|
Telenești District
Telenești () is a district () in central Moldova, with the administrative center at Telenești. History The oldest recorded settlements of the district are: Banești, Peciste and Telenești, mentioned in 1437. At the time, the landowners had the right to sell their estate, in parts or entirely. In the 16th and 17th centuries, the region's economy developed (trade, agriculture, winery), resulting in a significant increase in population. In 1812, after the Treaty of Bucharest, Bessarabia was occupied by the Russian Empire, and an intense process of russification of the native population followed. In 1918, as a result of the fall of the Russian Empire, Bessarabia was united with Romania, and the Romanian government enacted a land reform. Telenești became the center of a of Orhei County, along with 45 villages. The capital had a courthouse and a post office with telegraph and telephone. The Romanian land reform (as opposed to the Bolshevik one) made the peasants owners of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telenești
Telenești () is a city in Moldova, located 91 kilometres to the north of the capital city, Chișinău. Telenești is the administrative center of the Telenești District, eponymous district. Three villages are administered by the city: Mihălașa, Mihălașa Nouă and Izvoraș. As of 2004, it had a population of 6,855, 89 percent of whom were Moldovans, Moldovan. Media * Jurnal FM – 88.2 MHz Notable people * Angel Agache, Moldovan politician. * Nicoleta Dara, singer * Nachum Gutman (1898–1980), Teleneşti-born Israeli painter, sculptor, and author Religion Before World War II, the town had an important Jewish population. The Cathedral of St. Elijah from Telenești is one of the newest representative architectural monument. Țurcan Vasile is the priest of the St. Elijah Cathedral. The construction of Cathedral started in 2006. Further reading * Axentie Blanovschi: ''Telenești'', Ed. Timpul Chișinău, 1986 Teleneshty(p. 421) at Miriam Weiner (genealogist), M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
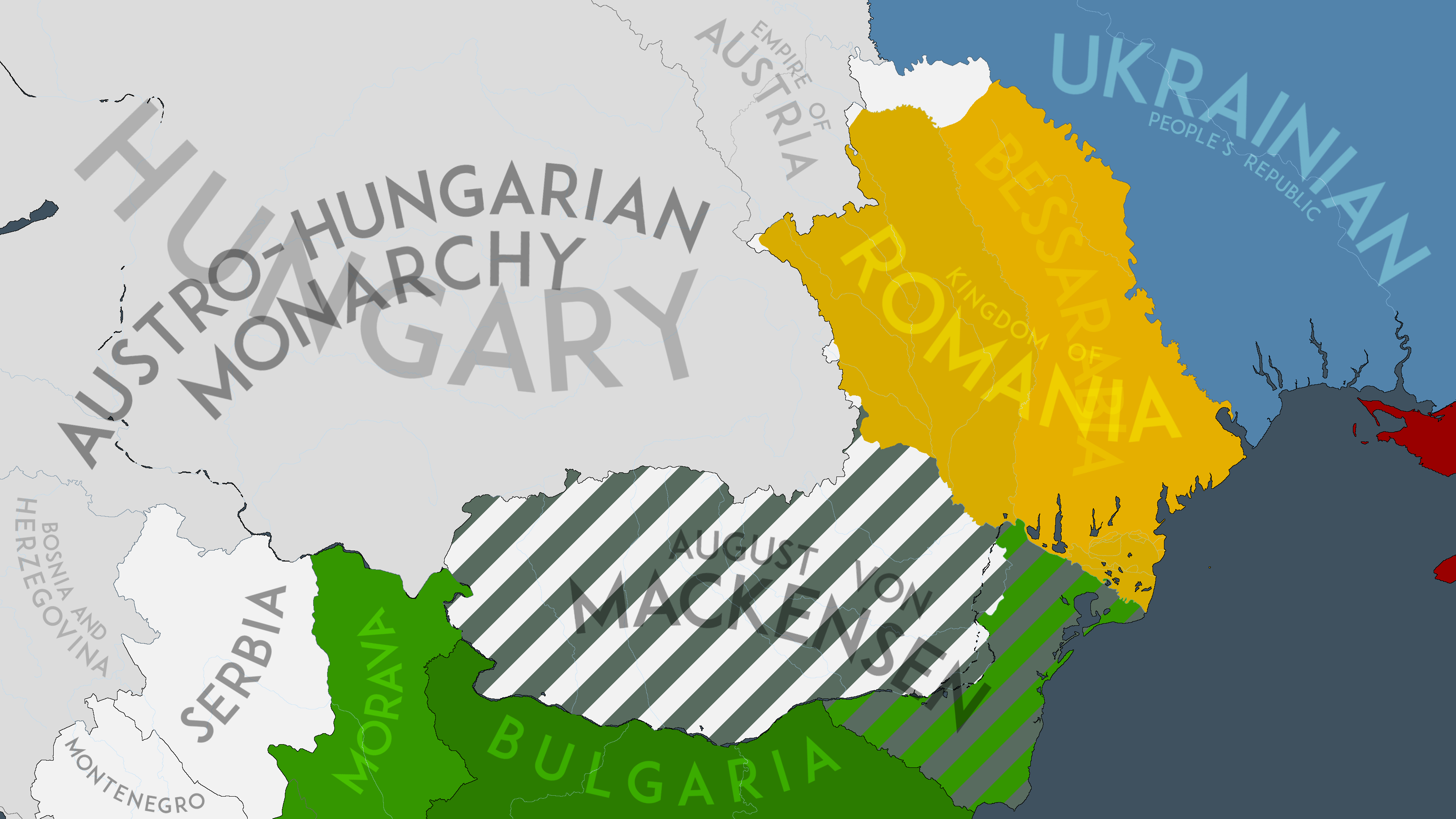
Bessarabia
Bessarabia () is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Bessarabia lies within modern-day Moldova, with the Budjak region covering the southern coastal region and part of the Ukrainian Chernivtsi Oblast covering a small area in the north. In the late 14th century, the newly established Principality of Moldavia encompassed what later became known as Bessarabia. Afterward, this territory was directly or indirectly, partly or wholly controlled by: the Ottoman Empire (as suzerain of Moldavia, with direct rule only in Budjak and Khotyn), the Russian Empire, Romania, the USSR. In the aftermath of the Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812), and the ensuing Treaty of Bucharest (1812), Peace of Bucharest, the eastern parts of the Moldavia, Principality of Moldavia, an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman vassal state, vassal, along with some areas formerly under direct Ottoman rule, were ceded to Imperial Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, Second Party Congress in 1903. The Bolshevik party, formally established in 1912, seized power in Russia in the October Revolution of 1917, and was later renamed the Russian Communist Party, All-Union Communist Party, and ultimately the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Its ideology, based on Leninism, Leninist and later Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist principles, became known as Bolshevism. The origin of the RSDLP split was Lenin's support for a smaller party of professional revolutionaries, as opposed to the Menshevik desire for a broad party membership. The influence of the factions fluctuated in the years up to 1912, when the RSDLP formally split in two. The political philosophy of the Bolsheviks was based on the Leninist pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Reform In Romania
Four major land reforms have taken place in Romania: in 1864, 1921, 1945 and 1991. The first sought to undo the feudal structure that had persisted after the unification of the Danubian Principalities in 1859; the second, more drastic reform, tried to resolve lingering peasant discontent and create social harmony after the upheaval of World War I and extensive territorial expansion; the third, imposed by a mainly Communist government, did away with the remaining influence of the landed aristocracy but was itself soon undone by collectivisation (considered by some as yet another land reform), which the fourth then unravelled, leading to almost universal private ownership of land today. 1864 reform The 1864 land reform was the first of its kind in Romania, taking place during the reign of Alexandru Ioan Cuza. It came on the heels of the secularization of monastery estates, achieved in December 1863 on Mihail Kogălniceanu's initiative and taking over a quarter of the country's area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into electronic signals that are transmitted via Electrical cable, cables and other communication channels to another telephone which reproduces the sound to the receiving user. The term is derived from and (, ''voice''), together meaning ''distant voice''. In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was the first to be granted a United States patent for a device that produced clearly intelligible replication of the human voice at a second device. This instrument was further developed by many others, and became rapidly indispensable in business, government, and in households. The essential elements of a telephone are a microphone (''transmitter'') to speak into and an earphone (''receiver'') which reproduces the voice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pigeon post is not. Ancient signalling systems, although sometimes quite extensive and sophisticated as in China, were generally not capable of transmitting arbitrary text messages. Possible messages were fixed and predetermined, so such systems are thus not true telegraphs. The earliest true telegraph put into widespread use was the Chappe telegraph, an optical telegraph invented by Claude Chappe in the late 18th century. The system was used extensively in France, and European nations occupied by France, during the Napoleonic era. The electric telegraph started to replace the optical telegraph in the mid-19th century. It was first taken up in Britain in the form of the Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, initially used mostly as an aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Office
A post office is a public facility and a retailer that provides mail services, such as accepting letter (message), letters and parcel (package), parcels, providing post office boxes, and selling postage stamps, packaging, and stationery. Post offices may offer additional services, which vary by country. These include providing and accepting government forms (such as passport applications), and processing government services and fees (such as road tax, Postal savings system, postal savings, or bank fees). The chief administrator of a post office is called a postmaster. During the 19th century, when the postal deliveries were made, it would often be delivered to public places. For example, it would be sent to bars and/or general store. This would often be delivered with newspapers and those who were expecting a post would go into town to pick up the mail, along with anything that was needed to be picked up in town. Before the advent of postal codes and the post office, postal syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages
A village is a human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church.-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''village'', from Latin ''villāticus'', ultimately from Latin ''villa'' (English ''villa''). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orhei County (Romania)
Orhei was a county (Romanian language, Romanian: ''județ'') in the Kingdom of Romania between 1925 and 1938, and again between 1941 and 1944, with the seat at Orhei. Geography The county was located in the northeastern part of the Greater Romania, in the eastern part of the historical region of Bessarabia, at the border with the Soviet Union. At present, its territory is part of the Republic of Moldova. It is bordered to the northwest by the counties of Soroca County (Romania), Soroca and Bălți County (Romania), Bălți, to the northeast and the east by the Soviet Union and to the south by Lăpușna County (Romania), Lăpușna County. Orhei County was the successor of the Orhei District of the Principality of Moldavia or the Russian Empire in the central part, bordering on the north with the Soroca District, in the east by the river Dniester, in the west by the Bălţi District, and in the south by Lăpuşna District. The northernmost of the settlements was Poiana, Șoldăneșt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasă
''Plasă'' (, plural ''plăși'' ) was a territorial division unit of Romania, ranking below county ('' județ'') and above commune. It was headed by a '' Pretor'', appointed by the county Prefect. The institution headed by the Pretor was called ''Pretură''. The division of counties into ''plăși'' was used starting from the rule of Carol I as '' Domnitor'', throughout the existence of a Romanian Kingdom, and during the first two years of the Romanian People's Republic, until they were replaced in 1950 by raions, following the Soviet The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ... system. In 1938, the country's 71 ''județe'' were divided into 429 ''plăși''. Petre Mihai Băcanu"Cum ar trebui să arate harta redesenată a României?" March 11, 2010; accessed February 17, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Bessarabia With Romania
The union of Bessarabia with Romania was proclaimed on by Sfatul Țării, the legislative body of the Moldavian Democratic Republic. This state had the same borders of the region of Bessarabia, which was annexed by the Russian Empire following the Treaty of Bucharest (1812), Treaty of Bucharest of 1812 and organized first as an ''Oblast'' (autonomous until 1828) and later as a Bessarabia Governorate, Governorate. Under Russian rule, many of the native Tatars were expelled from parts of Bessarabia and replaced with Moldavians, Wallachians, Bulgarians, Ukrainians, Greeks, Russians, Lipovans, Cossacks, Gagauzes and other peoples, although colonization was not limited to formerly Tatar-inhabited lands. Russia also tried to integrate the region by imposing the Russian language in administration and restricting education in other languages, notably by later banning the use of Romanian in schools and print. The beginning of World War I saw an increase in national awareness among the Bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |