|
Terrapin Hill
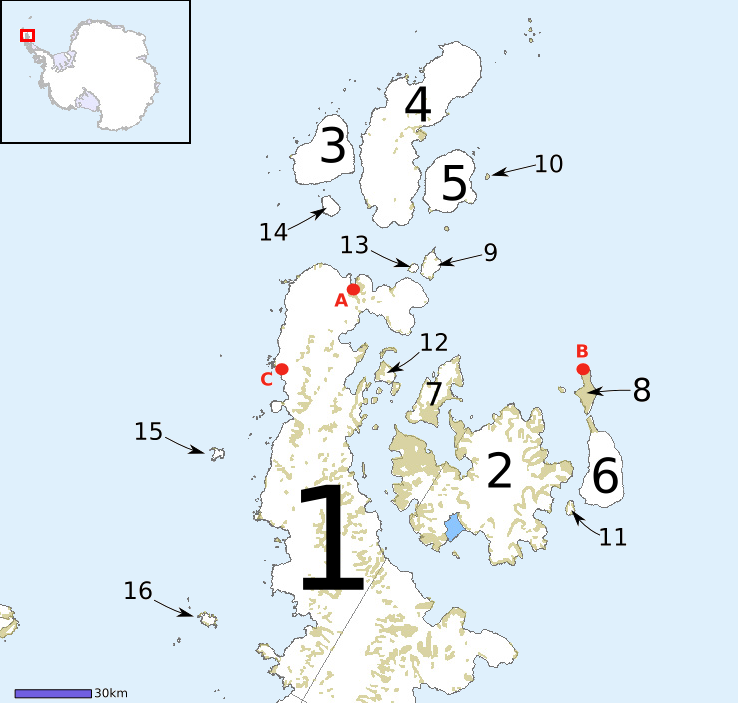
The Naze () is a peninsula in north James Ross Island, marking the southeast entrance to Herbert Sound and extending about northeast from Terrapin Hill toward the south-central shore of Vega Island. Location The Naze is to the east of Croft Bay extending north into Herbert Sound towards Vega Island. It is east of Ulu Peninsula, which forms the west side of Croft Bay, and north of Mount Haddington Mount Haddington is a massive high shield volcano comprising much of James Ross Island in Graham Land, Antarctica. It is wide and has had numerous subglacial eruptions throughout its history, forming many tuyas. Some of its single eruptions w .... Discovery and name The Naze was discovered and named "Nasudden" by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition (SwedAE), 1901-04, under Otto Nordenskjöld. The recommended form is the English version used by Nordenskjold. Features Terrapin Hill . Rounded, reddish-colored hill, high high, standing at the south end of The Naze. This a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Ross Island
James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to , it is irregularly shaped and extends in a north–south direction. It was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it for Sir James Clark Ross, the leader of a British expedition to this area in 1842 that discovered and roughly charted a number of points along the eastern side of the island. The style, "James" Ross Island is used to avoid confusion with the more widely known Ross Island in McMurdo Sound. It is one of several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land, which is closer to South America than any other part of that continent. The island was connected to the Antarctic mainland by an ice shelf until 1995, when the ice shelf collapsed, making the Prince Gustav Channel passable for the first time. Mendel Polar Station, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Sound
Herbert Sound is a sound in Antarctica extending from Cape Lachman and Keltie Head on the northwest to the narrows between The Naze and False Island Point on the southeast, separating Vega Island from James Ross Island and connecting Prince Gustav Channel The Prince Gustav Channel was named in 1903 after Crown Prince Gustav of Sweden (later King Gustav V) by Otto Nordenskiöld of the Swedish Antarctic Expedition. The channel is bounded on the west by the Antarctic Peninsula and on the east by Ja ... with Erebus and Terror Gulf. On January 6, 1843, Captain James Clark Ross discovered a broad embayment east of the sound, which he named "Sidney Herbert Bay" after Sidney Herbert, First Secretary to the Admiralty. The sound proper was discovered and charted by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Otto Nordenskiöld, who included it with the broad embayment under the name "Sidney Herbert Sound". The recommended application restricts Herbert Sound to the area we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega Island
Vega Island is a small island to the northwest of James Ross Island, on the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from James Ross Island by Herbert Sound. The island was named by Otto Nordenskjold, leader of the Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1901–04) in honour of the ship making the first voyage through the Northeast Passage, 1878-79. Vega Island is an important site for paleontology. The region is extremely rich in terrestrial and marine fossils which span the boundary of the Cretaceous and Tertiary periods, covering the point in time when dinosaurs became extinct. Fossils found on the island include hadrosaurs, plesiosaurs, and mosasaurs. Geography The island is a rare volcano type called a móberg, or tuya, which was formed by a three-stage eruption sequence below an ice cap. Stage one was a subglacial hyaloclastic eruption, which shattered the lava into glass, ash, and sand which has since weathered to yellow palagonite layers. The second phase was a lava eruption into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity Peninsula
Trinity Peninsula is the northernmost part of the Antarctic Peninsula. It extends northeastward for about 130 km (80 mi) to Cape Dubouzet from an imaginary line connecting Cape Kater on the north-west coast and Cape Longing on the south-east coast. Prime Head is the northernmost point of this peninsula. Some 20 kilometers southeast of Prime Head is Hope Bay with the year-round Argentinian Esperanza Base. History It was first sighted on 30 January 1820 by Edward Bransfield, Master, Royal Navy, immediately after his charting of the newly discovered South Shetland Islands nearby. In the century following the peninsula's discovery, chartmakers used various names (Trinity Land, Palmer Land, and Land of Louis Philippe) for this portion of it, each name having some historical merit. The recommended name derives from "Trinity Land", given by Bransfield during 1820 in likely recognition of the Corporation of Trinity House, Britain's historical maritime pilotage authority, altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croft Bay
Croft Bay () is a bay which indents the north-central side of James Ross Island and forms the southern part of Herbert Sound, south of the northeastern end of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was discovered in 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld. It was charted in 1945 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), who named it for W.N. Croft, a FIDS geologist at Hope Bay Hope Bay (Spanish: ''Bahía Esperanza'') on Trinity Peninsula, is long and wide, indenting the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and opening on Antarctic Sound. It is the site of the Argentinian Antarctic settlement Esperanza Base, established i ... in 1946. References * Bays of James Ross Island {{JamesRossIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulu Peninsula
Ulu Peninsula () is that portion of James Ross Island northwest of the narrow neck of land between Rohss Bay and Croft Bay, extending from Cape Obelisk to Cape Lachman. Named descriptively by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1987. In plan view the cove is shaped like an ulu, a type of knife A knife ( : knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced ... traditionally used by Inuit women. Peninsulas of Graham Land Landforms of James Ross Island {{JamesRossIsland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Haddington
Mount Haddington is a massive high shield volcano comprising much of James Ross Island in Graham Land, Antarctica. It is wide and has had numerous subglacial eruptions throughout its history, forming many tuyas. Some of its single eruptions were bigger in volume than a whole normal-sized volcano. Old eruption shorelines are widespread on the volcano's deeply eroded flanks. Haddington formed along the Larsen Rift dominantly during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs but more recent eruptions have produced tuff cones on its slopes. The youngest tuff cones and pyroclastic cones on the eastern slope are situated below the summit icecap and may have formed in the last few thousand years. Effusive eruptions have created large deltas composed of hyaloclastite breccia and lava flows. Mount Haddington was discovered on December 31, 1842 by the Ross expedition, a voyage of scientific exploration of the Antarctic from 1839 to 1843 led by James Clark Ross. Ross named the mountain after the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Antarctic Expedition
The Swedish Antarctic Expedition of 1901–1903 was a scientific expedition led by Otto Nordenskjöld and Carl Anton Larsen. It was the first Swedish endeavour to Antarctica in the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Background Otto Nordenskjöld, a Swedish geologist and geographer, organized and led a scientific expedition of the Antarctic Peninsula. The expedition's overall command was placed under the Norwegian Carl Anton Larsen, an experienced Antarctic explorer who served as captain of , and who had previously commanded a whaling reconnaissance mission in 1892–1893. Seven other scientists, including archaeologist Johan Gunnar Andersson, botanist Carl Skottsberg, and zoologist Axel Ohlin, along with 16 officers and men joined them on the voyage. On 16 October 1901, the ''Antarctic'' left the Port of Gothenburg. Events Despite its end and the great hardships endured, the expedition would be considered a scientific success, with the parties having explored muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Nordenskjöld
Nils Otto Gustaf Nordenskjöld (6 December 1869 – 2 June 1928) was a Finnish and Swedish geologist, geographer, and polar explorer. Early life Nordenskjöld was born in Hässleby in Småland in eastern Sweden, in a Finland Swedish family that included his maternal uncle, the polar explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld, and cousin Gustaf Nordenskiöld. His father and mother were cousins, but his father's family name was "Nordenskjöld", while his mother's family name was spelled "Nordenskiöld". He studied at Uppsala University, obtaining a doctorate in geology in 1894, and later became a lecturer and then associate professor in the university's geology department. Career Otto Nordenskjöld led mineralogical expeditions to Patagonia in the 1890s, and to Alaska and the Klondike area in 1898. Antarctic Expedition Nordenskjöld led the 1901–1904 Swedish Antarctic Expedition. Their ship ''Antarctic'', commanded by the seasoned Antarctic sailor Carl Anton Larsen, visited Bueno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey
The British Antarctic Survey (BAS) is the United Kingdom's national polar research institute. It has a dual purpose, to conduct polar science, enabling better understanding of global issues, and to provide an active presence in the Antarctic on behalf of the UK. It is part of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC). With over 400 staff, BAS takes an active role in Antarctic affairs, operating five research stations, one ship and five aircraft in both polar regions, as well as addressing key global and regional issues. This involves joint research projects with over 40 UK universities and more than 120 national and international collaborations. Having taken shape from activities during World War II, it was known as the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey until 1962. History Operation Tabarin was a small British expedition in 1943 to establish permanently occupied bases in the Antarctic. It was a joint undertaking by the Admiralty and the Colonial Office. At the end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee
The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) and the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI). Such names are formally approved by the Commissioners of the BAT and SGSSI respectively, and published in the BAT Gazetteer and the SGSSI Gazetteer maintained by the Committee. The BAT names are also published in the international Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica maintained by Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research, SCAR. The Committee may also consider proposals for new place names for geographical features in areas of Antarctica outside BAT and SGSSI, which are referred to other Antarctic place-naming authorities, or decided by the Committee itself if situated in the unclaimed sector of Antarctica. Names attributed by the committee * Anvil Crag, named for descriptive featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)