|
Terrington St Clement
Terrington St Clement is a village and civil parish in King's Lynn and West Norfolk borough and district in Norfolk, England. It is in the drained marshlands to the south of the Wash, west of King's Lynn, Norfolk, and east of Sutton Bridge, Lincolnshire, on the old route of the A17 trunk road. The parish covers an area of . Much of the farmland is of alluvial silt and clay which has been reclaimed from the sea amounting to approximately half of the total parish area. Terrington St Clement in area is the largest village in Norfolk, and the second largest in the country. History The name Terrington derives from the Old English for 'Farm/settlement of Tir(a)'s people' as ''-ingtūn'' means a settlement called after, or connected with... . In AD 1013 Godric, son of Æthelstan Mannessune gifted part of the lands of ''Turrintonea'' to the monks of Ramsey Abbey in his will where his brother, Eadnoth the Younger had been abbott. This is recorded in thS1518 Charter The settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Lynn And West Norfolk
King's Lynn and West Norfolk is a local government district with borough status in Norfolk, England. Its council is based in the town of King's Lynn. The population of the Local Authority at the 2011 Census was 147,451. History The district was formed in 1974 by the merger of the Municipal Borough of King's Lynn, Hunstanton and Downham Market urban districts along with Docking Rural District, Downham Rural District, Freebridge Lynn Rural District and Marshland Rural District. The district was originally known as just West Norfolk, and adopted its present name in 1981. Politics Elections to the borough council are held every four years, with all of the 55 councillors, representing 42 wards, on the council being elected at each election. After being under no overall control from the 1999 election, the Conservative party gained a majority at the 2003 election and has held one ever since, although losing a large number of seats due to the resurgence of the Independent Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Conquest Of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, Duchy of Brittany, Breton, County of Flanders, Flemish, and Kingdom of France, French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror. William's claim to the English throne derived from his familial relationship with the childless Anglo-Saxon king Edward the Confessor, who may have encouraged William's hopes for the throne. Edward died in January 1066 and was succeeded by his brother-in-law Harold Godwinson. The Norwegian king Harald Hardrada invaded northern England in September 1066 and was victorious at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September, but Godwinson's army defeated and killed Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge on 25 September. Three days later on 28 September, William's invasion force of thousands of men and hundreds of ships landed at Pevensey in Sussex in southern England. Harold march ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public House
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was used to differentiate private houses from those which were, quite literally, open to the public as "alehouses", "taverns" and "inns". By Georgian times, the term had become common parlance, although taverns, as a distinct establishment, had largely ceased to exist by the beginning of the 19th century. Today, there is no strict definition, but CAMRA states a pub has four characteristics:GLA Economics, Closing time: London's public houses, 2017 # is open to the public without membership or residency # serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed # has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals # allows drinks to be bought at a bar (i.e., not only table service) The history of pubs can be traced to Roman taverns in B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrington Railway Station
Terrington railway station is a former station in Terrington St Clement, Norfolk. It opened in 1866 and was closed in 1959. It was on the Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway between the Midlands and Melton Constable Melton Constable is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. It covers an area of and had a population of 518 in 225 households at the 2001 census. The population had increased to 618 at the 2011 Census. For the purposes of ....British Railways Atlas.1947. p.17 References Disused railway stations in Norfolk Former Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway stations Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1866 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1959 1866 establishments in England Terrington St Clement {{EastEngland-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salvation Army
Salvation (from Latin: ''salvatio'', from ''salva'', 'safe, saved') is the state of being saved or protected from harm or a dire situation. In religion and theology, ''salvation'' generally refers to the deliverance of the soul from sin and its consequences."Salvation." ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. 1989. "The saving of the soul; the deliverance from sin and its consequences." The academic study of salvation is called ''soteriology''. Meaning In Abrahamic religions and theology, ''salvation'' is the saving of the soul from sin and its consequences. It may also be called ''deliverance'' or ''redemption'' from sin and its effects. Depending on the religion or even denomination, salvation is considered to be caused either only by the grace of God (i.e. unmerited and unearned), or by faith, good deeds (works), or a combination thereof. Religions often emphasize that man is a sinner by nature and that the penalty of sin is death (physical death, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian period, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the '' Belle Époque'' era of Continental Europe. There was a strong religious drive for higher moral standards led by the nonconformist churches, such as the Methodists and the evangelical wing of the established Church of England. Ideologically, the Victorian era witnessed resistance to the rationalism that defined the Georgian period, and an increasing turn towards romanticism and even mysticism in religion, social values, and arts. This era saw a staggering amount of technological innovations that proved key to Britain's power and prosperity. Doctors started moving away from tradition and mysticism towards a science-based approach; medicine advanced thanks to the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Armagh
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdiocese ( with some exceptions), or are otherwise granted a titular archbishopric. In others, such as the Lutheran Church of Sweden and the Church of England, the title is borne by the leader of the denomination. Etymology The word archbishop () comes via the Latin ''archiepiscopus.'' This in turn comes from the Greek , which has as components the etymons -, meaning 'chief', , 'over', and , 'seer'. Early history The earliest appearance of neither the title nor the role can be traced. The title of "metropolitan" was apparently well known by the 4th century, when there are references in the canons of the First Council of Nicæa of 325 and Council of Antioch of 341, though the term seems to be used generally for all higher ranks of bishop, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Chancellor Of Ireland
The Lord High Chancellor of Ireland (commonly known as Lord Chancellor of Ireland) was the highest judicial office in Ireland until the establishment of the Irish Free State in 1922. From 1721 to 1801, it was also the highest political office of the Irish Parliament: the Chancellor was Speaker of the Irish House of Lords. The Lord Chancellor was also Lord Keeper of the Great Seal of Ireland. In all three respects, the office mirrored the Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain. Origins There is a good deal of confusion as to precisely when the office originated. Until the reign of Henry III of England, it is doubtful if the offices of Irish and English Chancellor were distinct. Only in 1232 is there a clear reference to a separate Court of Chancery (Ireland). Early Irish Lord Chancellors, beginning with Stephen Ridell in 1186, were simply the English Chancellor acting through a Deputy. In about 1244 the decision was taken that there must be separate holders of the office in England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
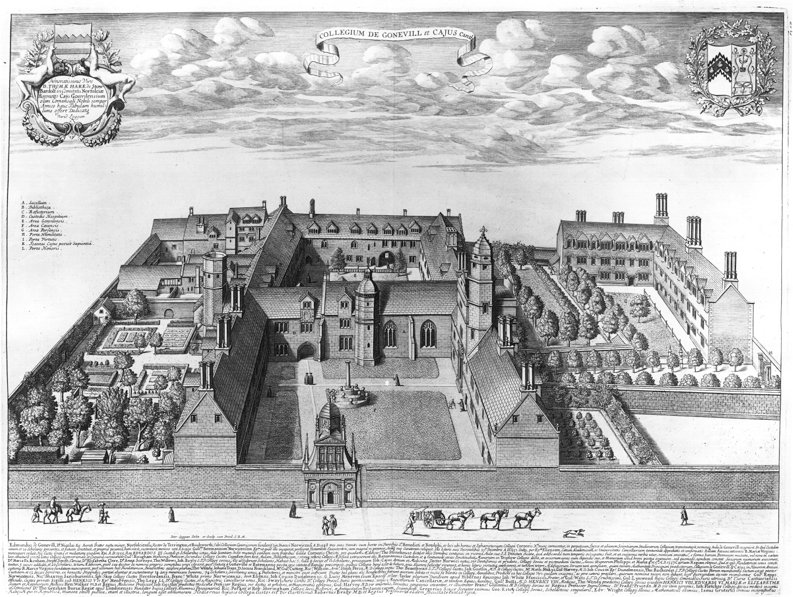
John Colton (archbishop)
John Colton ( 1320 – 1404) was a leading English-born academic, statesman and cleric of the fourteenth century. He was the first Master of Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge. He spent much of his career in Ireland, where he held the offices of Treasurer of Ireland, Lord Chancellor of Ireland and Archbishop of Armagh. He is chiefly remembered today for his book ''The Visitation of Derry'' (1397), which he either wrote or commissioned. Early career Little is known of his parents, or of his early years. He was born at Terrington St Clement in Norfolk.O'Flanagan J. Roderick ''The Lives of the Lord Chancellors of Ireland'' London 1870 He was in the service of William Bateman, who was Bishop of Norwich 1344–1355. He took a degree in divinity at the University of Cambridge in 1348 and the following year became the first Master of the new Gonville Hall, Cambridge, now Gonville and Caius College. The founder of the college, Edmund Gonville, had been a neighbour of Colton's in T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonville And Caius College
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge college after Trinity College, Cambridge. The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius (who gave the college the caduceus in its insignia) and William Harvey. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick (joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson), James Chadwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |