splice variants bind ET1, they exhibit different responses upon binding which suggests that they may be functionally distinct. Regulation In melanocytic cells the EDNRB gene is regulated by the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Mutations in either gene are links to Waardenburg syndrome. Clinical significance The multigenic disorder, Hirschsprung disease type 2, is due to mutation in endothelin receptor type B gene. Animals In horses, a mutation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin Receptor Antagonist
An endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) is a drug that blocks endothelin receptors. Three main kinds of ERAs exist: * selective ETA receptor antagonists ( sitaxentan, ambrisentan, atrasentan, BQ-123, zibotentan, edonentan), which affect endothelin A receptors. * dual antagonists (bosentan, macitentan, tezosentan), which affect both endothelin A and B receptors. * selective ETB receptor antagonists (BQ-788 and A192621) which affect endothelin B receptors are used in research but have not yet reached the clinical trial stage. Sitaxentan, ambrisentan and bosentan are mainly used for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension, while atrasentan is an experimental anti-cancer Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ... drug. References {{cardiova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actelion
Actelion is a pharmaceuticals and biotechnology company established in December 1997, headquartered in Allschwil near Basel, Switzerland. Actelion focuses on the manufacture of drugs that treat rare diseases and orphan diseases. Some of the drugs it has produced have been used to treat patients with symptoms related to central nervous system disorders, irregular heart conditions, immune system disorders and cancer. One of the focuses of Actelion is treating individuals with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a heart condition that leaves patients with a short life expectancy (7–9 years) even with treatment. Actelion scientists were among the first to work in the field of endothelian receptor antagonists. Actelion was initially financed with venture capital provided through a syndicate including Atlas Venture, Sofinnova and HealthCap. Actelion develops and sells drugs in the continents of Asia, Europe and North and South America. Actelion has 29 operative affiliates ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathing, breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes disease, pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, interstitial lung disease, congesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilators
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Therefore, dilation of arterial blood vessels (mainly the arterioles) decreases blood pressure. The response may be intrinsic (due to local processes in the surrounding tissue) or extrinsic (due to hormones or the nervous system). In addition, the response may be localized to a specific organ (depending on the metabolic needs of a particular tissue, as during strenuous exercise), or it may be systemic (seen throughout the entire systemic circulation). Endogenous substances and drugs that cause vasodilation are termed vasodilators. Such vasoactivity is necessary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrazoles
Tetrazoles are a class of synthetic organic heterocyclic compound, consisting of a 5-member ring of four nitrogen atoms and one carbon atom. The name tetrazole also refers to the parent compound with formula CH2N4, of which three isomers can be formulated. Structure and bonding Three isomers of the parent tetrazole exist, differing in the position of the double bonds: 1''H''-, 2''H''-, and 5''H''-tetrazole. The 1''H''- and 2''H''- isomers are tautomers, with the equilibrium lying on the side of 1''H''-tetrazole in the solid phase. In the gas phase, 2''H''-tetrazole dominates. These isomers can be regarded as aromatic, with 6 π-electrons, while the 5''H''-isomer is nonaromatic. Synthesis 1''H''-Tetrazole was first prepared by the reaction of anhydrous hydrazoic acid and hydrogen cyanide under pressure. Treatment of organic nitriles with sodium azide in the presence of iodine or silica-supported sodium bisulfate as a heterogeneous catalyst enables an advantageous synthesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridines
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties The molecular electric dipole moment is 2.2 debyes. Pyridine is diamagnetic and has a diamagnetic susceptibility of −48.7 × 10−6 cm3·mol−1. The standard enthalpy of formation is 100.2 kJ·mol−1 in the liquid phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidines
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug, zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol Ethers
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
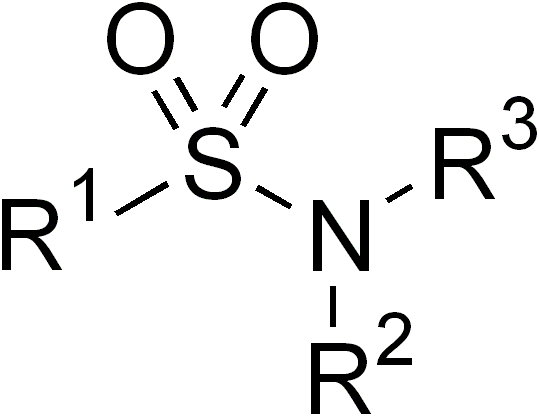
Sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |