|
Tenjiku Shogi
Tenjiku shogi (天竺将棋 ''tenjiku shōgi,'' "Indian chess" or 天竺大将棋 ''tenjiku dai shōgi'' "great Indian chess") is a large-board variant of shogi (Japanese chess). The game dates back to the 15th or 16th century and was based on the earlier chu shogi, which itself was based on dai shogi. Because of the terse and often incomplete wording of the historical sources for the large shogi variants, except for chu shogi and to a lesser extent dai shogi (which were at some points of time the most prestigious forms of shogi being played), the historical rules of tenjiku shogi are not clear. Different sources often differ significantly in the moves attributed to the pieces. The descriptions listed here are a likely reconstruction based on chu shogi, the primary basis of tenjiku shogi, but not all contemporary players follow these historically-based rules. It is not clear if the game was ever played much historically, as there is no record of sets ever having been made. Rules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenjiku Shogi Set
Tianzhu which also referred as Heaven is the historical East Asian name for India, Originally pronounced as l̥induk or *qʰl'iːn tuɡ 天竺 in Old Chinese, it comes from the Chinese transliteration of unattested Old Persian diminutive *Hinduka-, which is from attested '' 𐏃𐎡𐎯𐎢𐏁 h-i-du-u-š'' (Hindu), which is itself derived from the Proto-Indo-Iranian *síndʰuš, the etymon also of Sanskrit ''Sindhu'', the native name of the Indus River. Persians travelling in northwest India named the region after the river around the 6th century BC. ''Tianzhu'' is just one of several Chinese transliterations of Sindhu. ''Yuāndú'' ( OC ''n̥i �d]ˤuk'') appears in Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'' and ''Tiandu'' () is used in the ''Book of the Later Han''. ''Yintejia'' () comes from the Kuchean ''Indaka'', another transliteration of ''Hindu''. A detailed account of Tianzhu is given in the "Xiyu Zhuan" (Record of the Western Regions) in the ''Hou Hanshu'' com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōgi Zushiki
The ''Shōgi Zushiki'' (象戯図式), ''Sho Shōgi Zushiki'' (諸象戯図式), and ''Shōgi Rokushu no Zushiki'' (象棋六種之図式) are Edo period publications describing various variants Variant may refer to: In arts and entertainment * ''Variant'' (magazine), a former British cultural magazine * Variant cover, an issue of comic books with varying cover art * ''Variant'' (novel), a novel by Robison Wells * " The Variant", 2021 e ... of Japanese chess, otherwise known as '' shōgi''. The ''Shōgi Zushiki'' covers the setup and moves of standard '' shōgi, chū shōgi, dai shōgi, tenjiku shōgi, dai dai shōgi, maka dai dai shōgi,'' and '' tai shōgi.'' It also mentions '' wa shōgi, Tang shōgi'' (which is seven-person Chinese chess), '' kō shōgi,'' and '' taikyoku shōgi.'' The ''Sho Shōgi Zushiki'' (published 1694) covers the setup and moves of ''sho shōgi,'' standard shōgi, ''wa shōgi, chū shōgi, dai shōgi, tenjiku shōgi, dai dai shōgi, maka dai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dai Dai Shogi
Dai dai shōgi (大大将棋 'huge chess') is a large board variant of shogi (Japanese chess). The game dates back to the 15th century and is based on the earlier dai shogi. Apart from its size, the major difference is in the range of the pieces and the "promotion by capture" rule. It is the smallest board variant to use this rule. Because of the terse and often incomplete wording of the historical sources for the large shogi variants, except for chu shogi and to a lesser extent dai shogi (which were at some points of time the most prestigious forms of shogi being played), the historical rules of dai dai shogi are not clear. Different sources often differ significantly in the moves attributed to the pieces, and the degree of contradiction (summarised below with the listing of most known alternative moves) is such that it is likely impossible to reconstruct the "true historical rules" with any degree of certainty, if there ever was such a thing. It is not clear if the game was ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dai Shogi
Dai shogi (大将棋, 'large chess') or Kamakura dai shogi (鎌倉大将棋) is a chess variant native to Japan. It derived from Heian era shogi, and is similar to standard shogi (sometimes called Japanese chess) in its rules and game play. Dai shogi is only one of several large board shogi variants. Its name means ''large shogi'', from a time when there were three sizes of shogi games. Early versions of dai shogi can be traced back to the Kamakura period, from about AD 1230. It was the historical basis for the later, much more popular variant chu shogi. Rules of the game Other than the additional pieces (the iron and stone generals, knights, angry boars, cat swords, evil wolves, violent oxen, and flying dragons, which all promote to gold generals), the rules of dai shogi are thought to have corresponded very closely to those of its descendant chu shogi. Objective The objective of the game is to capture the opponent's king and, if present, the prince, which counts as a second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heian Dai Shogi
Heian dai shogi ( ja, 平安大将棋 'Heian (Era) large chess') is an early large board variant of shogi (Japanese chess) as it was played in the Heian period. The same 12th century document which describes the Heian form of shogi also describes this variant. Unfortunately, this description does not give enough information to actually play the game, but this has not stopped people from attempting to reconstruct this early form of shogi. A fairly complete and playable reconstruction is outlined here. Rules of the game Objective The objective of the game is to capture your opponent's king or to capture all the other pieces, leaving a bare king. Unlike standard shogi, pieces may not be dropped back into play after capture. Game equipment Two players, Black and White (or 先手 ''sente'' and 後手 ''gote''), play on a board ruled into a grid of 13 ''ranks'' (rows) by 13 ''files'' (columns) for a total of 169 squares. The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu Shogi
Chu shogi ( or Middle Shogi) is a strategy board game native to Japan. It is similar to modern shogi (sometimes called Japanese chess) in its rules and gameplay. Its name means "mid-sized shogi", from a time when there were three sizes of shogi variants that were regularly being played. Chu shogi seems to have been developed in the early 14th century as a derivative of dai shogi ('large shogi'). There are earlier references, but it is not clear that they refer to the game as we now know it. With fewer pieces than dai shogi, the game is considered more exciting, and was still commonly played in Japan in 1928–1939, especially in the Keihanshin region. The game largely died out after World War II despite the advocacy of prominent shogi players such as and Ōyama Yasuharu (who played chu shogi when young and credited it with the development of his personal cautious and tenacious shogi style). In 1976, there were about 30–40 masters of the game. It has gained some adherents in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wa Shogi
Wa shogi (和将棋, ''wa shōgi'', harmony chess) is a large board variant of shogi (Japanese chess) in which all of the pieces are named for animals. It is played either with or without drops. Because of the terse and often incomplete wording of the historical sources for the large shogi variants, except for chu shogi and to a lesser extent dai shogi (which were at some points of time the most prestigious forms of shogi being played), the historical rules of wa shogi are not clear. Different sources differ significantly in the moves attributed to the pieces. Presented here are the piece movements that are somewhat standard among modern players of wa shogi, among which the game is played with drops. Rules of the game Objective The objective of the game is to capture your opponent's crane king. Game equipment Two players, Black and White (or 先手 ''sente'' and 後手 ''gote''), play on a board ruled into a grid of 11 ''ranks'' (rows) by 11 ''files'' (columns). The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferz (chess)
The ferz or fers is a fairy chess piece that may move one square diagonally. at '''' It was used in orthodox chess before being replaced by the . History and nomenclature  The ferz is a very old piece, appearing in
The ferz is a very old piece, appearing in
|
Ellipsis
The ellipsis (, also known informally as dot dot dot) is a series of dots that indicates an intentional omission of a word, sentence, or whole section from a text without altering its original meaning. The plural is ellipses. The term originates from the grc, ἔλλειψις, meaning 'leave out'. Opinions differ as to how to render ellipses in printed material. According to ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', it should consist of three periods, each separated from its neighbor by a non-breaking space: . According to the ''AP Stylebook'', the periods should be rendered with no space between them: . A third option is to use the Unicode character U+2026 . Background The ellipsis is also called a suspension point, points of ellipsis, periods of ellipsis, or (colloquially) "dot-dot-dot".. According to Toner it is difficult to establish when the "dot dot dot" phrase was first used. There is an early instance, which is perhaps the first in a piece of fiction, in Virginia Woolf's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Numerals
The Japanese numerals are the number names used in Japanese. In writing, they are the same as the Chinese numerals, and large numbers follow the Chinese style of grouping by 10,000. Two pronunciations are used: the Sino-Japanese (on'yomi) readings of the Chinese characters and the Japanese yamato kotoba (native words, kun'yomi readings). Basic numbering in Japanese There are two ways of writing the numbers in Japanese: in Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3) or in Chinese numerals (, , ). The Arabic numerals are more often used in horizontal writing, and the Chinese numerals are more common in vertical writing. Most numbers have two readings, one derived from Chinese used for cardinal numbers (On reading) and a native Japanese reading (Kun reading) used somewhat less formally for numbers up to 10. In some cases (listed below) the Japanese reading is generally preferred for all uses. Archaic readings are marked with †. * The special reading 〇 ''maru'' (which means "round" or "circle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Chess Notation
Algebraic notation (or AN) is the standard method for recording and describing the moves in a game of chess. It is based on a system of coordinates to uniquely identify each square on the chessboard. It is used by most books, magazines, and newspapers. In English-speaking countries, the parallel method of descriptive notation was generally used in chess publications until about 1980. A few players still use descriptive notation, but it is no longer recognized by FIDE, the international chess governing body. Algebraic notation exists in various forms and languages and is based on a system developed by Philipp Stamma. Stamma used the modern names of the squares, but he used p for pawn moves and the original of a piece (a through h) instead of the initial letter of the piece name. The term "algebraic notation" may be considered a misnomer, as the system is unrelated to algebra. Other terms such as "standard notation" and "coordinate notation" have been proposed, but the traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalemate
Stalemate is a situation in the game of chess where the player whose turn it is to move is not in check and has no legal move. Stalemate results in a draw. During the endgame, stalemate is a resource that can enable the player with the inferior position to draw the game rather than lose. In more complex positions, stalemate is much rarer, usually taking the form of a swindle that succeeds only if the superior side is inattentive. Stalemate is also a common theme in endgame studies and other chess problems. The outcome of a stalemate was standardized as a draw in the 19th century. Before this standardization, its treatment varied widely, including being deemed a win for the stalemating player, a half-win for that player, or a loss for that player; not being permitted; and resulting in the stalemated player missing a turn. Stalemate rules vary in other games of the chess family. Etymology and usage The first recorded use of stalemate is from 1765. It is a compounding of Middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



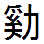
.jpg)