|
Otto Nordenskjöld
Nils Otto Gustaf Nordenskjöld (6 December 1869 – 2 June 1928) was a Finnish and Swedish geologist, geographer, and polar explorer. Early life Nordenskjöld was born in Hässleby in Småland in eastern Sweden, in a Finland Swedish family that included his maternal uncle, the polar explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld, and cousin Gustaf Nordenskiöld. His father and mother were cousins, but his father's family name was "Nordenskjöld", while his mother's family name was spelled "Nordenskiöld". He studied at Uppsala University, obtaining a doctorate in geology in 1894, and later became a lecturer and then associate professor in the university's geology department. Career Otto Nordenskjöld led mineralogical expeditions to Patagonia in the 1890s, and to Alaska and the Klondike area in 1898. Antarctic Expedition Nordenskjöld led the 1901–1904 Swedish Antarctic Expedition. Their ship ''Antarctic'', commanded by the seasoned Antarctic sailor Carl Anton Larsen, visited Bueno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Småland
Småland () is a historical province () in southern Sweden. Småland borders Blekinge, Scania, Halland, Västergötland, Östergötland and the island Öland in the Baltic Sea. The name Småland literally means ''Small Lands''. The Latinized form has been used in other languages. The highest point in Småland is Tomtabacken, at 377 metres (1,237 ft). In terms of total area, Småland is of a similar size as Belgium. Administration The traditional provinces of Sweden no longer serve any governmental purpose, but they do remain important historically and culturally. The province of Småland today is divided almost entirely into the three administrative counties of Jönköping, Kalmar, and Kronoberg. Some few small portions of historic Småland are situated in Halland and Östergötland Counties. Heraldry The current coat of arms, granted in 1569, displays a rampant red lion carrying a crossbow, all on a golden background. The arms may be surmounted by a ducal coronet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South America's southeastern coast. "Buenos Aires" can be translated as "fair winds" or "good airs", but the former was the meaning intended by the founders in the 16th century, by the use of the original name "Real de Nuestra Señora Santa María del Buen Ayre", named after the Madonna of Bonaria in Sardinia, Italy. Buenos Aires is classified as an alpha global city, according to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) 2020 ranking. The city of Buenos Aires is neither part of Buenos Aires Province nor the Province's capital; rather, it is an autonomous district. In 1880, after decades of political infighting, Buenos Aires was federalized and removed from Buenos Aires Province. The city limits were enlarged to include t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
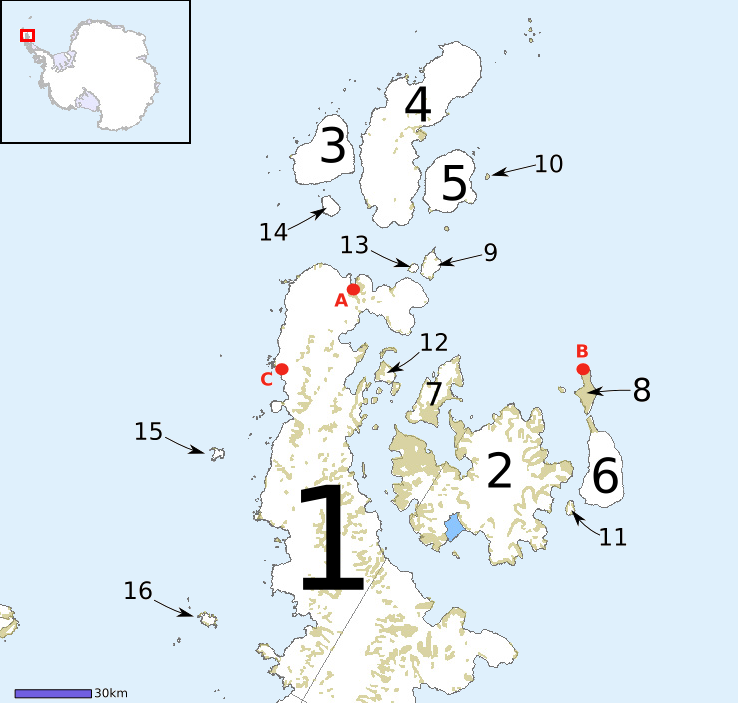
Palmer Archipelago
Palmer Archipelago, also known as Antarctic Archipelago, Archipiélago Palmer, Antarktiske Arkipel or Palmer Inseln, is a group of islands off the northwestern coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It extends from Tower Island in the north to Anvers Island in the south. It is separated by the Gerlache and Bismarck straits from the Antarctic Peninsula and Wilhelm Archipelago, respectively. Palmer Archipelago is located at . History Adrien de Gerlache, leader of the Belgian Antarctic Expedition (1897–1899), discovered the archipelago in 1898. He named it Archipelago Palmer for American Captain Nathaniel Palmer, who navigated these waters in 1820. Both Argentina and the United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ... have operated research stations there. Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joinville Island Group
Joinville Island group is a group of antarctic islands, lying off the northeastern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which Joinville Island group is separated by the Antarctic Sound. Joinville Island, located at , is the largest island of the Joinville Island group. Immediately north of Joinville Island and separated by Larsen Channel lies D'Urville Island, Antarctica, the northernmost island of the Joinville Island group, being located at . The Joinville Island group was discovered in 1838 by a French expedition under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville. See also * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR * Territorial claims in Antarctica Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and st ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Ross Island
James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to , it is irregularly shaped and extends in a north–south direction. It was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it for Sir James Clark Ross, the leader of a British expedition to this area in 1842 that discovered and roughly charted a number of points along the eastern side of the island. The style, "James" Ross Island is used to avoid confusion with the more widely known Ross Island in McMurdo Sound. It is one of several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land, which is closer to South America than any other part of that continent. The island was connected to the Antarctic mainland by an ice shelf until 1995, when the ice shelf collapsed, making the Prince Gustav Channel passable for the first time. Mendel Polar Station, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Longing
Cape Longing () is a rocky cape on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica, forming the south end of a large ice-covered promontory which marks the west side of the south entrance to Prince Gustav Channel. It was discovered by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld in 1902, and so named by him because from the position of his winter hut on Snow Hill Island the cape lay in the direction of his "land of longing" which he was anxious to explore. Cape Longing is the tip of Longing Peninsula (), which is long and situated at the northeast end of Nordenskjöld Coast where it separates the Larsen Ice Shelf from the Prince Gustav Ice Shelf. It was roughly charted by Nordenskiöld, and named after the cape by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) following British Antarctic Survey geological work in the area in 1987–88. Longing Gap () is a constriction in the promontory north of Cape Longing, where the land narrows to and forms a low isthmus. The gap is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graham Land
Graham Land is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula that lies north of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This description of Graham Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between the British Antarctic Place-names Committee and the US Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names, in which the name "Antarctic Peninsula" was approved for the major peninsula of Antarctica, and the names Graham Land and Palmer Land for the northern and southern portions, respectively. The line dividing them is roughly 69 degrees south. Graham Land is named after Sir James R. G. Graham, First Lord of the Admiralty at the time of John Biscoe's exploration of the west side of Graham Land in 1832. It is claimed by Argentina (as part of Argentine Antarctica), Britain (as part of the British Antarctic Territory) and Chile (as part of the Chilean Antarctic Territory). Graham Land is the closest part of Antarctica to South America. Thus it is the usual destination for small ships taking paying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julián Irízar
Admiral Julián Irízar (Capilla del Señor, Buenos Aires Province, January 7, 1869 – March 17, 1935) was an officer of the Argentine Navy. He became a key figure in the modernization of the navy's fleet, the commander of the First Division of the Navy and later Naval Center President, but his most memorable action was as commander of the corvette ''ARA Uruguay, Uruguay'' in the 1903 rescue of the Swedish Antarctic Expedition led by Otto Nordenskjöld, whose ship, the ''Antarctic (ship), Antarctic'' was destroyed by ice. At the time of the rescue he held the rank ''Capitán de Corbeta'' (Lieutenant Commander). (See ARA Uruguay, ARA ''Uruguay'' for more information.) Early career Irízar entered the Naval Academy on March 11, 1884. In 1898 he was part of the commission to monitor construction of the frigate ARA Presidente Sarmiento, ARA ''Presidente Sarmiento'' in England. When in 1899 that ship embarked on its first voyage of circumnavigation, he was an officer of the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARA Uruguay
The ''corbeta'' (corvette) ARA ''Uruguay'', built in England, is the largest ship afloat of its age in the ''Armada de la República Argentina'' (Argentine Navy), with more than 140 years passed since its commissioning in September 1874. The last of the legendary squadron of President Sarmiento, the ''Uruguay'' took part in revolutions, ransoms, expeditions, rescues, and was even floating headquarters of the Navy School. During its operational history 1874–1926 the ''Uruguay'' has served as a gunboat, school ship, expedition support ship, Antarctic rescue ship, fisheries base supply ship, and hydrographic survey vessel, and is now a museum ship in Buenos Aires. This ship may be the oldest in South America having been built in 1874 at Laird Bros. (now Cammell Laird) shipyard of Birkenhead, England, at a cost of £32,000. This ship is rigged to a barque sailplan (three masts, two of which have cross spars). The ship's steel hull is sheathed in teak. The ship's namesake is an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hope Bay
Hope Bay (Spanish: ''Bahía Esperanza'') on Trinity Peninsula, is long and wide, indenting the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and opening on Antarctic Sound. It is the site of the Argentinian Antarctic settlement Esperanza Base, established in 1952. Important Bird Area The bay has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports one of the largest Adélie penguin colonies in Antarctica with around 125,000 pairs. Other birds nesting at the site include gentoo penguins, brown skuas, Antarctic terns, Wilson's storm-petrels, kelp gulls and snowy sheathbills. History The Bay was discovered on January 15, 1902 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it in commemoration of the winter spent there by J. Gunnar Andersson and S.A. Duse, Toralf Grunden of his expedition after his ship (the '' Antarctic'') was crushed by the ice and lost. They were eventually rescued by Argentine corvette ''Uruguay''. Hop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paulet Island
Paulet Island is a circular island about in diameter, lying south-east of Dundee Island, off the north-eastern end of the Antarctic Peninsula. Because of its large penguin colony, it is a popular destination for sightseeing tours. Description The island is composed of lava flows capped by a cinder cone with a small summit crater. Geothermal heat keeps parts of the island ice-free, and the youthful morphology of the volcano suggests that it was last active within the last 1,000 years. The island is part of the James Ross Island Volcanic Group. Historic monuments Paulet Island was discovered by a British expedition (1839–1843) under James Clark Ross and named by him for Captain the Right Honorable Lord George Paulet, Royal Navy. In 1903 during the Swedish Antarctic Expedition led by Otto Nordenskiöld his ship ''Antarctic'' was crushed and sunk by the ice off the coast of the island. A stone hut built in February 1903 by shipwreck survivors, together with the grave of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

