|
Tetrahydrocannabiorcol
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabiorcol (Δ9-THCC, (C1)-Δ9-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in ''Cannabis'' pollen. It is a homologue of THC and THCV with the alkyl side chain replaced by a smaller methyl group. Unlike THC and THCV, THCC has negligible affinity for the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors because of the smaller methyl group and does not have psychoactive effects as a result, but conversely it is significantly more potent than THC or THCV as an activator of the TRPA1 calcium channel which plays an important role in pain perception, and it has been shown to produce analgesic effects via activation of spinal TRPA1 channels. See also * Abnormal cannabidiol * O-1602 * O-1918 * Tetrahydrocannabiphorol * Tetrahydrocannabutol Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol (tetrahydrocannabinol-C4, THC-C4, Δ9-THCB, (C4)-Δ9-THC, butyl-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in cannabis that is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main active component of Cannabis. Structurally, they ar ... R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THCV
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV, THV, O-4394, GWP42004) is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) having a propyl (3-carbon) side chain instead of a pentyl (5-carbon) group on the molecule, which makes it produce very different effects from THC. Natural occurrence THCV is prevalent in certain central Asian and southern African strains of ''Cannabis''. Chemistry Similar to THC, THCV has 7 possible double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers (see: Tetrahydrocannabinol#Isomerism). The alternative isomer Δ8-THCV is known as a synthetic compound with a code number of O-4395, but it is not known to have been isolated from ''Cannabis'' plant material. ] Description Plants with elevated levels of propyl cannabinoids (including THCV) have been found in populations of ''Cannabis sativa'' L. ssp. ''indica'' (= ''Cannabis indica'' Lam.) from China, India, Nepal, Thailand, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, as well as southern and western Africa. THCV levels up to 53.7% of total cannabinoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-1918
O-1918 is a synthetic compound related to cannabidiol, which is an antagonist at two former orphan receptors GPR18 and GPR55, that appear to be related to the cannabinoid receptors. O-1918 is used in the study of these receptors, which have been found to be targets for a number of endogenous and synthetic cannabinoid compounds, and are thought to be responsible for most of the non-CB1, non-CB2 mediated effects that have become evident in the course of cannabinoid research. See also * Abnormal cannabidiol * Cannabidiol dimethyl ether * CID-16020046 * CID-85469571 * O-1602 * Tetrahydrocannabiorcol Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabiorcol (Δ9-THCC, (C1)-Δ9-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in ''Cannabis'' pollen. It is a homologue of THC and THCV with the alkyl side chain replaced by a smaller methyl group. Unlike THC and THCV, THCC has negligible affi ... References {{Cannabinoidergics Cannabinoids Cyclohexenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytocannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abnormal Cannabidiol
Abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) is a synthetic regioisomer of cannabidiol, which unlike most other cannabinoids produces vasodilator effects, lowers blood pressure, and induces cell migration, cell proliferation and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in microglia, but without producing any psychoactive effects. Receptor activity It has been shown that the actions of abnormal cannabidiol are mediated through a site separate from the cannabinoid receptor 1, CB1 and cannabinoid receptor 2, CB2 receptors, which responds to abnormal cannabidiol, O-1602, and the endogenous ligands: anandamide (AEA), N-arachidonoyl glycine (NAGly) and N-arachidonoyl L-serine. Multiple lines of evidence support the proposed identification of this novel target in microglia Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytocannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabutol
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol (tetrahydrocannabinol-C4, THC-C4, Δ9-THCB, (C4)-Δ9-THC, butyl-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in cannabis that is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main active component of Cannabis. Structurally, they are only different by the pentyl side chain being replaced by a butyl side chain. Pharmacology Δ9-THCB, showed an affinity for the human CB1 (''K''i = 15 nM) and CB2 receptors (''K''i = 51 nM) comparable to that of Δ9-THC. The formalin test in vivo was performed on Δ9-THCB in order to reveal possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The tetrad test in mice showed a partial agonistic activity of Δ9-THCB toward the CB1 receptor. THCB has rarely been isolated from cannabis samples, but appears to be less commonly present than THC or THCV. It is metabolized in a similar manner to THC. In an analysis by the University of Rhode Island on phytocannabinoids it was found that THC-Butyl had the highest 3C-like protease inhibitor a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
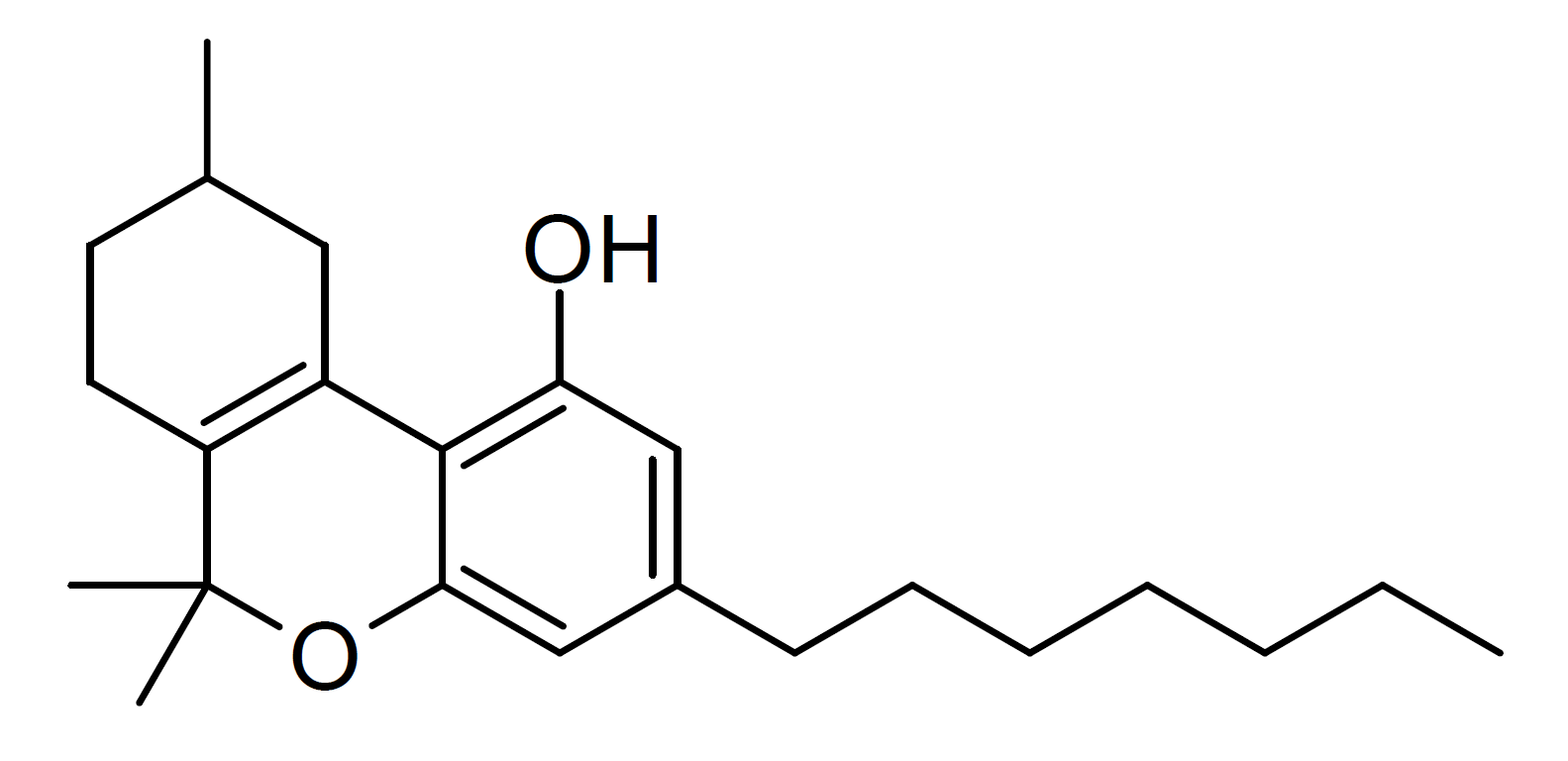
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of THC, but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from ''Cannabis sativa''. It is structurally similar to Δ9-THC, the main active component of cannabis, but with the pentyl side chain extended to heptyl. Since it has a longer side chain, its cannabinoid effects are "far higher than Δ9-THC itself." Tetrahydrocannabiphorol has a reported binding affinity approximately 33 times that of Delta-9-THC. Isomers Delta-3-THCP ] The Δ3/Δ6a(10a) isomer Δ3-THCP was synthesised in 1941, and was found to have around the same potency as Delta-3-Tetrahydrocannabinol, Δ3-THC, unlike the hexyl homologue parahexyl which was significantly stronger. Delta-8-THCP The Δ8 isomer is also known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code name JWH-091, It's unconfirmed whether or not Delta-8-THCP is found naturally in cannabis plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-1602
O-1602 is a synthetic compound most closely related to abnormal cannabidiol, and more distantly related in structure to cannabinoid drugs such as THC. O-1602 does not bind to the classical cannabinoid receptors CB1 or CB2 with any significant affinity, but instead is an agonist at several other receptors which appear to be related to the cannabinoid receptors, particularly GPR18 and GPR55. These previously orphan receptors have been found to be targets for a number of endogenous and synthetic cannabinoid compounds, and are thought to be responsible for most of the non-CB1, non-CB2 mediated effects that have become evident in the course of cannabinoid research. O-1602 produces some effects shared with classical cannabinoid compounds such as analgesic and antiinflammatory effects and appetite stimulation, but it does not produce sedation or psychoactive effects, and has several actions in the gut and brain that are not shared with typical cannabinoid agonists. See also * Cannabidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It is typically used to induce cooperation with a medical procedure. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, traditional analgesics are less effective, and there is often benefit from classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively, ''C. ruderalis'' may be included within ''C. sativa'', all three may be treated as subspecies of ''C. sativa'', or ''C. sativa'' may be accepted as a single undivided species. The genus is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from Asia. The plant is also known as hemp, although this term is often used to refer only to varieties of ''Cannabis'' cultivated for non-drug use. Cannabis has long been used for hemp fibre, hemp seeds and their oils, hemp leaves for use as vegetables and as juice, medicinal purposes, and as a recreational drug. Industrial hemp products are made from cannabis plants selected to produce an abundance of fibre. Various cannabis strains have been bred, often selectively to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." In medical diagnosis, pain is regarded as a symptom of an underlying condition. Pain motivates the individual to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general functioning. Simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |