|
Teletex
Teletex was ITU-T specification F.200 for a text and document communications service that could be provided over telephone lines. It was rapidly superseded by e-mail but the name ''Teletex'' lives on in several of the X.500 X.500 is a series of computer networking standards covering electronic directory services. The X.500 series was developed by the ITU-T, Telecommunication Standardization Sector of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T). ITU-T was former ... standard attributes used in Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. Overview Teletex was designed as an upgrade to the conventional telex service. The terminal-to-terminal communication service of telex would be turned into an office-to-office document transmission system by teletex. Teletex envisaged direct communication between electronic typewriters, word processors and personal computers. These units had storage for transmitting and receiving messages. The use of such equipment considerably enhanced th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals) and computers, ... such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members. The first meeting of the World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA), the sector's governing conference, took place on 1 March of that year. ITU-T has a permanent secretariat called the Telecommunication Standardization Bureau (TSB), which is based at the ITU headquarters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-mail
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP ) is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network. As examples, directory services may provide any organized set of records, often with a hierarchical structure, such as a corporate email directory. Similarly, a telephone directory is a list of subscribers with an address and a phone number. LDAP is specified in a series of Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Standard Track publications called Request for Comments (RFCs), using the description language ASN.1. The latest specification is Version 3, published aRFC 4511ref name="gracion Gracion.com. Retrieved on 2013-07-17. (a road map to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Typewriter
A typewriter is a mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an inked ribbon selectively against the paper with a type element. At the end of the nineteenth century, the term 'typewriter' was also applied to a ''person'' who used such a device. The first commercial typewriters were introduced in 1874, but did not become common in offices until after the mid-1880s. The typewriter quickly became an indispensable tool for practically all writing other than personal handwritten correspondence. It was widely used by professional writers, in offices, business correspondence in private homes, and by students preparing written assignments. Typewriters were a standard fixture in most offices up to the 1980s. Thereafter, they began to be largely supplanted by personal computers running word processing software. Nevertheless, typewri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Processor
A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features. Word processor (electronic device), Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word processors are word processor programs running on general purpose computers. The functions of a word processor program fall somewhere between those of a simple text editor and a fully functioned desktop publishing program. However, the distinctions between these three have changed over time and were unclear after 2010. Background Word processors did not develop ''out'' of computer technology. Rather, they evolved from mechanical machines and only later did they merge with the computer field. The history of word processing is the story of the gradual automation of the physical aspects of writing and editing, and then to the refinement of the technology to make it available to corporations and Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. Primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s, the term home computer was also used. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with the machines. While personal computer users may develop their own applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software (" freeware"), which is most often proprietary, or free and open-source software, which is provided in "ready-to-run", or binary, form. Software for personal computers is typically developed and distributed independently from the hardware or operating system ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Character Set
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using digital computers. The numerical values that make up a character encoding are known as " code points" and collectively comprise a "code space", a "code page", or a " character map". Early character codes associated with the optical or electrical telegraph could only represent a subset of the characters used in written languages, sometimes restricted to upper case letters, numerals and some punctuation only. The low cost of digital representation of data in modern computer systems allows more elaborate character codes (such as Unicode) which represent most of the characters used in many written languages. Character encoding using internationally accepted standards permits worldwide interchange of text in electronic form. History The history of character codes illustrates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Character
In computing and telecommunication, a control character or non-printing character (NPC) is a code point (a number) in a character set, that does not represent a written symbol. They are used as in-band signaling to cause effects other than the addition of a symbol to the text. All other characters are mainly printing, printable, or graphic characters, except perhaps for the "space" character (see ASCII printable characters). History Procedural signs in Morse code are a form of control character. A form of control characters were introduced in the 1870 Baudot code: NUL and DEL. The 1901 Murray code added the carriage return (CR) and line feed (LF), and other versions of the Baudot code included other control characters. The bell character (BEL), which rang a bell to alert operators, was also an early teletype control character. Control characters have also been called "format effectors". In ASCII There were quite a few control characters defined (33 in ASCII, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
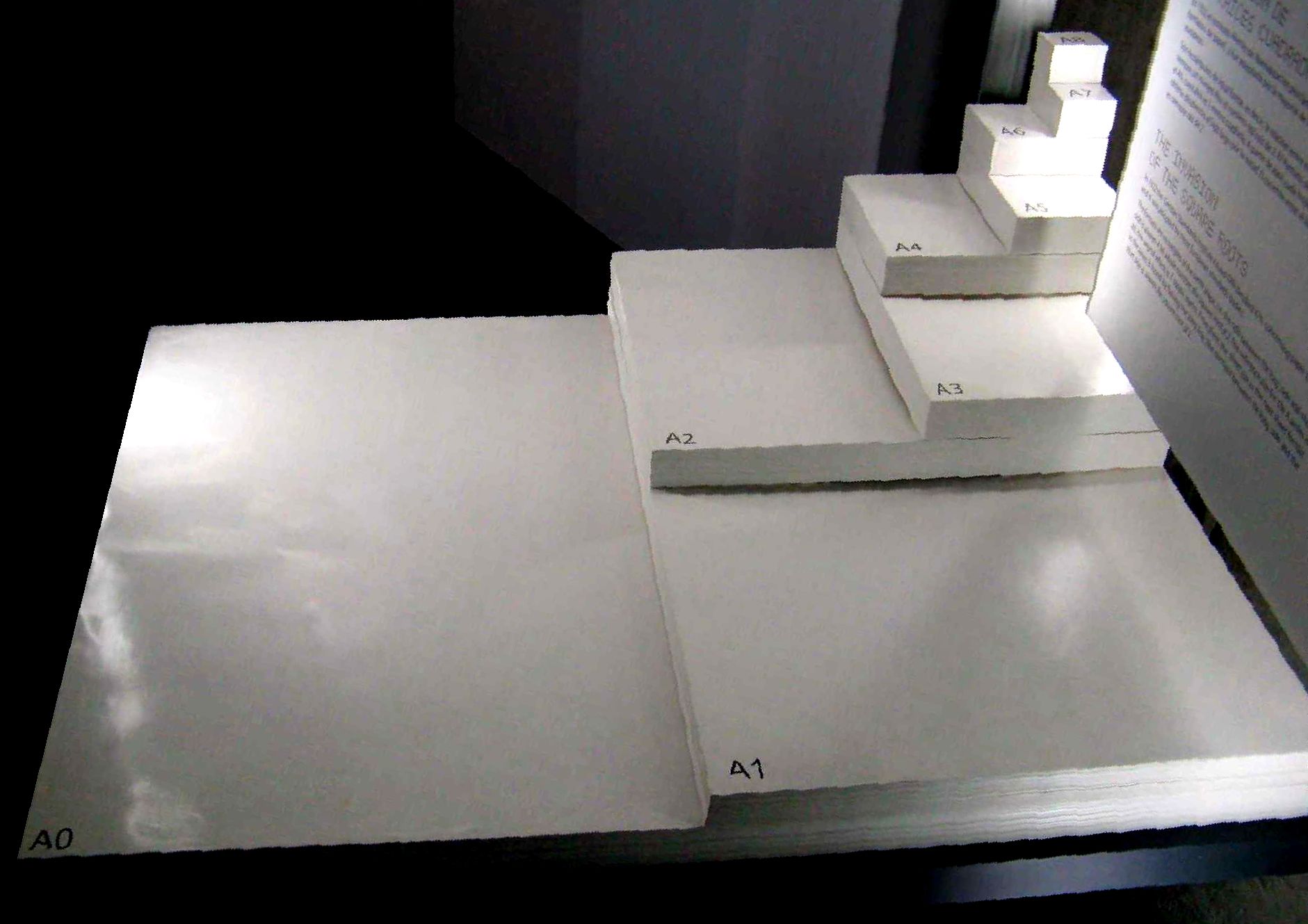
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Stationery
Continuous stationery (UK) or continuous form paper (US) is paper which is designed for use with dot-matrix and line printers with appropriate paper-feed mechanisms. Other names include ''fan-fold paper'', ''sprocket-feed paper'', ''burst paper'', ''lineflow'' (New Zealand), ''tractor-feed paper'', and ''pin-feed paper''. It can be single-ply (usually woodfree uncoated paper) or multi-ply (either with carbon paper between the paper layers, or multiple layers of carbonless copy paper), often described as multipart stationery or forms. Continuous stationery is often used when the final print medium is less critical in terms of the appearance at the edges, and when continuously connected individual sheets are not inconvenient for the application. Individual sheets can be separated at the perforation (leaving a slight serration), and sheets also have edges with punched holes, which also can be removed at the perforation (one typical format). Shape and form Most continuous form pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Header (computing)
In information technology, header refers to supplemental data placed at the beginning of a block of data being stored or transmitted. In data transmission, the data following the header is sometimes called the '' payload'' or '' body''. It is vital that header composition follows a clear and unambiguous specification or format, to allow for parsing. Examples * E-mail header: The text (body) is preceded by header lines indicating sender, recipient, subject, sending time stamp, receiving time stamps of all intermediate and the final mail transfer agents, and much more. * Similar headers are used in Usenet ( NNTP) messages, and HTTP headers. * In a data packet sent via the Internet, the data (payload) are preceded by header information such as the sender's and the recipient's IP addresses, the protocol governing the format of the payload and several other formats. The header's format is specified in the Internet Protocol. * In data packets sent by wireless communication, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)