|
Telkom-2
Telkom-2 was a geosynchronous communications satellite built by Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC) for Indonesia's state-owned telecommunications company, PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia Tbk (PT Telkom). Telkom-2 was successfully launched on 16 November 2005, at 23:46:00 UTC and positioned in geostationary orbit, at 118° East for replaced Palapa-B4. History Based on Orbital's highly successful and flight-proven STAR-2 satellite bus, Telkom-2 featured state-of-the-art communications satellite technology, and 24 C-band transponders. The new spacecraft replaced PT Telkom's on-orbit Palapa-B4 satellite, improved communications coverage across Indonesia, and allowed PT Telkom to expand its coverage area into southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Orbital also supplemented Telkom's existing ground station, and offered extensive mission operations support. There were several postponements prior to Telkom-2's launch. Three launch delays happened in November 2005 due to technic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telkom Indonesia
PT Telkom Indonesia (Persero) Tbk, also simply known as Telkom, is an Indonesian multinational telecommunications conglomerate. Telkom is listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange and has a secondary listing on the New York Stock Exchange. The government of Indonesia owns over half of Telkom's shares outstanding. Telkom has major business lines in fixed line telephony, internet, and data communications. It is operated as the parent company of the Telkom Group, which is engaged in a broad range of businesses which consist of telecommunication, multimedia, property, and financial services. Since 2008, Telkom Indonesia began changing its business focus, infrastructure, systems, organization, and human resources, as well as the corporate culture, in their effort to face rising competition. After privatization in 1995, Telkom Indonesia's total consumer base grew by 7.8% in 2010 to 129.8 million customers at the end of December 2011, making the company the nation's largest teleco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telkom-1
Telkom-1 was a geosynchronous communications satellite built by Lockheed Martin, ( Sunnyvale, California), for Indonesia's state-owned telecommunications company, PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia Tbk (PT Telkom). It operated for almost 18 years, more than two years past designed lifetime of 15 years. Launch Telkom-1 was successfully launched 12 August 1999, by an Ariane-42P H10-3, from Centre Spatial Guyanais, pad ELA-2, Kourou, French Guiana, at 22:52 UTC and positioned in geostationary orbit, at 108° East for replaced Palapa-B2R. Satellite description Based on Lockheed Martin A2100A satellite bus, Telkom-1 features communications satellite technology, with 24 C-band and 12 Enhanced C-band transponders. The new spacecraft replaced on-orbit Palapa-B2R satellite, improve communications coverage across Indonesia, and allow PT Telkom to expand its coverage area into Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Launch had been delayed because of problems with comsat manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It is launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) in French Guiana. It has been used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) or low Earth orbit (LEO). The launch vehicle had a streak of 82 consecutive successful launches between 9 April 2003 and 12 December 2017. Since 2014, Ariane 6, a direct successor system, is in development. The system was designed as an expendable launch system by the ''Centre national d'études spatiales'' (CNES), the French government's space agency, in cooperation with various European partners. Despite not being a direct derivative of its predecessor launch vehicle program, it is classified as part of the Ariane rocket family. ArianeGroup is the prime contractor for the manufacturing of the vehicles, leading a multi-country consortium of other European contractors. Ariane 5 was originally intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEOStar-2
The STAR-2 Bus is a fully redundant, flight-proven, spacecraft bus designed for geosynchronous missions. It is a satellite platform, designed and developed by Thomas van der Heyden for the Indonesian Cakrawarta satellite program in the early 1990s, now manufactured by Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems with an apogee kick motor to place a communications satellite into geostationary orbit, a thruster to provide the satellite with orbital station-keeping for a 15-year mission, and solar arrays to provide the satellite payload with 5 kW of electrical power. Advantages NGIS's GEOStar-2 bus design is unique within the satellite industry. NGIS's GEOStar-2 bus provides an affordable low-to-medium power satellite platform that is ideal for missions of this size. Rather than being a less efficient version of a larger, heavier product, NGIS's GEOStar-2 bus is designed specifically for the 1000 to 5550 watts payload class. Design The GEOStar-2 bus satellite is a modular, mass ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
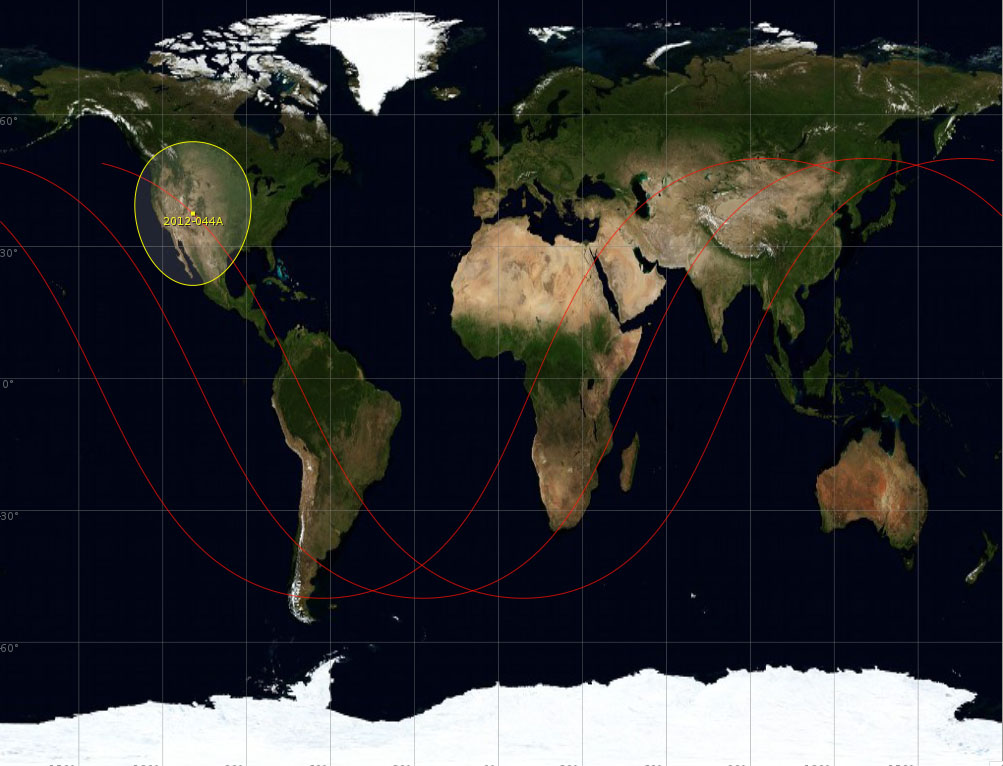
Telkom-3
Telkom-3 is an Indonesian communications satellite which failed to reach its target orbit due to a launch failure on 6 August 2012. It was built by ISS Reshetnev for Indonesian telecommunications provider PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia. It was based on the Ekspress-1000H bus and had 32 C band transponders and 16 Ku-band transponders. It was due to be located in geosynchronous orbit at 118° East above the equator. The satellite reentered the atmosphere and was destroyed on 5 February 2021. Launch Telkom-3 was launched along with Ekspress-MD2 by a Proton-M rocket with Briz-M upper stage on 6 August 2012 at 19:31:00 UTC. The satellites were launched from Site 81/24 at Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The first three stages of the Proton launched worked as expected and the satellites were attached to the Briz-M upper stage which would transfer them into geosynchronous orbit. The Briz-M undertakes a series of four burns with coasting stages to do this. The third burn was due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held. Bus-derived satellites are opposed to specially produced satellites. Bus-derived satellites are usually customized to customer requirements, for example with specialized sensors or transponders, in order to achieve a specific mission. They are commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly communications satellites, but are also used in spacecraft which occupy lower orbits, occasionally including low Earth orbit missions. Examples Some satellite bus examples include: * Boeing DS&S 702 * Lockheed Martin Space Systems A2100 * Alphabus * INVAP ARSAT-3K * Airbus D&S Eurostar * ISRO's I-1K, I-2K, I-3K, I-4K, I-6K, and Indian Mini Satellite bus * NASA Ames MCSB * SSL 1300 * Orbital ATK GEOStar * Mitsubishi Electric DS2000 * Spacecraft bus of the James Webb Space Telescope * SPUTNIX TabletSat * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosynchronous Satellite
A geosynchronous satellite is a satellite in geosynchronous orbit, with an orbital period the same as the Earth's rotation period. Such a satellite returns to the same position in the sky after each sidereal day, and over the course of a day traces out a path in the sky that is typically some form of analemma. A special case of geosynchronous satellite is the geostationary satellite, which has a geostationary orbit – a circular geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator. Another type of geosynchronous orbit used by satellites is the Tundra elliptical orbit. Geostationary satellites have the unique property of remaining permanently fixed in exactly the same position in the sky as viewed from any fixed location on Earth, meaning that ground-based antennas do not need to track them but can remain fixed in one direction. Such satellites are often used for communication purposes; a geosynchronous network is a communication network based on communication with or thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude above Earth's equator ( in radius from Earth's center) and following the direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to Earth's rotational period, one sidereal day, and so to ground observers it appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. The concept of a geostationary orbit was popularised by the science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke in the 1940s as a way to revolutionise telecommunications, and the first satellite to be placed in this kind of orbit was launched in 1963. Communications satellites are often placed in a geostationary orbit so that Earth-based satellite antennas do not have to rotate to track them but can be pointed permanently at the position in the sky where the sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palapa
Palapa is a series of Communications satellites owned by Indosat, an Indonesian telecommunications company (formerly by Perumtel and then by PT Satelit Palapa Indonesia/Satelindo). Starting with the first in July 1976, at which time Indonesia became the first developing country to operate its own domestic satellite system. The estimated cost for the project was US$1 billion. History The first satellite, Palapa-A1 of , was launched on 8 July 1976 at 23:31 UTC from Kennedy Space Center by a Delta 2914 launch vehicle, or at 06:31 Indonesian Time on 9 July 1976. Palapa-A2 was launched on 10 March 1977. The name "Palapa" was bestowed by then Indonesian President Suharto, after the Palapa oath sworn by Gajah Mada, the Prime Minister of Majapahit Kingdom, in 1334. According to the Pararaton (Book of Kings), Gajah Mada swore that he would not taste any ''palapa'' (historians suggest it refers to spice or a kind of flavouring), as long as he had not succeeded in unifying Nusa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |